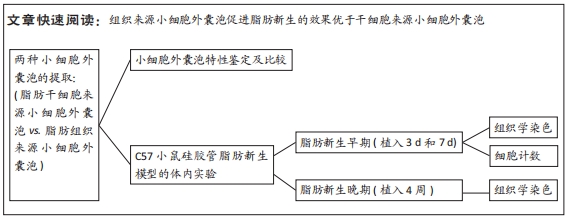
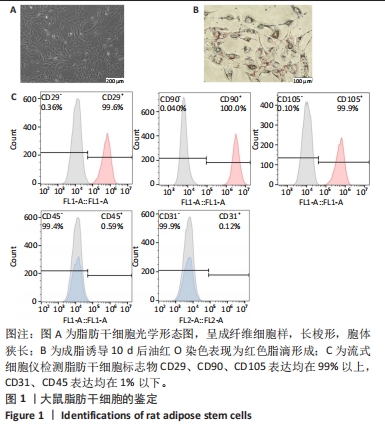
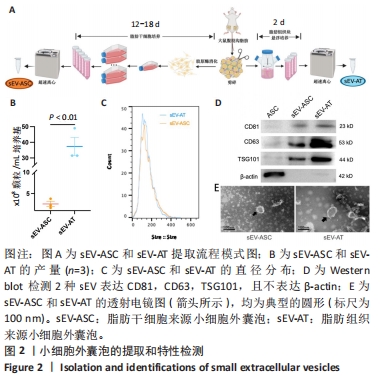
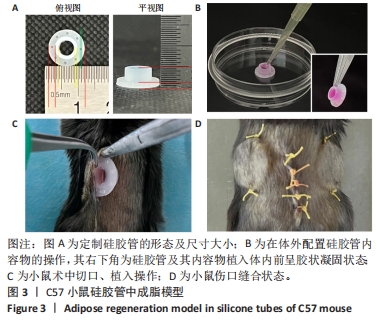
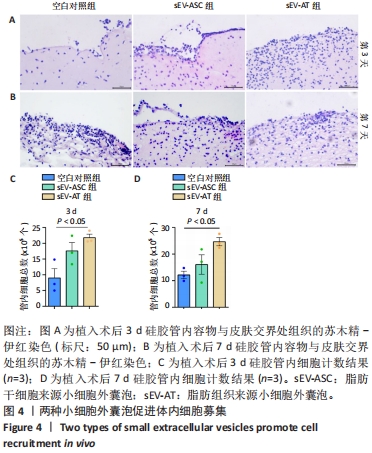
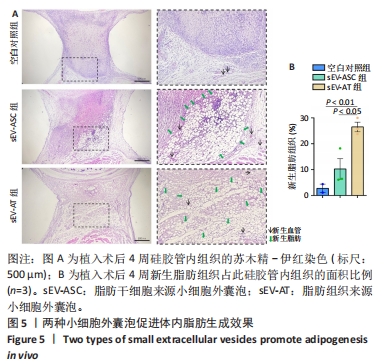
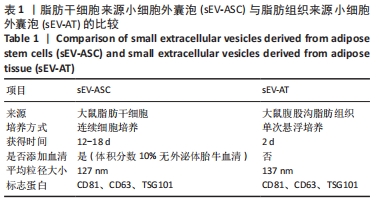
[1] PAREKKADAN B, MILWID JM. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:87-117.
[2] XIA H, LI X, GAO W, et al. Tissue repair and regeneration with endogenous stem cells. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3(7):174-193.
[3] DANESHMANDI L, SHAH S, JAFARI T, et al. Emergence of the Stem Cell Secretome in Regenerative Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020; 38(12):1373-1384.
[4] BARRECA MM, CANCEMI P, GERACI F. Mesenchymal and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: The New Frontier for Regenerative Medicine? Cells. 2020;9(5):1163.
[5] KOU M, HUANG L, YANG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):580.
[6] GUILLAMAT-PRATS R. The Role of MSC in Wound Healing, Scarring and Regeneration. Cells. 2021;10(7):1729.
[7] ALONSO-ALONSO ML, GARCÍA-POSADAS L, DIEBOLD Y. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review of Common Cargos. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):854-901.
[8] WITWER KW, THÉRY C. Extracellular vesicles or exosomes? On primacy, precision, and popularity influencing a choice of nomenclature. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1648167.
[9] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018; 7(1):1535750.
[10] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487-514.
[11] SHAO H, IM H, CASTRO CM, et al. New Technologies for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Chem Rev. 2018;118(4):1917-1950.
[12] JIA Y, YU L, MA T, et al. Small extracellular vesicles isolation and separation: Current techniques, pending questions and clinical applications. Theranostics. 2022;12(15):6548-6575.
[13] HAN YD, BAI Y, YAN XL, et al. Co-transplantation of exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes neovascularization and graft survival in fat grafting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):305-312.
[14] BORIANI F, PERUT F. Exosomes Are Comparable to Source Adipose Stem Cells in Fat Graft Retention with Up-Regulating Early Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;146(2):232e.
[15] ZHU YZ, ZHANG J, HU X, et al. Supplementation with Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Increases Fat Graft Survival and Browning in Mice: A Cell-Free Approach to Construct Beige Fat from White Fat Grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(5):1183-1195.
[16] DONG J, WU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Allogeneic and Xenogeneic Small Extracellular Vesicles in Soft Tissue Repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6975-6991.
[17] NIE J, YI Y, ZHU Y. Construction of tissue engineered adipose by human adipose tissue derived extracellular vesicle combined with decellularized adipose tissues scaffold. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(2):226-233.
[18] DAI M, YU M, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosome-Like Vesicles Derived from Adipose Tissue Provide Biochemical Cues for Adipose Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(21-22):1221-1230.
[19] NIE F, DING P, ZHANG C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from lipoaspirate fluid promote fat graft survival. Adipocyte. 2021;10(1): 293-309.
[20] NIE JY, ZHU YZ, WANG JW, et al. Preparing Adipogenic Hydrogel with Neo-Mechanical Isolated Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Adipose Tissue Engineering. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(2): 212e-222e.
[21] HONG P, XU X, HU X, et al. Therapeutic potential of small extracellular vesicles derived from lipoma tissue in adipose tissue regeneration-an in vitro and in vivo study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):222.
[22] HUANG H, FENG S, ZHANG W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell‑derived extracellular vesicles improve the survival of transplanted fat grafts. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3069-3078.
[23] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):555-568.
[24] CHEN L, QU J, MEI Q, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MenSCs) as a novel therapeutic impetus in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):433.
[25] SUN D, MOU S, CHEN L, et al. High yield engineered nanovesicles from ADSC with enriched miR-21-5p promote angiogenesis in adipose tissue regeneration. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):83.
[26] ZHAO R, ZHAO T, HE Z, et al. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 2021; 10(1):587-604.
[27] 四川大学.一种用于小动物软组织再生的皮下硅胶管装置及应用: CN201810705889.1[P]. 2018-11-02.
[28] 张雪亭.细胞治疗产品发展现状与展望[J].科学与财富,2022, 14(11):25-27.
[29] DING Y, LI Y, SUN Z, et al. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles and membranes for tissue repair. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):368.
[30] MA ZJ, YANG JJ, LU YB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(8):814-840.
[31] LI SR, MAN QW, GAO X, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: Present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175.
[32] KELLER S, RIDINGER J, RUPP AK, et al. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med. 2011;9:86.
[33] LÄSSER C, ALIKHANI VS, EKSTRÖM K, et al. Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages. J Transl Med. 2011;9:9.
[34] LIU H, YUAN W, PANG Q, et al. Single-particle analysis of tear fluid reveals abundant presence of tissue factor-exposing extracellular vesicles with strong coagulation activity. Talanta. 2022;239:123089.
[35] MURAOKA S, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, YANAMANDRA K, et al. Proteomic Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Cerebrospinal Fluid of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: A Pilot Study. Cells. 2020;9(9):1959.
[36] HA DH, KIM HK, LEE J, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells. 2020;9(5):1157.
[37] LO SICCO C, REVERBERI D, BALBI C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Endorsement of Macrophage Polarization. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):1018-1028.
[38] CHEN K, XIONG J, XU S, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Exosomes Improve Fat Graft Survival by Promoting Prolipogenetic Abilities through Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:5014895.
[39] ZHI Z, SUN Q, TANG W. Research advances and challenges in tissue-derived extracellular vesicles. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:1036746.
[40] DONG J, WU B, TIAN W. Adipose tissue-derived small extracellular vesicles modulate macrophages to improve the homing of adipocyte precursors and endothelial cells in adipose tissue regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1075233.
[41] THOMOU T, MORI MA, DREYFUSS JM, et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017;542(7642):450-455.
[42] ZHANG Y, YU M, DAI M, et al. miR-450a-5p within rat adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles promotes adipogenic differentiation by targeting WISP2. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(6):1158-1168.
|