中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4809-4816.doi: 10.12307/2023.507
• 组织工程骨材料 tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
不同比例羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙涂层支架修复骨缺损
宋美玲1,2,李征宇3,4,艾子政5,李京娜1,2,曾庆丰4,6,韩倩倩7,董谢平1,8,9,10
- 1江西省人民医院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006;2江西中医药大学研究生院,江西省南昌市 330004;3西安市中心医院,陕西省西安市 710003;4点云生物(杭州)有限公司,浙江省杭州市 310018;5南昌市第四医院,江西省南昌市 330104;6迈海材料基因组国际研究院,河北省廊坊市 065500;7中国食品药品检定研究院,北京市 102600;8南昌大学医学院,江西省南昌市 330006;9江西省卫生健康数字骨科重点实验室,江西省南昌市 330006;10南方科技大学医院南方科技大学粤港澳智能与数字外科创新中心,广东省深圳市 518000
Repair effect of different hydroxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate coated scaffolds on bone defects
Song Meiling1, 2, Li Zhengyu3, 4, Ai Zizheng5, Li Jingna1, 2, Zeng Qingfeng4, 6, Han Qianqian7, Dong Xieping1, 8, 9, 10
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Jiangxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Graduate School, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Xi’an Central Hospital, Xi’an 710003, Shaanxi Province, China; 4Particle Cloud Biotechnology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; 5The Fourth Hospital of Nanchang, Nanchang 330104, Jiangxi Province, China; 6MSEA International Institute for Materials Genome, Langfang 065500, Hebei Province, China; 7National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 102600, China; 8Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 9Digital Lab of Orthopeadics, Key Laboratory of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 10Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Intelligent and Digital Surgery Innovation Center, Southern University of Science and Technology Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
临界骨缺损:在动物骨缺损模型中,临界性骨缺损是一重要参数,是指实验动物在自然情况下不能自行愈合的最小尺寸骨缺损。羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙涂层多孔生物陶瓷支架:生物陶瓷材料具有理化性能稳定、生物相容性优异、耐腐蚀、无毒副作用的特点,被广泛应用于骨组织工程领域。此次实验主要是以羟基磷灰石为基体材料制备3D打印多孔生物陶瓷支架,但羟基磷灰石脆性大、韧性低,为提高支架的生物活性和生物降解性,在多孔生物陶瓷支架表面涂覆不同比例羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙(m∶m)双相磷酸钙陶瓷涂层。
背景:羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙双相磷酸钙陶瓷具有良好的生物相容性与骨传导能力,可以作为涂层材料联合用于超临界骨缺损修复,但羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙涂层的最佳质量比目前尚无明确报道。
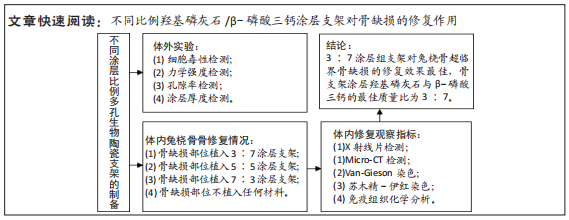
目的:在兔桡骨超临界骨缺损部位植入不同比例羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙涂层多孔生物陶瓷支架,评估其修复作用,以期获得最佳的涂层比例。
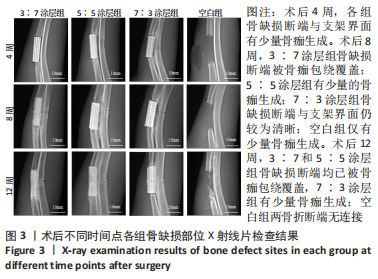
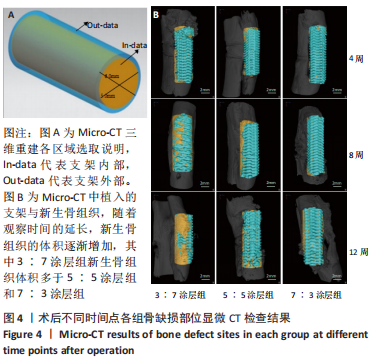
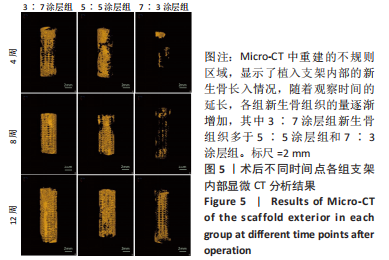
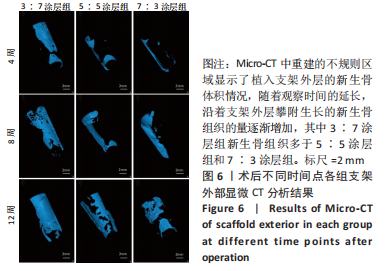
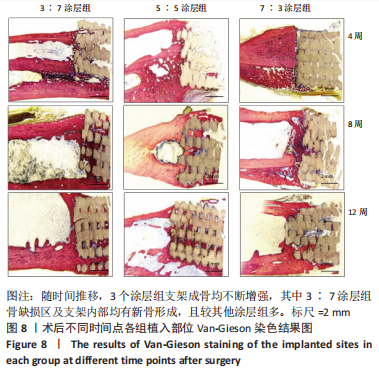
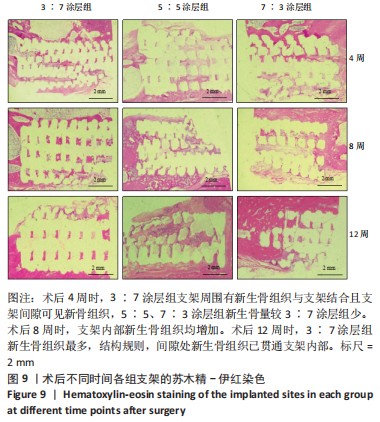
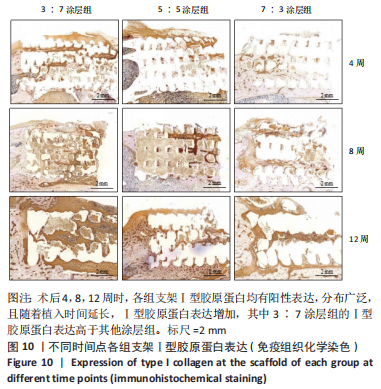
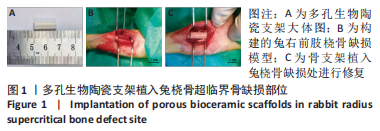
方法:采用3D打印技术制备羟基磷灰石多孔生物陶瓷支架,并在其表面使用不同比例的羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙(二者质量比分别为3∶7,5∶5,7∶3)进行涂层处理,然后对支架的细胞毒性、孔隙率、力学强度、涂层厚度等参数进行测试。在36只新西兰大白兔右前肢建立15.0 mm兔桡骨超临界骨缺损模型,随机分4组处理,每组9只:空白组不植入任何材料,3∶7涂层组、5∶5涂层组、7∶3涂层组分别植入对应质量比例涂层的羟基磷灰石多孔生物陶瓷支架,术后4,8,12周,分别进行X射线片及Micro-CT检查、Van-Gieson染色、苏木精-伊红染色及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白免疫组织化学分析。
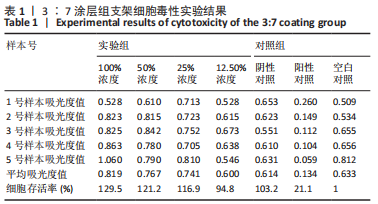
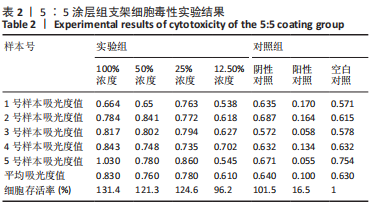
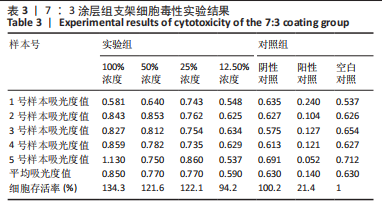
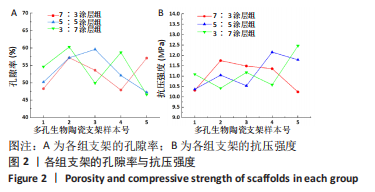
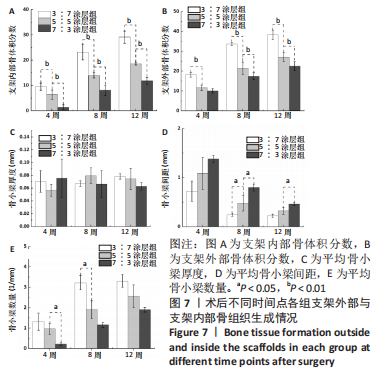
结果与结论:①3∶7、5∶5、7∶3涂层支架的细胞毒性均为0级,涂层厚度为(75.2±0.54) μm,孔隙率分别为(54.02±5.17)%,(53.28± 5.05)%,(52.82±4.55)%,抗压强度分别为(11.15±0.72),(11.18±0.78),(10.24±0.70) MPa;②X射线与Micro-CT检查结果显示,随着时间的增加,各组骨缺损有不同程度的修复,至术后12周时,3∶7涂层组骨缺损修复效果最佳,该组材料内部的骨长入体积与材料外表面的新生骨体积最多;③Van-Gieson染色与苏木精-伊红染色显示,术后12周时,3∶7涂层组骨缺损区及支架内部均有新骨形成,且新生骨组织最多、新生骨结构最为致密;免疫组织化学分析显示,术后12周时,3∶7涂层组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达高于其他两组;④结果表明,3∶7涂层组对兔桡骨超临界骨缺损的修复效果最佳,骨支架涂层羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙的最佳质量比为 3∶7。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8124-2586(宋美玲)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: