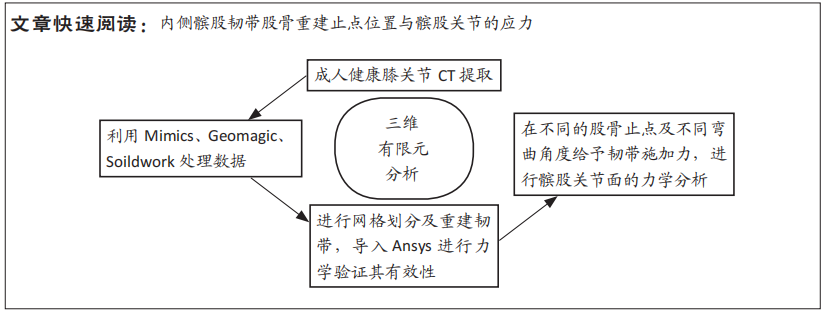
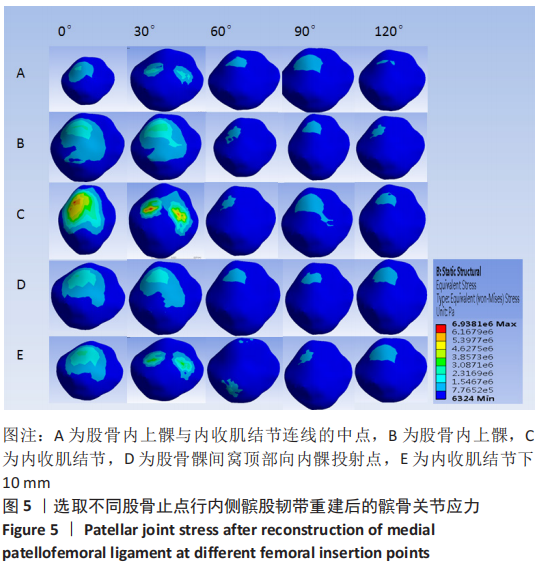
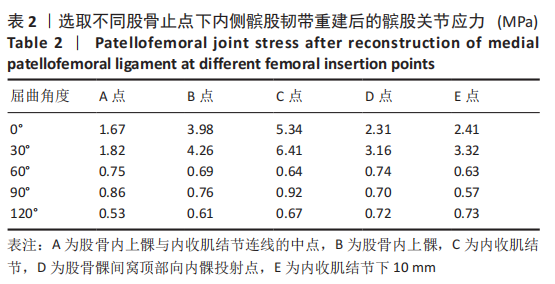
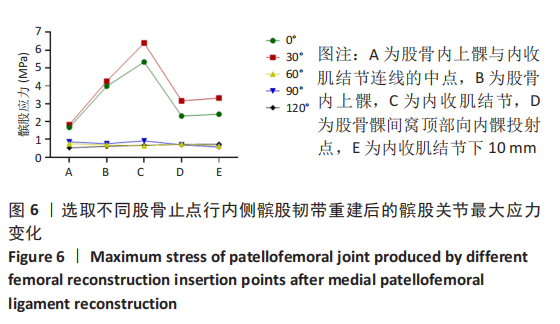
[1] 耿彬.甘肃省髌骨脱位诊疗专家共识(第一版2021年)[J].生物医学转化,2021,2(4):93-100.
[2] OLIVA F, MARSILIO E, MIGLIORINI F, et al. Complex ruptures of the quadriceps tendon: a systematic review of surgical procedures and outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):547.
[3] GRAVESEN KS, KALLEMOSE T, BLØND L, et al. High incidence of acute and recurrent patellar dislocations: a retrospective nationwideepidemiological study involving 24.154 primary dislocations. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(4):1204-1209.
[4] IZADPANAH K, MEINE H, KUBOSCH J, et al. Fluoroscopic guidedtunnel placement during medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction is not accurate in patients with severe trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(3):759-766.
[5] 张勇,程飚,杨林.关节镜辅助下内侧髌股韧带重建术治疗髌骨脱位股骨侧止点定位方法研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020, 34(10):1233-1237.
[6] FITZPATRICK CK, STEENSEN RN, TUMULURI A, et al. Computational analysis of factors contributing to patellar dislocation. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(3):444-453.
[7] 赵允,黄竞敏,李冬超,等.关节镜下内侧髌股韧带重建联合胫骨结节移位术治疗复发性髌骨脱位五年随访[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(8):960-964.
[8] 刘飞,冯呈,陈廖斌.早期内侧髌股韧带重建治疗急性创伤性髌骨脱位疗效分析[J].临床外科杂志,2019,27(4):295-298.
[9] 杨砥,刘炯,赵滨,等.关节镜下外侧支持带松解结合内侧髌股韧带重建治疗无严重骨畸形的复发性髌股关节脱位的临床疗效观察[J].贵州医药,2019,43(4):607-608.
[10] KERNKAMP WA, WANG C, LI C, et al. The medical patellofemoral ligment is a dynamic and anisometric structure:An in vivo study on length changes and isometry. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(7):1645-1653.
[11] CHRISTENSEN TC, SANDERS TL, PAREEK A, et al. Risk factors and time to recurrent ipsilateral and contralateral patellar dislocations. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(9):2105-2110.
[12] 房传武,刘伟,刘飞,等.关节镜下内侧髌股韧带双束解剖重建治疗髌骨脱位[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(4):443-445+449.
[13] 雷鸣鸣,华强.两种股骨隧道定位法内侧髌股韧带重建术比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(16):1461-1466.
[14] STEPHEN JM, KADER D, LUMPAOPONG P, et al. Sectioning the medial patellofemoral ligament alters patellofemoral joint kinematics and contact mechanics. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(9):1423-1429.
[15] LIND M, NIELSEN T, MILLER L, et al. No Difference in Outcome Between Femoral Soft-Tissue and Screw Graft Fixation for Reconstruction of the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(4):1130-1137.
[16] HUBER C, ZHANG Q, TAYLOR WR, et al. Properties and Function of the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2019;48(3):754-766.
[17] AMIS AA, FIRER P, MOUNTNEY J, et al. Anatomy and biomechanics of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee. 2003;10(3):215-220.
[18] NOMURA E, INOUE M, OSADA N. Anatomical analysis of the medial patellofemoral ligament of the knee, especially the femoral attachment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005;13(7):510-515.
[19] 王上增,李强,王禛,等.三联手术治疗成人习惯性髌骨脱位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(22):2084-2087.
[20] SCHTTLE PB, SCHMELING A, ROSENSTIEL N, et al. Radiographic landmarks for femoral tunnel placement in medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(5):801-804.
[21] SMIRK C, MORRIS H. The anatomy and reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee. 2003;10(3):221-227.
[22] ARAGAO JA, REIS FP, VASCONCELOS DP, et al. Metric measurements and attachments levels of the medial patellofemoral ligament: an anatomical study in cadavers. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008;(63):541-544.
[23] LA PRADE R, GILBERT T, BOLLOM T, et al. The magnetic esonance imaging appearance of individual structures of the posterolateral knee. A prospective study of normal knees and knees with surgically verified grade III injuries. Relat Res. 2017;29(4):256-268.
[24] PENA E, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomechan. 2006;39(9):1686-1701.
[25] GEESLIN AG, LA PRADE RF. Location of Bone Bruises and Other Osseous Injuries Associated with Acute Grade III Isolated and Combined Posterolateral Knee Injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(12):2502-2508.
[26] MAROUANE H, SHIRAZIADL A, HASHEMI J. Quantification of the role of tibial posterior slope in knee joint mechanics and ACL force in simulated gait. J Biomech. 2015;48(10):1899-1905.
[27] NANNAPARAJU M, MORTADA S, WIIK A, et al. Posterolateral corner injuries: Epidemiology, anatomy, biomechanics and diagnosis. Injury. 2018;49(6):1024-1031.
[28] AMIS AA, FIRER P, MOUNTNEY J, et al. Anatomy and biomechanics of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee. 2003;10(3):215-220.
[29] HIGUCHI T, ARAI Y, TAKAMIYA H, et al. An analysis of the medial patellofemoral ligament length change pattern using open-MRI. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(11):1470-1475.
[30] SANCHIS-ALFONSO V, RAMIREZ-FUENTES C, MONTESINOS-BERRY E, et al. Femoral insertion site of the graft used to replace the medial patellofemoral ligament influences the ligament dynamic changes during knee flexion and the clinical outcome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(8):2433-2441.
[31] 周继辉,李新志,周游,等.髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1440-1445.
[32] DALL’OCA C, ELENA N, LUNARDELLI E, et al. MPFL reconstruction: Indications and results. Acta Biomed. 2020;91(4-S):128-135.
[33] KRUCKEBERG BM, CHAHLA J, MOATSHE G, et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of the Medial Patellar Ligaments: An Anatomic and Radiographic Study. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(1):153-162.
[34] 赵定磷.退行性髌股关节炎的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1990, 28(2):69.
[35] MORSCHER E. Osteotomy of patella in chondromolacia. Arch OrthopTraumat Surg. 1978;92(2-3):139.
[36] 时孝晴,揭立士.软骨细胞衰老与骨关节炎的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2021,34(9):962-968.
[37] SHAH JN, HOWARD JS, FLANIGAN DC, et al. A Systematic Review of Complications and Failures Associated with Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(8):1916-1923.
[38] 林潮盛,刘雨微,朱伟民,等.内侧髌股韧带重建:移植物单双束选择、髌骨及股骨插入点的固定技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(26):4217-4222.
[39] DECANTE C, GEFFORY L, SALAND C, et al. Descriptive and dynamic study of the medical patellofemoral ligament(MPFL). Surg Radio Anat. 2019;41(7):763-774.
[40] 李常辉.内侧髌股韧带的解剖学特征和起止点足印的解剖学研究及临床意义[D].青岛:青岛大学,2017. |