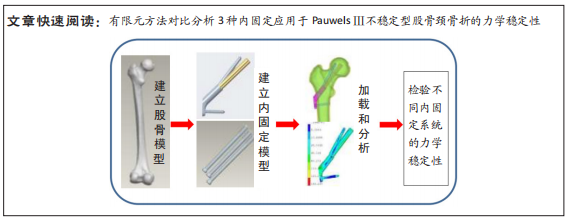
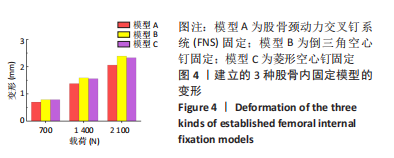
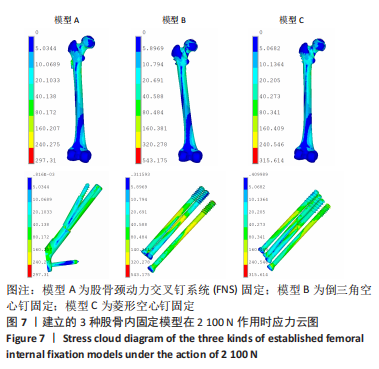
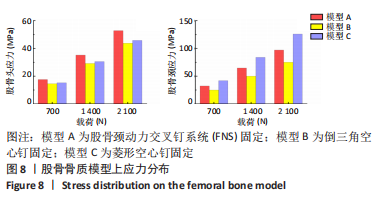
[1] FLORSCHUTZ AV, LANGFORD JR, HAIDUKEWYCH GJ, et al. Femoral Neck Fractures: Current Management. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):121-129.
[2] CHA YH, YOO JI, HWANG SY, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type III Femoral Neck Fractures: A Systematic Review of Various Fixation Methods. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):1-14.
[3] TIANYE L, PENG Y, JINGLI X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[4] GIORDANO V, ALVES DD, PAES RP, et al. The role of the medial plate for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: a coMParative mechanical study using two fixations with cannulated screws. J Exp Orthop. 2019;6(1):18.
[5] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels III Femoral Neck Fractures: A CoMParison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[6] NO AUTHORS.Surgical Technique of FNS System. DePuy Synthes CoMPanies.2021. https://www.jnjmedicaldevices.com/en-US/product/femoral-neck-system-fns.
[7] JUNG CH, CHA Y, YOON HS, et al. Mechanical effects of surgical variations in the femoral neck system on Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture : a finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(2):102-111.
[8] 杨亚军, 马涛, 张小钰, 等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统治疗股骨颈骨折近期疗效[J].骨与关节修复重建,2021,35(5):539-543.
[9] 严才平, 王星宽, 向超,等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统与空心加压螺钉治疗中青年股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].骨与关节修复重建,2021,35(10):1286-1292.
[10] 恽常军, 钱文杰, 张杰, 等.肱骨近端锁定接骨板固定治疗Vancouver B1型股骨假体周围骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021, 23(9):798-803.
[11] 艾克白尔•吐逊, 阿吉木•克热木, 谢增如,等.两种内固定方式固定青壮年不稳定型股骨颈骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2020,22(9):793-798.
[12] 王静, 孙彦豹, 金宝城,等.4枚空心钉菱形固定与动力髋螺钉加防旋钉治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的比较[J].创伤外科杂志,2022,24(2):128-132.
[13] LI J, WANG M, LI L, et al. Finite element analysis of different configurations of fully threaded cannulated screw in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):272.
[14] GARDNER MP, CHONG AC, POLLOCK AG, et al. Mechanical evaluation of large-size fourth-generation composite femur and tibia models. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010; 38(3):613-620.
[15] HEINER AD. Structural properties of fourth-generation composite femurs and tibias. J Biomech. 2008;41(15):3282-3284.
[16] MA L, ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation with finite element analysis of the reconstruction of femoral tumor defects by using a double-barrel free vascularized fibular graft combined with a locking plate. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(9):2425-2434.
[17] CHANG CW, CHEN YN, LI CT, et al. Role of the compression screw in the dynamic hip–screw system: A finite-element study. Med Eng Phys. 2015;37(12):1174-1179.
[18] TAYLOR ME, TANNER KE, FREEMAN MA, et al. Stress and strain distribution within the intact femur: compression or bending? Med Eng Phys. 1996;18(2):122-131.
[19] CUI Y, XING W, PAN Z, et al. Characterization of novel intramedullary nailing method for treating femoral shaft fracture through finite element analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):748-753.
[20] WANG J, MA JX, LU B, et al. CoMParative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[21] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659.
[22] TANG Y, ZHANG Z, WANG L, et al. Femoral neck system versus inverted cannulated cancellous screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures in adults: a preliminary coMParative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):504.
[23] 王青, 姜达君, 贾伟涛. Pauwels 三型股骨颈骨折不同内固定方式的meta分析[J].上海交通大学学报 (医学版),2018,38(9):1045-1052.
[24] ZHOU XQ, LI ZQ, XU RJ, et al. CoMParison of Early Clinical Results for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Screws in the Treatment of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(6):1802-1809.
[25] ZHANG YZ, LIN Y, LI C, et al. A CoMParative Analysis of Femoral Neck System and Three Cannulated Screws Fixation in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures: A Six-Month Follow-Up. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(4):686-693.
[26] 杨家赵, 周雪峰, 李黎,等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统和倒三角空心钉治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(9): 1111-1118.
[27] SCHOPPER C, ZDERIC I, MENZE J, et al. Higher stability and more predictive fixation with the Femoral Neck System versus Hansson Pins in femoral neck fractures Pauwels II. J Orthop Translat. 2020;24:88-95.
[28] 范智荣, 苏海涛, 周霖,等.新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2321-2328.
[29] 任栋, 程培焱, 宋朝晖,等.不同数量和空间构型的空心拉力螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,33(9):815-822.
[30] PAPINI M, ZDERO R, SCHEMITSCH EH, et al. The biomechanics of human femurs in axial and torsional loading: coMParison of finite element analysis, human cadaveric femurs, and synthetic femurs. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1):12-19.
|