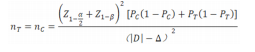[1] D’LIMA DD, URQUHART AG, BUEHLER KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(3):315-321.
[2] PATEL AB, WAGLE RR, USREY MM, et al. Guidelines for implant placement to minimize impingement during activities of daily living after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(8):1275-1281.e1.
[3] ALASTRUEY-LÓPEZ D, EZQUERRA L, SERAL B, et al. Using artificial neural networks to predict impingement and dislocation in total hip arthroplasty. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020; 23(10):649-657.
[4] BIEDERMANN R, TONIN A, KRISMER M, et al. Reducing the risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: the effect of orientation of the acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(6):762-769.
[5] ROWAN FE, BENJAMIN B, PIETRAK JR, et al. Prevention of Dislocation After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1316-1324.
[6] SEAGRAVE KG, TROELSEN A, MALCHAU H, et al. Acetabular cup position and risk of dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(1):10-17.
[7] KAHLENBERG CA, SWARUP I, KRELL EC, et al. Causes of Revision in Young Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019; 34(7):1435-1440.
[8] LIN YT, WU JS, CHEN JH. The study of wear behaviors on abducted hip joint prostheses by an alternate finite element approach. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016;131:143-155.
[9] AMSTUTZ HC, LE DUFF MJ. Aseptic loosening of cobalt chromium monoblock sockets after hip resurfacing. Hip Int. 2015;25(5):466-470.
[10] WEBER M, RENKAWITZ T, VOELLNER F, et al. Revision Surgery in Total Joint Replacement Is Cost-Intensive. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018: 8987104.
[11] LEWINNEK GE, LEWIS JL, TARR R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2):217-220.
[12] AU J, PERRIMAN DM, NEEMAN TM, et al. Standing or supine x-rays after total hip replacement - when is the safe zone not safe? Hip Int. 2014;24(6):616-623.
[13] HERNÁNDEZ A, LAKHANI K, NÚÑEZ JH, et al. Can we trust combined anteversion and Lewinnek safe zone to avoid hip prosthesis dislocation? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;21:101562.
[14] TEZUKA T, HECKMANN ND, BODNER RJ, et al. Functional Safe Zone Is Superior to the Lewinnek Safe Zone for Total Hip Arthroplasty: Why the Lewinnek Safe Zone Is Not Always Predictive of Stability. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(1):3-8.
[15] CALLANAN MC, JARRETT B, BRAGDON CR, et al. The John Charnley Award: risk factors for cup malpositioning: quality improvement through a joint registry at a tertiary hospital. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2):319-329.
[16] SCHLOEMANN DT, EDELSTEIN AI, BARRACK RL. Changes in acetabular orientation during total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(6_Supple_B):45-50.
[17] KANAZAWA M, NAKASHIMA Y, OHISHI M, et al. Pelvic tilt and movement during total hip arthroplasty in the lateral decubitus position. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(3):435-440.
[18] SNIJDERS TE, SCHLÖSSER TPC, HECKMANN ND, et al. The Effect of Functional Pelvic Tilt on the Three-Dimensional Acetabular Cup Orientation in Total Hip Arthroplasty Dislocations. J Arthroplasty. 2021; 36(6):2184-2188.e1.
[19] SYKES AM, HILL JC, ORR JF, et al. Pelvic orientation for total hip arthroplasty in lateral decubitus: can it be accurately measured? Hip Int. 2016;26(3):254-259.
[20] TSUKAMOTO M, KAWASAKI M, SUZUKI H, et al. Proposal of accurate cup placement procedure during total hip arthroplasty based on pelvic tilt discrepancies in the lateral position. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13870.
[21] HIDDEMA WB, VAN DER MERWE JF, VAN DER MERWE W. The Transverse Acetabular Ligament as an Intraoperative Guide to Cup Abduction. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(7):1609-1613.
[22] PARK J, KIM GL, YANG KH. Anatomical landmarks for acetabular abduction in adult hips: the teardrop vs. the inferior acetabular rim. Surg Radiol Anat. 2019;41(12):1505-1511.
[23] DIGIOIA AM 3RD, JARAMAZ B, PLAKSEYCHUK AY, et al. Comparison of a mechanical acetabular alignment guide with computer placement of the socket. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(3):359-364.
[24] KALTEIS T, HANDEL M, BÄTHIS H, et al. Imageless navigation for insertion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: is it as accurate as CT-based navigation? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(2): 163-167.
[25] LASS R, KUBISTA B, OLISCHAR B, et al. Total hip arthroplasty using imageless computer-assisted hip navigation: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(4):786-791.
[26] LASS R, OLISCHAR B, KUBISTA B, et al. Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Imageless Computer-Assisted Navigation-2-Year Follow-Up of a Prospective Randomized Study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1620.
[27] 崔可赜,郭祥,韩贵斌,等.MAKO机器人辅助后外侧入路全髋关节置换的学习曲线及临床早期效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(9):1313-1317.
[28] DOMB BG, REDMOND JM, LOUIS SS, et al. Accuracy of Component Positioning in 1980 Total Hip Arthroplasties: A Comparative Analysis by Surgical Technique and Mode of Guidance. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(12):2208-2218.
[29] 中国康复技术转化及发展促进会,周宗科,廖刃,等.中国骨科手术加速康复围手术期疼痛管理指南[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2019,12(12):929-938.
[30] SAXLER G, MARX A, VANDEVELDE D, et al. The accuracy of free-hand cup positioning--a CT based measurement of cup placement in 105 total hip arthroplasties. Int Orthop. 2004;28(4):198-201.
[31] HASSAN DM, JOHNSTON GH, DUST WN, et al. Accuracy of intraoperative assessment of acetabular prosthesis placement. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(1):80-84.
[32] BROWN ML, DUNN JM, EARLY S, et al. The impact of failed novel technology and technical errors on the revision burden in total hip arthroplasty: what percentage of revision hip arthroplasty was potentially avoidable? Hip Int. 2021:1120700021996654.
[33] ASARI T, ROKUNOHE D, SASAKI E, et al.Occupational ionizing radiation-induced skin injury among orthopedic surgeons: A clinical survey. J Orthop Sci. 2022;27(1):266-271.
[34] ELLAPPARADJA P, MAHAJAN V, ATIYA S, et al. Leg length discrepancy in computer navigated total hip arthroplasty - how accurate are we? Hip Int. 2016;26(5):438-443.
[35] WOON CY, MUIR JM, SU EP. Using Imageless Optical Navigation to Identify the New Hip Center in Crowe IV Dysplasia. Orthopedics. 2020;43(2):e119-e122.
[36] KALTEIS T, HANDEL M, HEROLD T, et al. Position of the acetabular cup -- accuracy of radiographic calculation compared to CT-based measurement. Eur J Radiol. 2006;58(2):294-300.
[37] SCHWARZKOPF R, VIGDORCHIK JM, MILLER TT, et al. Quantification of Imaging Error in the Measurement of Cup Position: A Cadaveric Comparison of Radiographic and Computed Tomography Imaging. Orthopedics. 2017;40(6):e952-e958.
[38] SHIN WC, LEE SM, LEE KW, et al. The reliability and accuracy of measuring anteversion of the acetabular component on plain anteroposterior and lateral radiographs after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(5):611-616.
[39] WIDMER KH. A simplified method to determine acetabular cup anteversion from plain radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3):387-390.
[40] MURPHY MP, KILLEN CJ, RALLES SJ, et al. A precise method for determining acetabular component anteversion after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(9):1042-1049.
[41] PARRATTE S, ARGENSON JN. Validation and usefulness of a computer-assisted cup-positioning system in total hip arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(3): 494-499.
[42] OKAMOTO M, KAWASAKI M, OKURA T, et al. Comparison of accuracy of cup position using portable navigation versus alignment guide in total hip arthroplasty in supine position. Hip Int. 2021;31(4):492-499.
[43] PETERS TM. Image-guided surgery: from X-rays to virtual reality. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2000;4(1):27-57.
[44] PETERS TM. Image-guidance for surgical procedures. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(14):R505-R540.
[45] SARIALI E, BOUKHELIFA N, CATONNE Y, et al. Comparison of Three-Dimensional Planning-Assisted and Conventional Acetabular Cup Positioning in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(2):108-116.
[46] ALEXANDER C, LOEB AE, FOTOUHI J, et al. Augmented Reality for Acetabular Component Placement in Direct Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(6):1636-1641.e3.
[47] OGAWA H, HASEGAWA S, TSUKADA S, et al. A Pilot Study of Augmented Reality Technology Applied to the Acetabular Cup Placement During Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(6):1833-1837.
[48] LIU H, AUVINET E, GILES J, et al. Augmented Reality Based Navigation for Computer Assisted Hip Resurfacing: A Proof of Concept Study. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(10):1595-1605.
[49] POUR AE, SCHWARZKOPF R, PATEL KP, et al. Is Combined Anteversion Equally Affected by Acetabular Cup and Femoral Stem Anteversion? J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(7):2393-2401.
[50] MCKNIGHT BM, TRASOLINI NA, DORR LD. Spinopelvic Motion and Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(7S): S53-S56.
[51] BUCKLAND AJ, ABOTSI EJ, VASQUEZ-MONTES D, et al. Lumbar Spine Degeneration and Flatback Deformity Alter Sitting-Standing Spinopelvic Mechanics-Implications for Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020; 35(4):1036-1041.
[52] 王鑫光,赵旻暐,田华.脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡关系对全髋关节置换术髋臼杯安放角度影响的研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2019, 99(27):2154-2157.
[53] CLEMENT ND, GASTON P, BELL A, et al. Robotic arm-assisted versus manual total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(1):22-30.
[54] DOMB BG, EL BITAR YF, SADIK AY, et al. Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional acetabular cup placement in THA: a matched-pair controlled study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(1):329-336.
[55] FU H, YAN CH, CHEUNG A, et al. Robotic-Arm Assistance Simplifies Hip Arthrodesis Conversion to Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6(4):877-887.
|