[1] Wang W, Pei B, Pei Y, et al. Biomechanical effects of posterior pedicle fixation techniques on the adjacent segment for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a biomechanical analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(13):1083-1092.
[2] Aono H, Tobimatsu H, Ariga K, et al. Surgical outcomes of temporary short-segment instrumentation without augmentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2016;47(6):1337-1344.
[3] Mi J, Sun XJ, Zhang K, et al. Prediction of MRI findings including disc injury and posterior ligamentous complex injury in neurologically intact thoracolumbar burst fractures by the parameters of vertebral body damage on CT scan. Injury. 2018;49(2):272-278.
[4] Aono H, Ishii K, Tobimatsu H, et al. Temporary short-segment pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: comparative study with or without vertebroplasty. Spine J. 2017;17(8):1113-1119.
[5] Haiyun Y, Rui G, Shucai D, et al. Three-column reconstruction through single posterior approach for the treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(8):E295-302.
[6] Lin B, Chen ZW, Guo ZM, et al. Anterior Approach Versus Posterior Approach With Subtotal Corpectomy, Decompression, and Reconstruction of Spine in the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(6):309-317.
[7] De Iure F, Lofrese G, De Bonis P, et al. Vertebral body spread in thoracolumbar burst fractures can predict posterior construct failure. Spine J. 2018;18(6):1005-1013.
[8] Ding S, Lu X, Liu Z, et al. Reduce the fractured central endplate in thoracolumbar fractures using percutaneous pedicle screws and instrumentational maneuvers: Technical strategy and radiological outcomes. Injury. 2021;52(4):1060-1064.
[9] Lee KY, Kim MW, Seok SY, et al. The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult Patients with Thoracolumbar Stable Burst Fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(4):465-471.
[10] Liao JC,Chen WJ. Short-Segment Instrumentation with Fractured Vertebrae Augmentation by Screws and Bone Substitute for Thoracolumbar Unstable Burst Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 4780426.
[11] McCormack T, Karaikovic E,Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(15):1741-1744.
[12] Vaccaro AR, Zeiller SC, Hulbert RJ, et al. The thoracolumbar injury severity score: a proposed treatment algorithm. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):209-215.
[13] Vaccaro AR, Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, et al. The surgical algorithm for the AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(4):1087-1094.
[14] Vaccaro AR, Oner C, Kepler CK, et al. AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: fracture description, neurological status, and key modifiers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(23):2028-2037.
[15] Richardson B, Paulzak A, Rusyniak WG, et al. Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy with Expandable Titanium Cage Reconstruction: A Case Series of 42 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2017;108:317-324.
[16] Li C, Pan J, Gu Y, et al. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture. Int J Surg. 2016;36(Pt A):255-260.
[17] Saglam N, Dogan S, Ozcan C, et al. Comparison of Four Different Posterior Screw Fixation Techniques for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Junction Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e773-e780.
[18] Kwon WK, Park WB, Lee GY, et al. Decompression with Lateral Pediculectomy and Circumferential Reconstruction for Unstable Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Surgical Techniques and Results in 18 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2018; 20:e53-e62.
[19] Lindtner RA, Mueller M, Schmid R, et al. Monosegmental anterior column reconstruction using an expandable vertebral body replacement device in combined posterior-anterior stabilization of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(7): 939-951.
[20] Liao JC,Fan KF. Posterior short-segment fixation in thoracolumbar unstable burst fractures - Transpedicular grafting or six-screw construct. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;153:56-63.
[21] Yang S, Shang DP, Lu JM, et al. Modified Posterior Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Lumbar Burst Fractures with Incomplete Neurological Deficit. World Neurosurg. 2018;119: e977-e985.
[22] Smits AJ, Noor A, Bakker FC, et al. Thoracoscopic anterior stabilization for thoracolumbar fractures in patients without spinal cord injury: quality of life and long-term results. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(7):1593-1603.
[23] Hao D, Wang W, Duan K, et al. Two-year follow-up evaluation of surgical treatment for thoracolumbar fracture-dislocation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(21):E1284-1290.
[24] Liang C, Liu B, Zhang W, et al. Clinical Effects of Posterior Limited Long-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures. J Invest Surg. 2020;33(1):25-30.
[25] Kapoen C, Liu Y, Bloemers FW, et al. Pedicle screw fixation of thoracolumbar fractures: conventional short segment versus short segment with intermediate screws at the fracture level-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(10):2491-2504.
[26] Xiong C, Huang B, Wei T, et al. Effect of the short-segment internal fixation with intermediate inclined-angle polyaxial screw at the fractured vertebra on the treatment of Denis type B thoracolumbar fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):182.
[27] Basaran R, Efendioglu M, Kaksi M, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Short- Versus Long-Segment Posterior Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture. World Neurosurg. 2019;128:e1109-e1117.
[28] Dobran M, Nasi D, Brunozzi D, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures: short-segment pedicle fixation with inclusion of the fracture level versus long-segment instrumentation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158(10):1883-1889.
[29] Kocanli O, Komur B, Duymuş TM, et al. Ten-year follow-up results of posterior instrumentation without fusion for traumatic thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. J Orthop. 2016;13(4):301-305.
[30] D’Oro A, Spoonamore MJ, Cohen JR, et al. Effects of fusion and conservative treatment on disc degeneration and rates of subsequent surgery after thoracolumbar fracture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3): 476-482.
[31] Ankomah F, Ikpeze T, Mesfin A. The Top 50 Most-Cited Articles on Thoracolumbar Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2018;118:e699-e706.
[32] Sensale M, Vendeuvre T, Schilling C, et al. Patient-Specific Finite Element Models of Posterior Pedicle Screw Fixation: Effect of Screw’s Size and Geometry. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:643154.
[33] Machino M, Yukawa Y, Ito K, et al. The complement of the load-sharing classification for the thoracolumbar injury classification system in managing thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(1):81-86.
[34] Liu J, Yang S, Zhou F, et al. The feasibility of short-segment Schanz screw implanted in an oblique downward direction for the treatment of lumbar 1 burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):537.
[35] Liu J, Yang S, Lu J, et al. Biomechanical effects of USS fixation with different screw insertion depths on the vertebrae stiffness and screw stress for the treatment of the L1 fracture. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(2):285-297.
[36] Zhou F, Yang S, Liu J, et al. Finite element analysis comparing short-segment instrumentation with conventional pedicle screws and the Schanz pedicle screw in lumbar 1 fracture. Neurosurg Rev. 2020; 43(12):301-312.
[37] Welch-Phillips A, Gibbons D, Ahern DP, et al. What Is Finite Element Analysis? Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(8):323-324.
[38] Ye Y, You W, Zhu W, et al. The Applications of Finite Element Analysis in Proximal Humeral Fractures. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017;2017:4879836.
[39] Goel VK, Nyman E. Computational Modeling and Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 7:S6-7.
[40] Quah C, Yeoman MS, Cizinauskas A, et al. Finite element investigation of the effect of a bifid arch on loading of the vertebral isthmus. Spine J. 2014;14(4):675-682.
[41] Webb JD, Blemker SS, Delp SL. 3D finite element models of shoulder muscles for computing lines of actions and moment arms. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2014;17(8):829-837.
[42] Benca E, Amini M, Pahr DH. Effect of CT imaging on the accuracy of the finite element modelling in bone. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):51.
[43] Kulduk A, Altun NS, Senkoylu A. Biomechanical comparison of effects of the Dynesys and Coflex dynamic stabilization systems on range of motion and loading characteristics in the lumbar spine: a finite element study. Int J Med Robot. 2015;11(4):400-405.
[44] Han Y, Wang X, Wu J, et al. Biomechanical finite element analysis of vertebral column resection and posterior unilateral vertebral resection and reconstruction osteotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):88.
[45] Eggermont F, van der Wal G, Westhoff P, et al. Patient-specific finite element computer models improve fracture risk assessments in cancer patients with femoral bone metastases compared to clinical guidelines. Bone. 2020;130:115101.
[46] Widmer J, Fasser MR, Croci E, et al. Individualized prediction of pedicle screw fixation strength with a finite element model. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(4):155-167.
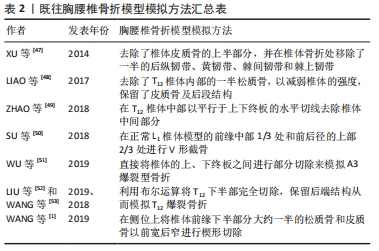
[47] Xu G, Fu X, Du C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of mono-segment transpedicular fixation with short-segment fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(10):1005-1013.
[48] Liao JC, Chen WP, Wang H. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by short-segment pedicle screw fixation using a combination of two additional pedicle screws and vertebroplasty at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 18(1):262.
[49] Zhao WT, Qin DP, Zhang XG, et al. Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):32.
[50] Su Y, Wang X, Ren D, et al. A finite element study on posterior short segment fixation combined with unilateral fixation using pedicle screws for stable thoracolumbar fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e12046.
[51] Wu Y, Chen CH, Tsuang FY, et al. The stability of long-segment and short-segment fixation for treating severe burst fractures at the thoracolumbar junction in osteoporotic bone: A finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211676.
[52] Liu H, Wang H, Liu J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior intermediate screw fixation techniques with hybrid monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screws in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):122.
[53] Wang H, Mo Z, Han J, et al. Extent and location of fixation affects the biomechanical stability of short- or long-segment pedicle screw technique with screwing of fractured vertebra for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: An observational study using finite element analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(26):e11244.
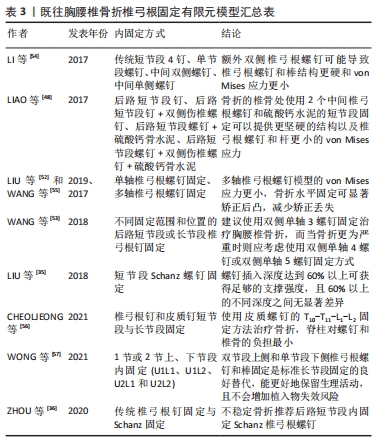
[54] Li C, Zhou Y, Wang H, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fractures through short segment pedicle screw fixation techniques using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99156.
[55] Wang H, Zhao Y, Mo Z, et al. Comparison of short-segment monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screw fixation combined with intermediate screws in traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element study and clinical radiographic review. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2017;72(10):609-617.
[56] CheolJeong K, Min SS, Hoon CS, et al. Numerical Evaluation of Spinal Stability after Posterior Spinal Fusion with Various Fixation Segments and Screw Types in Patients with Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Using Finite Element Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3243.
[57] Wong CE, Hu HT, Tsai CH, et al. Comparison of Posterior Fixation Strategies for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Finite Element Study. J Biomech Eng. 2021;143(7):071007.
|