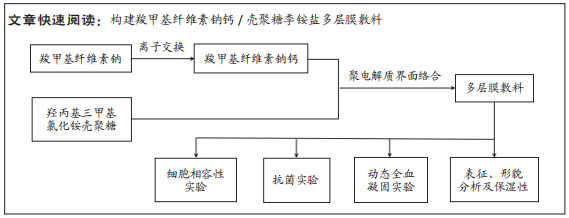
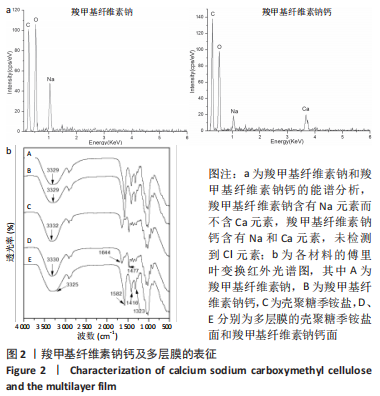
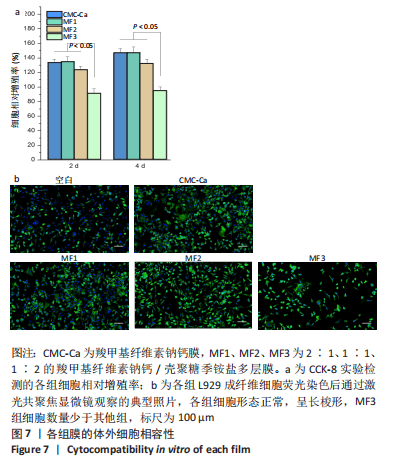
[1] NUUTILA K, ERIKSSON E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. Adv Wound Care. 2021;10(12):685-698.
[2] VARAPRASAD K, JAYARAMUDU T, KANIKIREDDY V, et al. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application:A mini review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;236:116025.
[3] SOOD A, GRANICK MS, TOMASELLI NL. Wound Dressings and Comparative Effectiveness Data. Adv Wound Care. 2014;3(8):511-529.
[4] KONG D, ZHANG Q, YOU J, et al. Adhesion loss mechanism based on carboxymethyl cellulose-filled hydrocolloid dressings in physiological wounds environment. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;235:115953.
[5] HOMAEIGOHAR S, BOCCACCINI AR. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020;107:25-49.
[6] SIMOES D, MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, et al. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 127:130-141.
[7] HUANG WC, YING R, WANG W, et al. A Macroporous Hydrogel Dressing with Enhanced Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities for Accelerated Wound Healing. Adv Func Mater. 2020;30(21):2000644.
[8] RAHIMI M, NORUZI EB, SHEYKHSARAN E, et al. Carbohydrate polymer-based silver nanocomposites: Recent progress in the antimicrobial wound dressings. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;231:115696.
[9] PHAECHAMUD T, ISSARAYUNGYUEN P, PICHAYAKORN W. Gentamicin sulfate-loaded porous natural rubber films for wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85:634-644.
[10] MOGHADDAM MA, DI MARTINO A, SOPIK T, et al. Polylactide/Polyvinylalcohol-Based Porous Bioscaffold Loaded with Gentamicin for Wound Dressing Applications. Polymers. 2021;13(6):921.
[11] FELGUEIRAS HP, AMORIM MTP. Functionalization of electrospun polymeric wound dressings with antimicrobial peptides. Colloids Surf B. 2017;156:133-148.
[12] ZHOU D, YANG R, YANG T, et al. Preparation of chitin-amphipathic anion/quaternary ammonium salt ecofriendly dressing and its effect on wound healing in mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:4157-4169.
[13] GHARIBI R, KAZEMI S, YEGANEH H, et al. Utilizing dextran to improve hemocompatibility of antimicrobial wound dressings with embedded quaternary ammonium salts. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;131:1044-1056.
[14] AO H, JIANG W, NIE Y, et al. Engineering quaternized chitosan in the 3D bacterial cellulose structure for antibacterial wound dressings. Polym Test. 2020;86:106490.
[15] PENG ZX, WANG L, DU L, et al. Adjustment of the antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan by varying the degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;81(2):275-283.
[16] TAN H, MA R, LIN C, et al. Quaternized Chitosan as an Antimicrobial Agent: Antimicrobial Activity, Mechanism of Action and Biomedical Applications in Orthopedics. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(1):1854-1869.
[17] FAN L, YANG J, WU H, et al. Preparation and characterization of quaternary ammonium chitosan hydrogel with significant antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;79:830-836.
[18] RAHIMI M, AHMADI R, KAFIL HS, et al. A novel bioactive quaternized chitosan and its silver-containing nanocomposites as a potent antimicrobial wound dressing: Structural and biological properties. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:360-369.
[19] LUO F, SUN TL, NAKAJIMA T, et al. Oppositely charged polyelectrolytes form tough, self-healing, and rebuildable hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2015; 27(17):2722-2727.
[20] GOMES NETO RJ, GENEVRO GM, PAULO LDA, et al. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of chitosan/konjac glucomannan bilayer film as a wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;212:59-66.
[21] CHEN X, YAN Y, LI H, et al. Evaluation of absorbable hemostatic agents of polyelectrolyte complexes using carboxymethyl starch and chitosan oligosaccharide both in vitro and in vivo. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(12): 3332-3344.
[22] WAN ACA, CUTIONGCO MFA, TAI BCU, et al. Fibers by interfacial polyelectrolyte complexation - processes, materials and applications. Mater Today. 2016;19(8):437-450.
[23] CHEN F, CAO X, CHEN X, et al. Calcium-modified microporous starch with potent hemostatic efficiency and excellent degradability for hemorrhage control. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(19):4017-4026.
[24] CHEN X, LI S, YAN Y, et al. Absorbable nanocomposites composed of mesoporous bioglass nanoparticles and polyelectrolyte complexes for surgical hemorrhage control. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 109:110556.
[25] KIM GH, IM JN, KIM TH, et al. Preparation and characterization of calcium carboxymethyl cellulose/chitosan blend nonwovens for hemostatic agents. Text Res J. 2018;88(16):1902-1911.
[26] MOEINI A, PEDRAM P, MAKVANDI P, et al. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115839.
[27] OP ‘T VELD RC, WALBOOMERS XF, JANSEN JA, et al. Design Considerations for Hydrogel Wound Dressings: Strategic and Molecular Advances. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(3):230-248.
[28] XUAN CK, HAO LJ, LIU XM, et al. Wet-adhesive, haemostatic and antimicrobial bilayered composite nanosheets for sealing and healing soft-tissue bleeding wounds. Biomaterials. 2020;252:120018.
[29] OHTA S, NISHIYAMA T, SAKODA M, et al. Development of carboxymethyl cellulose nonwoven sheet as a novel hemostatic agent. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015;119(6):718-723.
[30] SHI LX, LIU X, WANG WS, et al. A Self-Pumping Dressing for Draining Excessive Biofluid around Wounds. Adv Mater. 2019;31(5):1804187.
[31] JAYAKUMAR R, PRABAHARAN M, KUMAR PTS, et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(3):322-337.
[32] YANG Y, YANG S, WANG Y, et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016; 46:112-128.
|