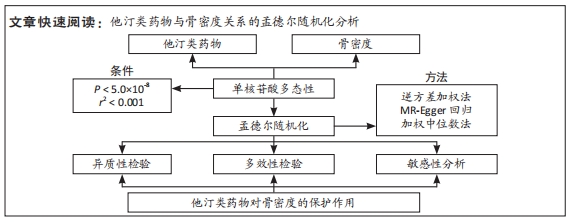
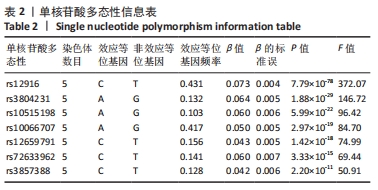
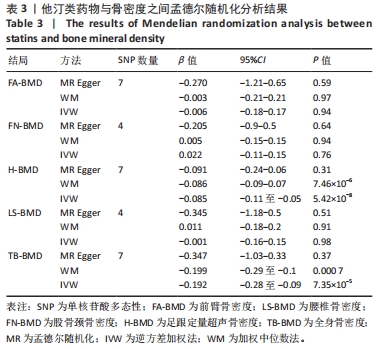
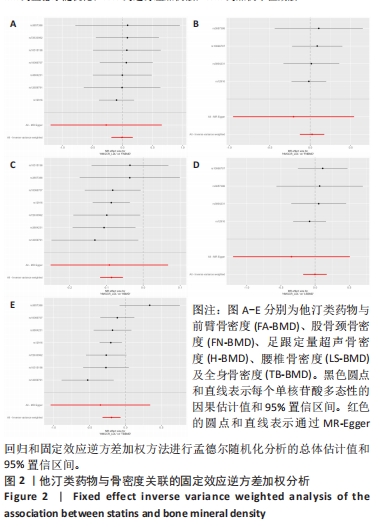
[1] LI J, CHEN X, LU L, et al. The relationship between bone marrow adipose tissue and bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;52:88-98.
[2] XU Q, LI D, CHEN J, et al. Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and postmenopausal osteoporosis: Mechanisms and applications. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:108998.
[3] MARTÍN-GONZÁLEZ C, GONZÁLEZ-REIMERS E, QUINTERO-PLATT G, et al. Lipid profile and bone mineral density in heavy alcoholics. Clin Nutr. 2018; 37(6 Pt A):2137-2143.
[4] LI S, GUO H, LIU Y, et al. Relationships of serum lipid profiles and bone mineral density in postmenopausal Chinese women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015;82(1): 53-58.
[5] ALLA VM, AGRAWAL V, DENAZARETH A, et al. A reappraisal of the risks and benefits of treating to target with cholesterol lowering drugs. Drugs. 2013;73(10): 1025-1054.
[6] UZZAN B, COHEN R, NICOLAS P, et al. Effects of statins on bone mineral density: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Bone. 2007;40(6):1581-1587.
[7] LIN TK, CHOU P, LIN CH, et al. Long-term effect of statins on the risk of new-onset osteoporosis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. PLoS One. 2018; 13(5):e0196713.
[8] VAN DER BAAN FH, KLUNGEL OH, EGBERTS AC, et al. Pharmacogenetics in randomized controlled trials: considerations for trial design. Pharmacogenomics. 2011;12(10):1485-1492.
[9] GRECO M FD, MINELLI C, SHEEHAN NA, et al. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med. 2015;34(21):2926-2940.
[10] BOWDEN J, HOLMES MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(4):486-496.
[11] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265.
[12] LIU L, ZENG P, XUE F, et al. Multi-trait transcriptome-wide association studies with probabilistic Mendelian randomization. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108(2):240-256.
[13] FERENCE BA. Interpreting the Clinical Implications of Drug-Target Mendelian Randomization Studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;80(7):663-665.
[14] WISHART DS, FEUNANG YD, GUO AC, et al. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1): D1074-D1082.
[15] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
[16] WILLER CJ, SCHMIDT EM, SENGUPTA S, et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat Genet. 2013;45(11):1274-1283.
[17] CAMACHO PM, PETAK SM, BINKLEY N, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis-2020 Update. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(Suppl 1):1-46.
[18] ZHENG HF, FORGETTA V, HSU YH, et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature. 2015;526(7571):112-117.
[19] MORRIS JA, KEMP JP, YOULTEN SE, et al. An atlas of genetic influences on osteoporosis in humans and mice [published correction appears in Nat Genet. 2019;51(5):920]. Nat Genet. 2019;51(2):258-266.
[20] MEDINA-GOMEZ C, KEMP JP, TRAJANOSKA K, et al. Life-Course Genome-wide Association Study Meta-analysis of Total Body BMD and Assessment of Age-Specific Effects. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(1):88-102.
[21] ZHANG X, GENG T, LI N, et al. Associations of Lipids and Lipid-Lowering Drugs with Risk of Vascular Dementia: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022;15(1):69.
[22] HUANG W, XIAO J, JI J, et al. Association of lipid-lowering drugs with COVID-19 outcomes from a Mendelian randomization study. Elife. 2021;10: e73873.
[23] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data [published correction appears in PLoS Genet. 2017;13(12 ):e1007149]. PLoS Genet. 2017; 13(11):e1007081.
[24] YUAN S, XIONG Y, LARSSON SC. An atlas on risk factors for multiple sclerosis: a Mendelian randomization study. J Neurol. 2021;268(1):114-124.
[25] MASSON W, CORRAL P, BARBAGELATA L, et al. Reduction of cardiovascular events with the use of lipid-lowering medication in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia or severe primary hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review. J Clin Lipidol. 2022;16(5):562-573.
[26] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304-314.
[27] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method [published correction appears in Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):391-392]. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389.
[28] JIA N, DONG L, LU Q, et al. The causal effect of schizophrenia on fractures and bone mineral density: a comprehensive two-sample Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry. BMC Psychiatry. 2023;23(1):692.
[29] LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, STERNE JA, et al. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. 2008;27(8):1133-1163.
[30] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[31] WU X, ZHANG W, ZHAO X, et al. Investigating the relationship between depression and breast cancer: observational and genetic analyses. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):170.
[32] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med. 2017;36(11):1783-1802.
[33] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases [published correction appears in Nat Genet. 2018;50(8):1196]. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698.
[34] MA W, ZHOU X, HUANG X, et al. Causal relationship between body mass index, type 2 diabetes and bone mineral density: Mendelian randomization. PLoS One. 2023;18(10):e0290530.
[35] WANG JS, TOKAVANICH N, WEIN MN. SP7: from Bone Development to Skeletal Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(2):241-252.
[36] XU J, CAO B, LI C, et al. The recent progress of endocrine therapy-induced osteoporosis in estrogen-positive breast cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 2023;13: 1218206.
[37] LIU Q, TOOKI T, DI D, et al. Role of lifestyle factors in mediating the effect of educational attainment on bone mineral density: a Mendelian randomization study. Arch Osteoporos. 2023;18(1):120.
[38] HE X, HU W, ZHANG Y, et al. Cellular senescence in skeletal disease: mechanisms and treatment. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):88.
[39] LI Y, SI Y, MA Y, et al. Application and prospect of metabolomics in the early diagnosis of osteoporosis: a narrative review. Bioanalysis. 2023;15(22): 1369-1379.
[40] AN T, HAO J, SUN S, et al. Efficacy of statins for osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(1):47-57.
[41] LIU J, ZHU LP, YANG XL, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. Bone. 2013;54(1):151-156.
[42] WANG Z, LI Y, ZHOU F, et al. Effects of Statins on Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk: A PRISMA-compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(22):e3042.
[43] REJNMARK L, OLSEN ML, JOHNSEN SP, et al. Hip fracture risk in statin users--a population-based Danish case-control study. Osteoporos Int. 2004; 15(6):452-458.
[44] XIONG M, XUE Y, ZHU W, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of statins for osteoporosis: a study protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):e054158.
[45] REID IR, HAGUE W, EMBERSON J, et al. Effect of pravastatin on frequency of fracture in the LIPID study: secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Long-term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease. Lancet. 2001;357(9255):509-512.
[46] PEÑA JM, ASPBERG S, MACFADYEN J, et al. Statin therapy and risk of fracture: results from the JUPITER randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(2): 171-177.
[47] PEDERSEN TR, WILHELMSEN L, FAERGEMAN O, et al. Follow-up study of patients randomized in the Scandinavian simvastatin survival study (4S) of cholesterol lowering. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86(3):257-262.
[48] WARREN T, MCALLISTER R, MORGAN A, et al. The Interdependency and Co-Regulation of the Vitamin D and Cholesterol Metabolism. Cells. 2021; 10(8):2007.
[49] PRABHU AV, LUU W, LI D, et al. DHCR7: A vital enzyme switch between cholesterol and vitamin D production. Prog Lipid Res. 2016;64:138-151.
[50] GÓMEZ-CORONADO D, LASUNCIÓN MA, MARTÍNEZ-BOTAS J, et al. Role of cholesterol metabolism in the anticancer pharmacology of selective estrogen receptor modulators. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;73:101-115.
[51] YU D, LIAO JK. Emerging views of statin pleiotropy and cholesterol lowering. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(2):413-423.
[52] ABDUL-RAHMAN T, BUKHARI SMA, HERRERA EC, et al. Lipid Lowering Therapy: An Era Beyond Statins. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022;47(12):101342.
[53] RAY KK. Changing the paradigm for post-MI cholesterol lowering from intensive statin monotherapy towards intensive lipid-lowering regimens and individualized care. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(3):253-256.
[54] OXLUND H, DALSTRA M, ANDREASSEN TT. Statin given perorally to adult rats increases cancellous bone mass and compressive strength. Calcif Tissue Int. 2001;69(5):299-304.
[55] TIAN L, YU X. Lipid metabolism disorders and bone dysfunction--interrelated and mutually regulated (review). Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(1):783-794.
[56] NIU J, DING G, ZHANG L. Effects of simvastatin on the osteogenic differentiation and immunomodulation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(6):8237-8240.
[57] XU R, SHI G, XU L, et al. Simvastatin improves oral implant osseointegration via enhanced autophagy and osteogenesis of BMSCs and inhibited osteoclast activity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(5):1209-1219.
[58] CHAMANI S, LIBERALE L, MOBASHERI L, et al. The role of statins in the differentiation and function of bone cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51(7): e13534. |