中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 3052-3060.doi: 10.12307/2023.636
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
工程化外泌体研究现状与临床转化的挑战
张 琪,于 湄,刘 磊,田卫东
- 四川大学华西口腔医(学)院,口腔再生医学国家地方联合工程实验室,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2022-07-14接受日期:2022-08-29出版日期:2023-07-08发布日期:2022-11-28 -
通讯作者:于湄,博士,副教授,四川大学华西口腔医(学)院,口腔再生医学国家地方联合工程实验室,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:张琪,女,1995 年生,四川省德阳市人,汉族,四川大学华西口腔医学院在读硕士。 -
基金资助:四川省科技计划重点研发项目(2019YFS0312),项目负责人:于湄;四川省科技计划应用基础研究项目(2020YJ0278),项目负责人:刘磊;国家自然科学基金区域创新发展联合基金(U21A20369),项目负责人:田卫东
Recent advances of engineered exosomes and challenges on clinical translational research
Zhang Qi, Yu Mei, Liu Lei, Tian Weidong
- National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-14Accepted:2022-08-29Online:2023-07-08Published:2022-11-28 -
Contact:Yu Mei, PhD, Associate professor, National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Qi, Master candidate, National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Key Technology Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province, No. 2019YFS0312 (to YM); Applied Basic Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Program, No. 2020YJ0278 (to LL); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U21A20369 (to TWD)
摘要:
文题释义:
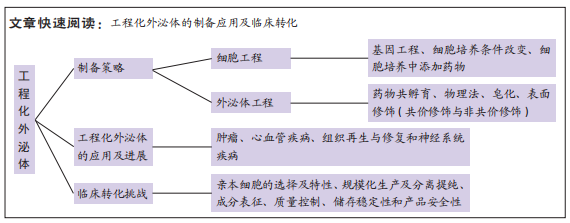
工程化外泌体:主要是指天然外泌体经过生物工程技术处理后,具有增强的载药效率、靶向性以及抵抗机体清除率等特点的一类被改造修饰的外泌体。通常这类外泌体的大小和形状不会发生明显变化,但是根据不同的研究目的,其膜负载物或内容物会有明显区别。临床转化:主要是指把基础医学研究获得的知识、成果转化为临床治疗的新方法,打破基础医学与临床医学之间固有的屏障,弥补基础实验研发与临床应用间的鸿沟,为开发新药及研究新的治疗方法开辟出的一条新途径。
背景:目前许多研究者正在探索外泌体作为一种药物载体的新形式,即通过一系列生物工程技术对天然外泌体进行改造和修饰,通过装载的药物得到增强的特性和功能的工程化外泌体。
目的:文章就工程化外泌体的制备策略、研究进展以及临床转化面临的挑战进行了综述。
方法:检索PubMed数据库收录的相关文献以及FDA网站,英文检索词为“extracellular vesicles,exosomes,drug delivery,engineering,engineered,treatment,clinical translation,scale production,isolation,characterization,quality control,storage,safety”,最终纳入73篇文献与1篇网页声明进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①工程化外泌体可以通过细胞工程和外泌体工程制得,此2种策略制造的工程化外泌体的增强特性均已在基础研究中得到了验证,证实其具有巨大的临床应用前景,但同时均存在着一系列生物安全性、载药效率低下等问题亟待解决。②工程化外泌体已经在肿瘤、心血管疾病、组织再生与修复以及神经系统疾病等各个领域被证实具有良好的临床应用潜力,且均比天然外泌体展现出了更好的治疗效果及靶向性。③工程化外泌体的临床转化面临着诸多问题与挑战:各种常见细胞均可用于外泌体生产制造,细胞的代数及培养血清等变化也会导致外泌体的不同;扩大细胞培养规模是大量生产外泌体最直接的方法,不同的提取方法会影响其产量以及外泌体亚群的均一性,细胞培养的规模化以及分离提取流程需要标准化;合格的体外表征与量化可以预测载药外泌体系统的预期治疗潜力,需要进一步寻找开发外泌体量化以及分子和物理特征描述的金标准;外泌体产品需要额外程序进行把控,以确保外泌体终产品满足关键质量属性;冷冻干燥最有利于外泌体类治疗药物的商业化;监管机构至今尚未发布如何测试这些外泌体的安全性和有效性的指导意见,需要对现有的方法进行改进或者寻找新方法对工程化外泌体的安全性和有效性进行证明。④虽然目前仍然没有任何一种工程化外泌体正式进入临床转化,但其治疗潜力是无可厚非的。商业化的工程化外泌体产品的面市,还需要一定时间。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8787-0548 (张琪);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0306-6817 (于湄)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张 琪, 于 湄, 刘 磊, 田卫东. 工程化外泌体研究现状与临床转化的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 3052-3060.
Zhang Qi, Yu Mei, Liu Lei, Tian Weidong. Recent advances of engineered exosomes and challenges on clinical translational research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 3052-3060.
2.1.1 细胞工程 外泌体由细胞产生,即使微小的细胞变化也能够使外泌体发生巨大的改变。因此,学者们首先对亲本细胞进行改造,细胞工程也成为最常用的工程化外泌体制备方法之一,见图3。
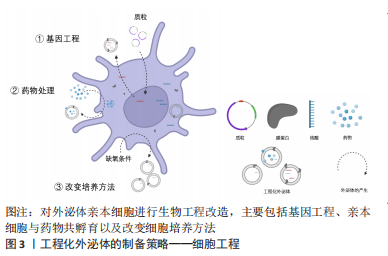
对亲本细胞进行基因工程是常用的细胞工程技术,即在外泌体生物发生时直接对外泌体进行修饰。ALVAREZ-ERVITI等[9]首次发现神经元特异性狂犬病毒糖蛋白与外泌体溶酶体相关膜蛋白2b(lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2b,Lamp2b)融合的质粒转染的树突状细胞所分泌的外泌体可以靶向性地将siRNA递送到大脑。由此开创了把目的蛋白与Lamp2b融合以定位于外泌体表面的先河。XU等[10]将间充质干细胞结合多肽E7与Lamp2b融合,从而将E7定位于外泌体膜表面,使其具有靶向滑液间充质干细胞的能力,并且能够携带更多药物,诱导更高程度的软骨分化。此外,有研究还构建了一种程序性细胞死亡配体1阳性的间充质干细胞[11],这种细胞来源的外泌体能在体外将各种激活的免疫细胞调节到免疫抑制状态,并且在炎症组织中的积聚显著增加,展现出令人满意的对自身免疫性疾病的疗效和靶向性。上述研究表明基因工程技术不仅能成功构建出高靶向性的工程化外泌体,还能够显著提高工程化外泌体的载药量,进而实现更精准的治疗。然而,考虑到基因工程的生物安全性问题,仍需更多研究考察其未来应用前景。
细胞的培养条件也会影响外泌体的发生和分泌,进而可能改变外泌体的生物特性。PATTON等[12]在缺氧条件下培养胰腺癌细胞,发现其释放的外泌体数量增加,并且外泌体的大小主要向平均粒径减小的方向发展,为胰腺癌细胞的适应性生长提供了优势条件。由此看来,改变细胞生长条件是一种增加外泌体产量的有效方法,但考虑到其产量增大的程度不足,仍不能成为一种大量生产外泌体的主流方法。
将亲本细胞与药物进行共孵育,是另一种常用的工程化外泌体制备方法。有研究将紫杉醇(paclitaxel,PTX)与小鼠间充质干细胞细胞孵育24 h,然后从经PTX孵育的(间充质干细胞-PTX)和未经PTX孵育的间充质干细胞的培养基中分离外泌体,发现间充质干细胞-PTX衍生的外泌体对胰腺癌有较强的抗增殖活性。这项研究首次展示了如何通过药物与骨髓间充质干细胞直接孵育,在体外通过外泌体包装和输送活性药物[13]。细胞与药物共孵育不需要多余设备,相对来说是比较容易实施的一种细胞工程方法,但缺点是其生产的外泌体载药量总是较低。
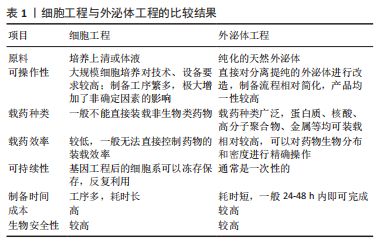
2.1.2 外泌体工程 相比于细胞工程的低效率性和高难度性,直接对纯化的天然外泌体进行修饰,可以直接、高效快速地获得大量工程化外泌体,并且减少了细胞培养过程中的不确定性,对工程化外泌体的大量生产具有重要意义。细胞工程与外泌体工程的比较结果见表1。
外泌体工程,即在适当的条件下,使用特定的技术对纯化的外泌体的表面蛋白或内容物进行修饰,此过程主要分为孵育法、物理法、皂化以及表面修饰,见图4,关于这几种制备策略各自的优缺点比较见表2。
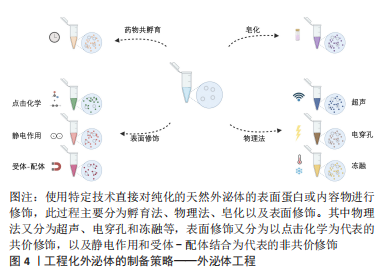
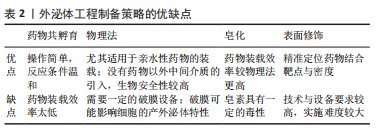
药物共孵育:外泌体与药物室温共孵育是一种常用的载药方法。DIDIOT等[14]证明疏水修饰的小干扰RNA在共孵育时有效地装载到外泌体中,携带针对Huntingtin mRNA的小干扰RNA的外泌体能被原代小鼠皮质神经元有效地内化,并促进Huntingtin mRNA和蛋白的剂量依赖性沉默,携带小干扰RNA的外泌体进入大脑的广泛分布和有效性有望推动亨廷顿病和其他神经退行性疾病治疗方法的发展。KIM等[15]将PTX与另一种抗癌药物吲哚青绿(indocyanine green,ICG)共同孵育,获得了双载药的外泌体[(EV/(ICG/PTX)],EV/(ICG/PTX)表现出了比游离药物或者单载药外泌体更优越的抗癌效果。虽然这种方法简单,但外泌体自身的体积和其表面小的膜孔尺寸限制了药物进入,通常导致载药效率低下[16]。
物理制备法:利用超声、电穿孔及冻融等物理方法,破坏外泌体的膜完整性,可以使药物分子更容易进入外泌体,达到工程化外泌体的目的。例如,DU等[17]利用超声技术将铁死亡诱导剂(erastin,Er)和孟加拉玫瑰(rose bengal,RB)负载到外泌体(Er/Rb@ExosCD47)内,体外体内实验均证明Er/Rb@ExosCD47能促进肿瘤细胞的铁死亡,发挥抗肿瘤作用。
电穿孔法装载亲水类药物,如DNA和RNA时效率很高。MOMEN-HERAVI等[18]通过此种方法将miRNA-155负载到外泌体中,显著增加了原代小鼠肝细胞和miRNA-155基因敲除小鼠肝脏中miRNA-155的水平,并发现当电压为0.13-0.20 kV,外泌体质量浓度为500-1 000 g/L时,负载效率最高。有研究发现电穿孔可以诱导囊泡或siRNA聚集,从而破坏工程化外泌体的结构或降低负载药物的治疗效果[19],但是在反应中加入海藻糖脉冲介质或螯合剂,如乙二胺四乙酸[20],这种问题可以得到改善。DUMONTEL等[21]通过反复冻融,将纳米级氧化锌加载至外泌体,在此基础上进一步获得CD20+的外泌体,达到将氧化锌的毒性作用特异性靶向癌细胞的目的。
通过以上物理方法得到的外泌体的大小、形态以及载药效率强烈依赖于制备方法[22],通过物理方法制备的工程化外泌体,减少了药物以外中间介质的引入,具有更高的生物安全性。
皂化:皂素是一种表面活性剂,常被用作膜渗透剂诱导脂质膜内形成小孔,该过程被称为皂化[23],利用皂化的作用,能使亲水的非膜透性药物或其他分子进入外泌体,进而辅助外泌体的药物装载[24]。FUHRMANN等[8]使用内皮细胞、肿瘤细胞和干细胞提取外泌体后,通过皂化、电穿孔、挤压和透析将卟啉加载到外泌体中,无论采用何种负载方法,卟啉负载量均较好,但与其他几种方法相比,皂素处理增加了卟啉在外泌体中的载量和细胞摄取。上述研究表明皂素比一般的物理方法能够更大程度增加外泌体的药物装载效率[25],但是皂素本身是一种毒性物质,具有一定的危险性,当其改造的外泌体应用于体内或者体外实验时应该被洗涤[8,22,25]。
外泌体表面修饰:除了短暂破坏外泌体膜结构之外,还可以通过共价修饰和非共价修饰两种方式对外泌体表面膜蛋白进行修饰,以达到工程化外泌体的目的。
共价修饰主要包括化学偶联,即通过点击化学将配体直接连接到外泌体表面。WANG等[26]首先利用电穿孔的方法,将ICG和PTX加载进入巨噬细胞来源的外泌体中制备出ICG/PTX@EV,然后采用点击化学,通过磺酰叠氮环点击加成反应将RGE多肽偶联至外泌体膜上,制成的ICG/PTX@RGE-EV可以作为ICG/PTX联合治疗胶质瘤的潜在药物传递系统,其在血液循环中的滞留时间延长,并增加在肿瘤中的蓄积,从而促进抗肿瘤作用和降低毒性。点击化学可以在短时间内将多种分子连接到外泌体表面,此外,具有不同特性的多个配体可以同时连接,并且通过调节反应物的比例来精确调节不同配体的定位与密度[27],生产率高、副产物无害,展现出了优于其他改造策略的更强的可控性、安全性与韧性,具有更广泛的应用价值。
非共价修饰主要是指利用静电、受体-配体及其他方式改变外泌体表面的受体或者蛋白。外泌体表面的Zeta电位为负,即通过静电力,高价阳离子可以结合到带负电荷的外泌体表面,这对利用静电对外泌体表面进行药物加载提供了理论基础[28]。TAMURA等[29]发现阳离子普鲁兰多糖表面修饰的外泌体在肝脏中的蓄积显著增加,促进了肝脏的生物学功能,对肝损伤有较好的治疗作用。然而,某些阳离子纳米材料可能引起细胞毒性,并且通过内吞作用进入细胞,导致溶酶体降解并降低外泌体装载效率[30]。ZHAN等[31]将血液外泌体设计成一种多功能的组合递送系统,将内溶肽L17Eh和磁性分子分别通过静电作用和配体-受体偶联结合到外泌体上,该工程化外泌体显示出改善的内体逃逸和增强的肿瘤聚集能力,从而特异且高效地将包裹的货物运送到肿瘤细胞。此外,叶酸受体是一种存在于细胞膜表面的糖蛋白,在肿瘤细胞中高度表达[32]。因此,叶酸可以作为靶点制备叶酸受体介导的肿瘤细胞靶向外泌体,以增加肿瘤靶向药物的输送[33]。无论是天然受体还是人工添加或者增强的相应受体,都可以通过受体-配体反应实现工程化外泌体的制备。但是受体-配体反应的结合力较弱,此种方式传递的药物分子的黏附性可能不强。
2.2 工程化外泌体的应用及进展 目前工程化外泌体已经被证明在肿瘤、心血管疾病、神经系统及组织再生与修复等领域均有广阔的临床应用前景。随着工程化外泌体的发展,不仅仅局限于单载药系统,更多双载药、甚至三载药系统已经被开发,以便更好地发挥相互促进、增强疗效的作用。不仅如此,多种制备策略联合运用的情况也越来越多,为工程化外泌体的研究进步提供了更多的可能性。总体而言,工程化外泌体均比天然外泌体展现出了更好的治疗效果及靶向性。
2.2.1 肿瘤 由于肿瘤的高复发率和死亡率、耐药性、转移能力和预后差,对人类健康构成了严重威胁,因此对肿瘤的研究一直以来都是经久不衰的热点,在工程化外泌体领域也不例外。外泌体已经被证明可以运输用于肿瘤治疗的抗肿瘤药物。此外,可以通过改变外泌体的内容物和表面物质来提高其临床治疗效果,从而提高靶向性及载药率。例如,LOU等[34]通过基因工程构建了miR-199a修饰的工程化外泌体,发现它可以有效地将miR-199a转移到肝癌细胞,miR-199a修饰的工程化外泌体在体外显著增加了肝癌细胞对阿霉素的敏感性,且在体内也能显著促进阿霉素对肝癌的抗肿瘤作用。来源于肿瘤细胞的外泌体,表面携带着亲本细胞衍生的信号分子,可能能够重新定向母系肿瘤细胞。根据肿瘤细胞外泌体的归巢特性,QIAO等[35]发现肿瘤外泌体可以优先与亲本癌细胞结合,并且延长了阿霉素在肿瘤组织中的滞留时间,为肿瘤的靶向治疗提供了新的方向。外泌体还可以通过影响肿瘤微环境来调节免疫系统功能,从而抑制肿瘤进展。通过电穿孔将siRNA和奥沙利铂负载到骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体,阻断了肿瘤细胞与巨噬细胞的连接,从而抑制了肿瘤微环境中巨噬细胞的极化,此外还增强了奥沙利铂对胰腺导管癌的抗肿瘤作用[36]。
2.2.2 心血管疾病 心血管疾病是除肿瘤以外另一大困扰人类的主要死亡原因。关于心血管疾病的研究有动脉粥样硬化和脑卒中,但大多数集中在缺血性心脏病和心肌梗死。首个将间充质干细胞外泌体应用于心血管疾病的研究发表于2010年,在小鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤模型中,间充质干细胞外泌体可以缩小心肌梗死的范围[37]。此后,工程化外泌体的相关研究也越来越多。例如,与常规条件下培养的细胞收集的外泌体相比,从低氧条件下培养的心脏前体细胞外泌体增加了体外培养的心脏内皮细胞的成管能力,减少了体外培养的心脏成纤维细胞中促纤维化基因的表达,并改善了梗死心脏的功能[38]。在另一项研究中,使用电穿孔技术将miRNA-322加载至心球来源的细胞外泌体中,与天然外泌体相比,减少了心肌梗死小鼠模型中的梗死面积和纤维化,并增加了新生血管的形成[39]。外泌体的共给药系统可用于进一步提高外泌体的药物输送效率,比如,WANG等[40]发现缺氧诱导因子1α过表达外泌体在大鼠急性心肌梗死模型中具有抗细胞凋亡和血管生成的作用,而且当使用生物相容性的水凝胶和外泌体偶联以后,工程化外泌体的心脏修复效果得到了增强。
2.2.3 组织再生与修复 作为一种无细胞治疗手段,工程化外泌体在损伤或缺失的组织及器官的再生医学研究中也发挥了不容忽视的作用。ZHA等[41]构建了负载血管内皮生长因子的工程化外泌体,它具有诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化和调节血管内皮生长因子基因控制传递的双重功能。工程化外泌体通过特定的连接物与3D打印的多孔骨支架结合,有效地增加了节段性骨缺损的成骨和血管生成。该研究具有类似和同等的血管化骨重建的治疗潜力,工程化外泌体的使用为寻找种子细胞的替代和构建无细胞组织工程方面提供了另一种思路。WOO等[42]发现人脂肪来源的干细胞外泌体通过调节免疫反应,可促进人骨关节炎软骨细胞的增殖和迁移,抑制巨噬细胞向滑膜的浸润,有效地保护软骨免于退变,延缓骨关节炎的进展。在此基础上,LIANG等[43]利用基因工程设计了特异性靶向软骨细胞的外泌体,成功地将miR-140靶向输送到软骨深层的软骨细胞,并严格限制在软骨内,而不会明显扩散到其他组织,同时减缓了大鼠模型骨关节炎的进展。
2.2.4 神经系统疾病 近年来越来越多的证据表明,外泌体在一些脑部疾病的发病机制、诊断和治疗模式中发挥作用,包括缺血性脑卒中、阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、多发性硬化症和脑肿瘤等。由于外泌体能穿越血脑屏障,作为脑内给药的治疗性药物载体已受到广泛关注。2010年,SUN等[44]首次将姜黄素装载至外泌体中,说明外泌体通过简单的共孵育可以作为疏水性药物的潜在载体。因此,ZHUANG等[45]接下来用这种方法将姜黄素或葫芦素Ⅰ包裹到外泌体中,外源性姜黄素或葫芦素Ⅰ通过局部鼻腔给药进入脑内,从而显著抑制脂多糖激活的小胶质细胞激活和体内肿瘤生长,延缓实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎疾病的发展。有研究利用点击化学的方法,对间充质干细胞外泌体表面进行脑内皮细胞靶向肽修饰,证实了该外泌体能够很好的靶向短暂性大脑中动脉闭塞小鼠模型的脑缺血区后,在此基础上加载姜黄素至工程化外泌体,发现能够强烈抑制病变区域的炎症反应以及细胞凋亡[27]。在另一项实验中,研究人员评价了干扰素γ激活的间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体治疗多发性硬化症的效果,发现其能够抑制外周血单个核细胞的增殖,减少促炎细胞因子,并在体外增强Treg细胞的诱导;减少神经炎症和脱髓鞘,并改善慢性实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠模型的功能结局[46]。
2.3 工程化外泌体临床转化的问题与挑战 工程化外泌体通过增强特定特性,能够满足特定的治疗需求,工程化外泌体的工业生产是其临床转化的必由之路。然而,外泌体的工业化生产还处于初级阶段,迫切需要建立大规模生产和分离纯化技术。通常,一个合适的工业化过程需要满足以下要求:高产率、简单、省时和可重复,而现有的外泌体提纯方法都无法满足工业化要求。是否能提供充足的技术设备,是否具有相关技术人员,以及是否具有科学和高效率的质量管理系统等也是亟待解决的首要难点。因此,从产外泌体细胞的选择及特性、规模化生产及分离提纯、成分表征、质量控制、储存稳定性和产品安全性几个方面,讨论工程化外泌体的临床转化存在的问题与挑战。
2.3.1 亲本细胞的选择及特性研究 外泌体的生产可以从经典生物制剂(即抗体和蛋白质生产)和细胞疗法的技术发展中得到启发。亲本细胞的选择和培养构成了外泌体生产的首要关键步骤。目前,对于外泌体生产的最佳技术还未达成共识。需要根据外泌体的活性和组织归巢特性以及潜在的免疫原性和致癌性来选择亲本细胞。此外,遗传稳定性、宿主细胞杂质(如病原体,尤其是病毒)和外泌体产量在亲本细胞的选择过程中起主要作用。常见的产外泌体亲本细胞主要是各种间充质干细胞、肿瘤细胞,树突状细胞、神经前体细胞及内皮细胞等也可用于外泌体生产制造[10,47-49]。
至于亲本细胞的培养,比如亲本细胞的代数及培养血清种类等变化,也是外泌体生产过程需要考虑的关键问题。从早代数细胞培养上清液中获得的外泌体可能与从晚代数细胞培养上清中获得的外泌体在性质上有所不同。目前有3种不同类型的培养基用于获得细胞培养来源的外泌体:含血清培养基、无血清培养基和化学成分替代培养基。与无血清培养相比,含血清培养基更有利于细胞生长和外泌体的产生[50]。
2.3.2 规模化生产及分离提纯 外泌体是异质性囊泡,外泌体的分子组成和生物学功能不仅依赖于细胞类型,培养过程中的微小变化可能会改变外泌体的生物学特性,对外泌体产生深远的影响。使用不同的培养基,得到的工程化外泌体表现出不同的特性,BOST等[51]研究者发现,与传统DMEM培养基相比,使用Opti-MEM培养基从整体上显著增加了工程化外泌体的产量,并且这种产量增加与外泌体的分泌途径无关。大量研究均表明,即使来源于相同的亲本细胞最后得到的外泌体也有可能不同,这都会影响药物的传递效率[52]。
与可以大规模生产的合成载体不同,外泌体的生物产生是一个自然过程,扩大具有治疗效果的外泌体数量是一个巨大的挑战。常用的细胞培养方法包括多层培养瓶、生物反应器以及中空纤维盒。对于小规模的细胞培养,细胞可以在摇瓶、旋转器、滚筒、波浪袋或生物反应器中进行扩增。对于大规模的细胞培养,细胞可以在不锈钢生物反应器(高达20 000 L)、平台摇杆式波袋(高达500 L)或一次性生物反应器(高达2 000 L)中扩增。从生产过程安全性的角度来看,最好使用封闭式系统,然而,这些系统比开放式系统更难监控[53]。许多的证据表明,牛奶来源的外泌体可能是获得大量生物相容性外泌体的有效替代来源。尽管使用牛奶外泌体作为药物载体的可行性研究正在进行中[54],但从复合牛奶中大规模分离提纯外泌体的技术仍需优化。
经过亲本细胞的大规模培养收集到大量细胞培养液后,外泌体的分离纯化也是一个不容忽视的关键程序。不同的分离提纯方法得到的外泌体产量差距悬殊,外泌体亚群也有所不同。FREITAS等[55]使用不同的技术提取外泌体,差速离心、密度梯度离心和尺寸排阻色谱获得的外泌体显示出相似的蛋白质和糖链图谱,而总体外泌体分离法却分离出不同的外泌体亚群。此外,差速离心、密度梯度离心和尺寸排阻色谱提取的携带肿瘤相关糖唾液酸氨基转移酶的外泌体样本中有相当多的癌症相关蛋白,而总外泌体分离法分离的外泌体中没有检测到这些蛋白质。由此,在转化研究中,最佳分离纯化操作选择也是至关重要的,因为最终得到的外泌体亚群很有可能会影响临床治疗效果。
2.3.3 成分表征 由于外泌体的大小和复杂性,从生产和质量控制的角度,现有技术可能会限制工程化外泌体产品的物理化学、免疫化学或功能的细节表征。目前有限的产品表征能力也对工程化外泌体产品的机制理解有一定影响,并可能类似于其他纳米颗粒产品,使转化过程变得繁琐且具有风险性。
与合成载体相比,外泌体的病毒样大小和复杂性,在一定程度上导致工程化外泌体具有优异的药物递送能力,但与此同时其全面表征和质量保证却面临巨大挑战[53]。通常,外泌体的表征集中在测量颗粒大小和数量,以及检测特定的表面蛋白和货物。透射电子显微镜成像是表征外泌体结构和大小的标准方法。此外,扫描电子显微镜和动态光散射可以对外泌体进行表征。纳米颗粒跟踪分析可以通过跟踪和分析颗粒的布朗运动来计算外泌体的大小和浓度[56]。成像流式细胞术是在传统流式细胞术的基础上发展起来的一种更为有效的检测方法,它结合了流式细胞术和成像功能来采集信号,并通过电荷耦合器件摄像机探测到的图像对其进行量化[57]。一些实验室常用的生化手段(蛋白质免疫印迹法、酶联免疫吸附法、聚合酶链式反应)也常被用来检测工程化外泌体成分。此外,高通量技术,如下一代测序和质谱学[58](蛋白质组学、脂组学和转录组学),以及冷冻电子显微镜,在评估外泌体的分子组成和结构方面做出了巨大贡献。
合格的体外表征与量化可以预测载药外泌体系统的预期治疗潜力,但是至今仍然缺乏外泌体量化以及分子和物理特征描述的金标准,寻找开发外泌体最佳表征与量化方式是目前研究中不可忽视的一部分。
2.3.4 质量控制 一般来说,生物制品中的活性物质比非生物药品中的活性物质更为复杂。目前,这种复杂程度的物质和构造只能由活器官产生。然而,这样的生产方法本质上面临着一定程度的内在生物变异性,这可能会导致产物的异质性。从工艺设计的角度来看,这种异质性既受表达生物制品的细胞内的生物加工的影响,也受生产生物制品的制造工艺的影响[59]。值得注意的是培养条件,如细胞传代、细胞密度和外泌体收获频率,强烈影响产物质量的各个方面,包括产量、外泌体组成和外泌体生物活性[60]。与用于细胞治疗的哺乳动物细胞不同,哺乳动物细胞的这种偏差至少可以通过表型适应和从头合成来部分补偿,外泌体是相对静态的产品,因此,它们在提取后预计不会发生实质性变化(降解除外)。
在外泌体生产过程中检测和评估产品质量的变化比在蛋白质生产过程中更具挑战性。总体而言,由于微小的变化可能对产品质量和活性产生相当大的影响,外泌体制造过程的稳定性比细胞和抗体生产过程的稳定性要低。尽管存在这一限制,外泌体制造仍可以建立在这些工艺的基础上[61]。但外泌体的大小以及成分和结构的复杂性是独一无二的,因此需要额外的程序对外泌体生产进行把控。这些过程可能包括测量大小和浓度、排除污染物、识别功能标记物和评估载药量以评估每一数量的外泌体的治疗活性等措施,以确保外泌体终产品满足先前确定的关键质量属性[62]。
2.3.5 储存稳定性 最近的研究主要集中在通过评估外泌体的大小、电荷和数量来模拟和储存外泌体的条件(如-80 ℃和4 ℃),但没有发现很强的相关性[63-64]。已证明在4 ℃下储存会对外泌体结构造成聚集和损坏[65]。此外,尽管外泌体的大小和数量在-80 ℃
下保持不变,但却造成了一些生物活性的改变[66]。虽然目前建议在-80 ℃下存储,但其高昂的储存和运输的成本使这种方法无法普及。因此学者们提出了其他的替代方法。WU等[67]提出将外泌体保存在GelMA水凝胶中从而减少外泌体聚集,达到保存外泌体的目的,将来是否能够应用于临床还需要更多的结果验证。另一种较常见的保存方法是冷冻干燥,CHAROENVIRIYAKUL等[68]发现冻干的外泌体可以在室温下储存,且能够保持外泌体的囊泡大小和蛋白质含量、结构完整性、生物活性及运送药物分子的药代动力学等关键属性,效果可以与新鲜外泌体媲美,但是冷冻干燥剂的应用是必须的。由此看来比起低温冷冻、凝胶保存,冷冻干燥法有利于外泌体类治疗药物的商业化。
2.3.6 产品安全性 纳米药物可能会导致一些不良免疫反应发生,比如过敏反应、细胞因子释放综合征、生物活性的中和、与内源性蛋白对应物的交叉反应和非急性免疫反应等。因此,对工程化外泌体的安全性和有效性加以证明对研究人员来说是一项挑战[69]。
目前,产品制造商被要求注明药物中所有能够引起药理、免疫或新陈代谢作用的物质,并且在最终配方中使用的非活性成分(称为赋形剂)也应予以申报。国际胞外囊泡协会声明,如果整个治疗效果可以归因于外泌体的负载药物,而不是载药外泌体系统中的外泌体,则外泌体可以被视为赋形剂。在这种情况下,仅需要外泌体的安全性描述,而不需要描述其作用方式或机制。如果安全和质量标准均充分达到要求,并且提供了可信的作用方式和机制,则可以允许进行Ⅰ期临床试验[70]。
免疫排斥是临床转化中的首要关注问题,自体外泌体产品能够较好地规避这种风险。虽然已有一些制药公司开发了商业化自体外泌体产品,例如Brianstorm公司的自体骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体[71],但目前主要的产业结构仍然是小规模的学术研究,而不是大规模的制药生产,其生产成本也使很多公司望而却步。并且,生产自体外泌体的时间和临床首次治疗的时间一般很难匹配。在特定患者外泌体制造和质控这段时间内,患者的病情可能会恶化,因此缩短个体化外泌体产品的临床转化时间是亟待解决的首要问题。DONG等[72]的研究表明,同种和异种来源的外泌体都不造成免疫排斥,为异种外泌体的应用提供了可能性。
同种异体外泌体,甚至异种外泌体要转化为安全有效的临床治疗产品,需要通过持续监测来严格把控亲本细胞的选择、免疫学和致癌效应的评估以及病毒污染的风险等问题。监测方法的选择,特别是它们的灵敏度,是确定外泌体药物载体临床转化所需时间的关键挑战。虽然已有多种外泌体产品被测试,但每个实验室和公司的测试方法却并不统一[73],监管机构至今尚未发布关于如何测试这些外泌体的安全性和有效性的指导意见,因此需要对现有的测试方法进行改进或者寻找新方法对工程化外泌体的安全性和有效性进行证明,争取工程化外泌体产业在不久的将来能够得到统一规制,为进入临床应用阶段迈出坚实一步。

| [1] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487-514. [2] YU B, ZHANG X, LI X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157. [3] ZHANG Y, YU M, TIAN W. Physiological and pathological impact of exosomes of adipose tissue. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(1):3-13. [4] RAPOSO G, STOORVOGEL W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383. [5] KOOIJMANS SAA, FLIERVOET LAL, VAN DER MEEL R, et al. PEGylated and targeted extracellular vesicles display enhanced cell specificity and circulation time. J Control Release. 2016;224:77-85. [6] LI S, WU Y, DING F, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted chemotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer. Nanoscale. 2020;12(19):10854-10862. [7] MILBANK E, DRAGANO NRV, GONZALEZ-GARCIA I, et al. Small extracellular vesicle-mediated targeting of hypothalamic AMPKalpha1 corrects obesity through BAT activation. Nat Metab. 2021;3(10):1415-1431. [8] FUHRMANN G, SERIO A, MAZO M, et al. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Control Release. 2015;205:35-44. [9] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y, YIN H, et al. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29(4):341-345. [10] XU X, LIANG Y, LI X, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120539. [11] XU F, FEI Z, DAI H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles with high pd-l1 expression for autoimmune diseases treatment. Adv Mater. 2021:e2106265. [12] PATTON MC, ZUBAIR H, KHAN MA, et al. Hypoxia alters the release and size distribution of extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer cells to support their adaptive survival. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(1):828-839. [13] PASCUCCI L, COCCÈ V, BONOMI A, et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: a new approach for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;192:262-270. [14] DIDIOT MC, HALL LM, COLES AH, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of hydrophobically modified siRNA for huntingtin mRNA silencing. Mol Ther. 2016;24(10):1836-1847. [15] KIM S, KANG JH, NGUYEN CAO TG, et al. Extracellular vesicles with high dual drug loading for safe and efficient combination chemo-phototherapy. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(11):2817-2830. [16] RAGHAV A, JEONG GB. A systematic review on the modifications of extracellular vesicles: a revolutionized tool of nano-biotechnology. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):459. [17] DU J, WAN Z, WANG C, et al. Designer exosomes for targeted and efficient ferroptosis induction in cancer via chemo-photodynamic therapy. Theranostics. 2021;11(17):8185-8196. [18] MOMEN-HERAVI F, BALA S, BUKONG T, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-155 inhibitor to macrophages. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(7):1517-1527. [19] KOOIJMANS SAA, STREMERSCH S, BRAECKMANS K, et al. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J Control Release. 2013; 172(1):229-238. [20] HOOD JL, SCOTT MJ, WICKLINE SA. Maximizing exosome colloidal stability following electroporation. Anal Biochem. 2014;448:41-49. [21] DUMONTEL B, SUSA F, LIMONGI T, et al. Nanotechnological engineering of extracellular vesicles for the development of actively targeted hybrid nanodevices. Cell Biosci. 2022;12(1):61. [22] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207: 18-30. [23] CIECHOMSKA IA, TOLKOVSKY AM. Non-autophagic GFP-LC3 puncta induced by saponin and other detergents. Autophagy. 2007;3(6): 586-590. [24] HETTICH BF, BADER JJ, LEROUX JC. Encapsulation of hydrophilic compounds in small extracellular vesicles: loading capacity and impact on vesicle functions. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(5):e2100047. [25] GOH WJ, LEE CK, ZOU S, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded cell-derived nanovesicles: an alternative targeted approach for anti-tumor therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2759-2767. [26] WANG M, LV CY, LI SA, et al. Near infrared light fluorescence imaging-guided biomimetic nanoparticles of extracellular vesicles deliver indocyanine green and paclitaxel for hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy against glioma. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):210. [27] TIAN T, ZHANG H X, HE CP, et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;150:137-149. [28] KADDOUR H, PANZNER TD, WELCH JL, et al. Electrostatic surface properties of blood and semen extracellular vesicles: implications of sialylation and HIV-induced changes on EV internalization. Viruses. 2020;12(10):1117. [29] TAMURA R, UEMOTO S, TABATA Y. Augmented liver targeting of exosomes by surface modification with cationized pullulan. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:274-284. [30] FROHLICH E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7: 5577-5591. [31] ZHAN Q, YI K, QI H, et al. Engineering blood exosomes for tumor-targeting efficient gene/chemo combination therapy. Theranostics. 2020;10(17):7889-7905. [32] SHEN J, HU Y, PUTT K S, et al. Assessment of folate receptor alpha and beta expression in selection of lung and pancreatic cancer patients for receptor targeted therapies. Oncotarget. 2018;9(4):4485-4495. [33] FENG C, XIONG Z, WANG C, et al. Folic acid-modified Exosome-PH20 enhances the efficiency of therapy via modulation of the tumor microenvironment and directly inhibits tumor cell metastasis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(4):963-974. [34] LOU G, CHEN L, XIA C, et al. MiR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):4. [35] QIAO L, HU S, HUANG K, et al. Tumor cell-derived exosomes home to their cells of origin and can be used as Trojan horses to deliver cancer drugs. Theranostics. 2020;10(8):3474-3487. [36] ZHOU W, ZHOU Y, CHEN X, et al. Pancreatic cancer-targeting exosomes for enhancing immunotherapy and reprogramming tumor microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120546. [37] LAI RC, ARSLAN F, LEE MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3): 214-222. [38] GRAY W D, FRENCH K M, GHOSH-CHOUDHARY S, et al. Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiac progenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ Res. 2015;116(2): 255-263. [39] YOUN SW, LI Y, KIM YM, et al. Modification of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes by miR-322 provides protection against myocardial infarction through Nox2-dependent angiogenesis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(1):18. [40] WANG Q, ZHANG L, SUN Z, et al. HIF-1alpha overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-encapsulated arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD) hydrogels boost therapeutic efficacy of cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Mater Today Bio. 2021;12:100171. [41] ZHA Y, LI Y, LIN T, et al. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397-409. [42] WOO CH, KIM HK, JUNG GY, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1):1735249. [43] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36938-36947. [44] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614. [45] ZHUANG X, XIANG X, GRIZZLE W, et al. Treatment of brain inflammatory diseases by delivering exosome encapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs from the nasal region to the brain. Mol Ther. 2011;19(10):1769-1779. [46] RIAZIFAR M, MOHAMMADI MR, PONE EJ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes as nanotherapeutics for autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders. ACS Nano. 2019;13(6):6670-6688. [47] TIEU A, LALU MM, SLOBODIAN M, et al. An analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for preclinical use. ACS Nano. 2020;14(8):9728-9743. [48] KOK VC, YU CC. Cancer-derived exosomes: their role in cancer biology and biomarker development. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8019-8036. [49] CAO L, TIAN T, HUANG Y, et al. Neural progenitor cell-derived nanovesicles promote hair follicle growth via miR-100. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):20. [50] STAUBACH S, BAUER FN, TERTEL T, et al. Scaled preparation of extracellular vesicles from conditioned media. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;177:113940. [51] BOST JP, SAHER O, HAGEY D, et al. Growth media conditions influence the secretion route and release levels of engineered extracellular vesicles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;11(5):e2101658. [52] LI S, XU J, QIAN J, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy: recent advances and challenges in clinical translation. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(24):6978-6991. [53] ROHDE E, PACHLER K, GIMONA M. Manufacturing and characterization of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical testing. Cytotherapy. 2019;21(6):581-592. [54] MUNAGALA R, AQIL F, JEYABALAN J, et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016;371(1):48-61. [55] FREITAS D, BALMANA M, POCAS J, et al. Different isolation approaches lead to diverse glycosylated extracellular vesicle populations. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1621131. [56] GERCEL-TAYLOR C, ATAY S, TULLIS RH, et al. Nanoparticle analysis of circulating cell-derived vesicles in ovarian cancer patients. Anal Biochem. 2012;428(1):44-53. [57] GÖRGENS A, BREMER M, FERRER-TUR R, et al. Optimisation of imaging flow cytometry for the analysis of single extracellular vesicles by using fluorescence-tagged vesicles as biological reference material. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1587567. [58] KREIMER S, BELOV AM, GHIRAN I, et al. Mass-spectrometry-based molecular characterization of extracellular vesicles: lipidomics and proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(6):2367-2384. [59] VULTO AG, JAQUEZ OA. The process defines the product: what really matters in biosimilar design and production? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(suppl_4):iv14-iv29. [60] PATEL DB, GRAY KM, SANTHARAM Y, et al. Impact of cell culture parameters on production and vascularization bioactivity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017;2(2):170-179. [61] IANCU EM, KANDALAFT LE. Challenges and advantages of cell therapy manufacturing under Good Manufacturing Practices within the hospital setting. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2020;65:233-241. [62] BHATIA SN, CHEN X, DOBROVOLSKAIA MA, et al. Cancer nanomedicin. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;8:1-7. [63] DE JONG OG, KOOIJMANS SAA, MURPHY DE, et al. Drug delivery with extracellular vesicles: from imagination to innovation. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(7):1761-1770. [64] DEVILLE S, BERCKMANS P, VAN HOOF R, et al. Comparison of extracellular vesicle isolation and storage methods using high-sensitivity flow cytometry. PLoS One. 2021;16(2):e0245835. [65] PAGANINI C, CAPASSO PALMIERO U, POCSFALVI G, et al. Scalable production and isolation of extracellular vesicles: available sources and lessons from current industrial bioprocesses. Biotechnol J. 2019; 14(10):e1800528. [66] LORINCZ AM, TIMAR CI, MAROSVARI KA, et al. Effect of storage on physical and functional properties of extracellular vesicles derived from neutrophilic granulocytes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3:25465. [67] WU K, HE C, WU Y, et al. Preservation of small extracellular vesicle in gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel through reduced particles aggregation for therapeutic applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:7831-7846. [68] CHAROENVIRIYAKUL C, TAKAHASHI Y, NISHIKAWA M, et al. Preservation of exosomes at room temperature using lyophilization. Int J Pharm. 2018;553(1-2):1-7. [69] HERRMANN IK, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759. [70] LENER T, GIMONA M, AIGNER L, et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:30087. [71] KASPI H, SEMO J, ABRAMOV N, et al. MSC-NTF (NurOwn®) exosomes: a novel therapeutic modality in the mouse LPS-induced ARDS model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):72. [72] DONG J, WU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of the therapeutic effect of allogeneic and xenogeneic small extracellular vesicles in soft tissue repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6975-6991. [73] SHEARN AIU, ADAY S, BEN-AICHA S, et al. Analysis of neat biofluids obtained during cardiac surgery using nanoparticle tracking analysis: methodological considerations. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:367. [74] Consumer Alert on Regenerative Medicine Products Including Stem Cells and Exosomes. 2020. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/consumers-biologics/consumer-alert-regenerative-medicine-products-including-stem-cells-and-exosomes. |
| [1] | 农复香, 蒋志雄, 李英豪, 许文聪, 施智兰, 罗 慧, 张晴朗, 钟 爽, 唐梅文. 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病诊断治疗中的应用与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | 潘钟杰, 秦志鸿, 郑铁军, 丁晓飞, 廖世杰. 股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | 李启程, 邓 进, 付小洋, 韩 娜. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体对成肌细胞缺氧状态的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [4] | 王 敏, 尹秀山, 王盈熹, 张 妍, 赵 龙, 夏书月. 吸入骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体减轻慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎性损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [5] | 张厚君, 邓博文, 蒋昇源, 赵 毅, 任敬佩, 徐 林, 穆晓红. 脑性瘫痪儿童脑脊液内外泌体的蛋白质组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [6] | 高 婷, 马小红, 李晓荣. 三种不同来源卵巢颗粒细胞外泌体的提取及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [7] | 袁 博, 谢利德, 付秀美. 许旺细胞源性外泌体促进损伤周围神经的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [8] | 许其静, 杨伊春, 雷 微, 杨 莹, 余 江, 夏婷婷, 张 萌, 章 涛, 张 潜. 糖尿病皮肤慢性创面无细胞治疗的进展与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [9] | 陈冠廷, 张琳琪, 李清茹. 外泌体miRNA对慢性肾脏病诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [10] | 刘文涛, 冯兴超, 杨 毅, 白生宾. M2型巨噬细胞外泌体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [11] | 张伟业, 展嘉文, 朱立国, 王尚全, 陈 明, 魏 戌, 冯敏山, 于 杰, 韩 涛, 蔡楚豪, 周帅琪, 邵晨晨. 循环牵张力作用下髓核外泌体对终板软骨细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(2): 223-229. |
| [12] | 张雨薇, 刘川川, 毛稼琦, 张晴晴, 刘 红, 陈 英, 马 兰. 低氧预处理脐带间充质干细胞源外泌体抑制肺动脉平滑肌细胞的增殖[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 2986-2992. |
| [13] | 陈 三, 杨润泽, 吴家媛. 预处理来源外泌体在细胞增殖分化及凋亡中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 3029-3039. |
| [14] | 赵 延, 夏秋秋, 向少杰, 毛启名, 孔维军, 杜 迁, 廖文波, 辛志军. 外泌体miRNA参与脊柱关节退行性疾病修复的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 3040-3051. |
| [15] | 黄双霜, 向小娜, 余 曦, 何 竟. 富血小板血浆来源外泌体治疗膝骨关节炎的机制与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2420-2426. |
工程化外泌体主要是指天然外泌体经过生物工程技术处理后,具有增强的载药效率、靶向性以及抵抗机体清除率等特点的一类被改造修饰的外泌体。通常这类外泌体的大小和形状不会发生明显变化[5-8],但是根据不同的研究目的,其膜负载物或内容物会有明显区别。
虽然工程化外泌体已经被证实在肿瘤、心血管疾病、组织再生与修复及神经系统疾病等多个领域有显著的应用前景,然而至今仍然没有任何一项研究使其迈入临床研究的新阶段,最终将工程化外泌体用于临床还面临着药物装载、大规模生产、成分表征、质量控制、储存与转运以及安全性等多个问题和挑战。以往关于工程化外泌体的文章大多侧重于工程化外泌体的制备策略、分离提纯,或者在各个疾病领域的研究进展,而文章不仅对目前工程化外泌体主要组织工程改造策略的最新研究及进展进行了概括,总结了目前工程化外泌体在基础研究中的主要应用,而且还把目光聚焦于工程化外泌体的临床转化面临的诸多问题和挑战,并对此进行了总结讨论,期望为工程化外泌体的临床转化研究提供更确切的理论基础与实践依据。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索2007-2022年发表的相关文献,重点检索2018-2022年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed 数据库和美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)网站。
1.1.4 检索词 以“exosomes,extracellular vesicles,drug delivery,engineering,engineered,modified,treatment,clinical translation,scale production,isolation,characterization,quality,storage,safety”为检索词检索。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述和网页声明。
1.1.6 检索策略 PudMed数据库检索策略见图1。
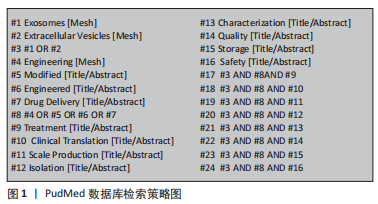
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索文献874篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 纳入工程化外泌体研究现状及其临床转化挑战研究相关的文献;
1.2.2 排除标准 与此研究目的及内容无关的文献或重复性研究。
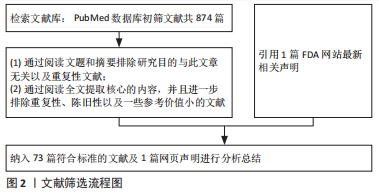
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 根据文章题目及摘要进行初步筛选,通过文献泛读和精读后提炼出与文章内容相关的研究原著、综述及FDA网页声明,排除与研究目的相关性差及内容陈旧、质量不高、重复文献801篇,纳入73篇符合标准的文献及1篇网页声明进行综述。文献筛选流程图,见图2。
 细胞工程是指对外泌体亲本细胞进行改造,主要有基因工程、改变培养条件及药物共孵育等方法。细胞工程中亲本细胞来源广泛且易得,尤其是基因工程的方法,只要对亲本细胞加以基因修饰,就算是稀有细胞类型的功能也可以转移至更容易获得的细胞上,便可以通过细胞培养而源源不断地获得大量外泌体。但是区别于正常生长的细胞,细胞工程改造后的细胞是否会发生产外泌体特性的改变仍需要进一步研究证实,不能一概而论。而外泌体工程是直接对外泌体进行改造,可以分为孵育法、物理法、皂化以及表面修饰等。相比于细胞工程的低效率性和高难度性,直接对纯化的天然外泌体进行修饰,可以直接、高效快速地获得大量工程化外泌体,并且减少了细胞培养及外泌体分离提纯过程中的不确定性,使得获得的工程化外泌体更加均一,对工程化外泌体临床应用的规模化生产具有重要意义。然而,无论是细胞工程还是外泌体工程,均面临着一系列生物安全性、载药效率低下等问题亟待解决。
细胞工程是指对外泌体亲本细胞进行改造,主要有基因工程、改变培养条件及药物共孵育等方法。细胞工程中亲本细胞来源广泛且易得,尤其是基因工程的方法,只要对亲本细胞加以基因修饰,就算是稀有细胞类型的功能也可以转移至更容易获得的细胞上,便可以通过细胞培养而源源不断地获得大量外泌体。但是区别于正常生长的细胞,细胞工程改造后的细胞是否会发生产外泌体特性的改变仍需要进一步研究证实,不能一概而论。而外泌体工程是直接对外泌体进行改造,可以分为孵育法、物理法、皂化以及表面修饰等。相比于细胞工程的低效率性和高难度性,直接对纯化的天然外泌体进行修饰,可以直接、高效快速地获得大量工程化外泌体,并且减少了细胞培养及外泌体分离提纯过程中的不确定性,使得获得的工程化外泌体更加均一,对工程化外泌体临床应用的规模化生产具有重要意义。然而,无论是细胞工程还是外泌体工程,均面临着一系列生物安全性、载药效率低下等问题亟待解决。工程化外泌体已经被用于肿瘤、心血管疾病、组织再生与修复与神经系统疾病等各个领域的研究中,并且均展示出了优越的治疗效果。尽管间充质干细胞来源的天然外泌体已经在接受临床评估当中,有望为工程化外泌体的临床转化应用奠定基础。但用于治疗人类疾病或者病症的外泌体产品都需要受到严格监管,目前仍然没有任何的外泌体产品得到美国食品药品监督管理局的批准[74],距离外泌体产品的正式面世还有一段很长的路要走。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此前,关于工程化外泌体的文章大多侧重于工程化外泌体的制备策略、分离提纯,或者在各个疾病领域的研究进展,但是没有一篇文章系统、全面地概括工程化外泌体的临床转化面临的实际问题和挑战。
文章首先从细胞工程与外泌体工程两个方面概括了工程化外泌体的制备策略,分别对每种策略进行了阐述以及优缺点的比较。然后概括了工程化外泌体在疾病治疗领域的最近研究进展。最后,文章创新性的把目光聚焦于工程化外泌体的临床应用上,从外泌体细胞的选择及特性、规模化生产及分离提纯、成分表征、质量控制、储存稳定性和产品安全性等6个方面,总结讨论了目前工程化外泌体的临床转化存在的问题与挑战。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于目前仍然没有工程化外泌体用于临床的研究,研究者们对研究结果的讨论仍然不够深入,对工程化外泌体临床转化面临的问题与挑战总结归纳也不够全面。但随着国内外相关研究结果的进一步发展,一定会得到相应的改善。
3.4 综述的重要意义 对工程化外泌体主要制备策略进行了综述,并且分别比较了各种方法的优缺点,使研究者们能够快速明了的根据需要选择最高效、最适用的工程化外泌体制备策略。对各个领域工程化外泌体研究的总结能够帮助学者们尽快掌握研究的发展脉络与最新成果。同时,全面深入地探讨了工程化外泌体临床转化的难点与痛点,给研究者们带来很多启发,为工程化外泌体的临床转化研究提供了确切的理论基础与实践依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 想要实现工程化外泌体的临床转化,需要解决外源性分子的插入是否会引起外泌体初始生物特性的变化,如增强外泌体的免疫原性、降低其稳定性、增加意外毒性等一系列问题。同时,由于外泌体的异质性,整个生产过程的标准化也迫在眉睫。它不仅需要完善统一的生产、分离、表征和储存程序,公认的安全性和有效性评价系统,还要建立临床给药方案的指南,这对于外泌体纳米载体的新兴领域是一个极具挑战性的过程。外泌体的储存也是一个很大的障碍,冷冻干燥可能是一种有利于外泌体类治疗药物商业化的方法,但临床数据尚需完善。考虑到这些问题,外泌体的临床转化仍需要持续的努力。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
工程化外泌体:主要是指天然外泌体经过生物工程技术处理后,具有增强的载药效率、靶向性以及抵抗机体清除率等特点的一类被改造修饰的外泌体。通常这类外泌体的大小和形状不会发生明显变化,但是根据不同的研究目的,其膜负载物或内容物会有明显区别。临床转化:主要是指把基础医学研究获得的知识、成果转化为临床治疗的新方法,打破基础医学与临床医学之间固有的屏障,弥补基础实验研发与临床应用间的鸿沟,为开发新药及研究新的治疗方法开辟出的一条新途径。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
外泌体近年来受到了大量的关注,它是从细胞中释放出来的纳米级别的膜性小泡,粒径大小为40-100 nm,在蔗糖溶液中的密度为1.13-1.19 g/mL,可通过100,000×g的高速离心将其沉淀。外泌体生物相容性高、免疫原性低,这使得外泌体在运送核酸序列和化疗药物等方面具有巨大的潜力。但是有研究表明天然外泌体大部分在体内的生物半衰期较短(<6 h)。而且天然外泌体内容物成分受限于亲本细胞,并不负载药物分子,治疗效果有限。因此,科学家们通过生物工程技术改造天然外泌体,增强其药物递送、靶向以及减缓聚集、蛋白质吸附和肾脏清除等能力,工程化外泌体的研究应运而生。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||