中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (22): 3537-3543.doi: 10.12307/2023.356
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
第3代multiloc髓内针、普通弯型髓内针与肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折的比较
刘 涛,查明建,柯荣军
- 镇江瑞康医院骨科,江苏省镇江市 212000
Comparison of the third generation multiloc intramedullary nail, common curved intramedullary nail and proximal humeral locking plate in the treatment of complex proximal humeral fractures
Liu Tao, Zha Mingjian, Ke Rongjun
- Department of Orthopedics, Zhenjiang Ruikang Hospital, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
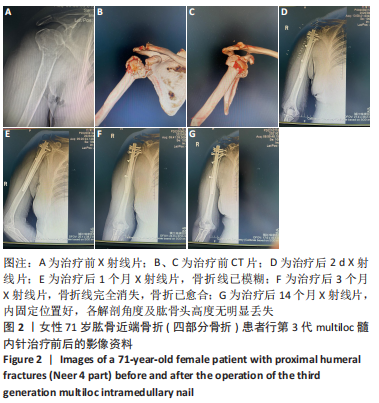
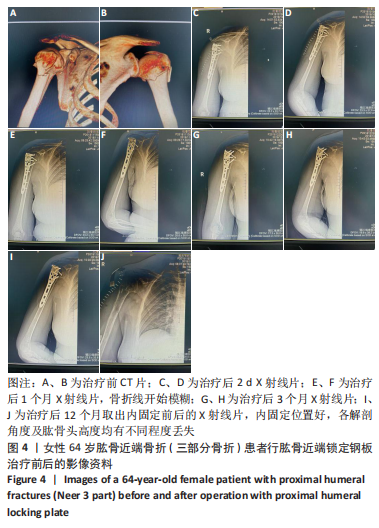
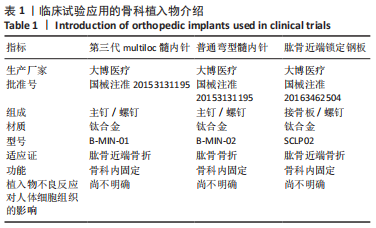
复杂肱骨近端骨折:Neer分型法将肱骨近端分为4部分——肱骨头、大结节、小结节及肱骨干近端部。分型中的移位含义有2个,骨折移位大于1 cm,骨折成角大于45°。肱骨外科颈骨折如果出现大小结节单独骨折移位,则为“三部分骨折”,如果大小结节同时骨折移位,则为“四部分骨折”。小结节骨折移位大于1 cm、伴有肱骨外科颈骨折移位时,属于“三部分骨折”。肱骨近端骨折并盂肱关节脱位,骨折可为“三部分”“四部分”骨折,“三部分”“四部分”骨折为处理相对棘手的复杂肱骨近端骨折。第3代multiloc髓内针:为中心髓内固定的一种,力矩较短,把持力更强。第3代multiloc髓内针的进针点为肱二头肌腱结节间沟后方1 cm、大结节与关节面交界处内侧1 cm处,位于肱骨头最高点,较普通弯型髓内针的进针点更偏内;有近端锁定螺钉和远端锁定螺钉设计,并根据情况可置入数量不等的钉中钉。
背景:对于较为复杂的肱骨近端骨折,临床中多采取植入物内固定治疗,关于何种固定方式更有优势目前仍无定论。
目的:比较第3代multiloc髓内针、普通弯型肱骨髓内针与肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折(Neer 3、4部分)的效果。
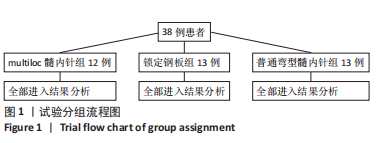
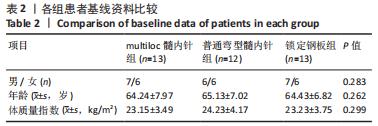
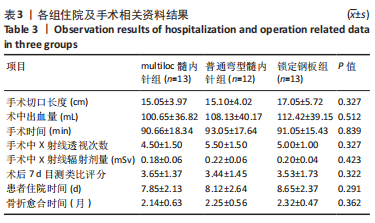
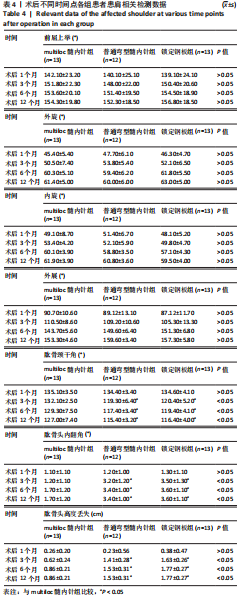
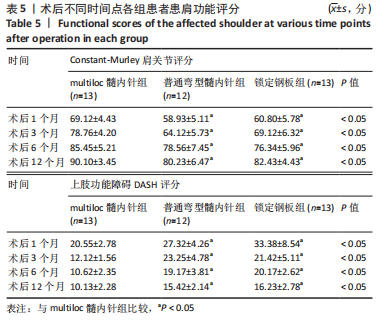
方法:选择2018年8月至2022年3月在镇江瑞康医院接受治疗且进行术后随访的复杂肱骨近端骨折( Neer3、4部分)患者38例,男20例,女18例,年龄57-74岁,其中13例接受第3代multiloc髓内针内固定治疗,12例接受普通弯型髓内针内固定治疗,13例接受肱骨近端锁定钢板内固定治疗。术后随访观察3组骨折愈合时间、目测类比评分、Constant-Murley肩关节评分、上肢功能障碍DASH评分与影像学检查结果。
结果与结论:①38例患者均获得术后随访,随访时间12-18个月,3组间术后7 d的目测类比评分比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),3组间骨折愈合时间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②3组间术后1,3,6,12个月的患肩前屈上举、外旋、内旋、外展角度比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);影像学检查结果显示,multiloc髓内针组术后3,6,12个月的肱骨颈干角大于普通弯型髓内针组、锁定钢板组(P < 0.05),术后3,6,12个月的肱骨头内翻角、肱骨头高度丢失小于普通弯型髓内针组、锁定钢板组(P < 0.05);③multiloc髓内针组术后1,3,6,12个月的Constant-Murley肩关节评分高于普通弯型髓内针组、锁定钢板组(P < 0.05),术后1,3,6,12个月的上肢功能障碍DASH评分低于普通弯型髓内针组、锁定钢板组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,对于复杂肱骨近端骨折(Neer 3、4部分),第3代multiloc髓内针具有显著抗压缩、抗内翻及维持颈干角度的固定优势,并具有肩关节功能恢复快等特点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7809-9755 (刘涛)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: