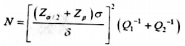中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (35): 5577-5582.doi: 10.12307/2022.973
• 组织构建与生物力学 tissue construction and biomechanics • 下一篇
多点薄膜压力测试系统采集不同扳动方式下侧卧定点踩跷法的力学特征
刘沛娜1,李远明2,范志勇2
- 1广州中医药大学第二临床医学院,广东省广州市 510120;2广东省中医院推拿科,广东省广州市 510120
Mechanical characteristics of stepping lumbus of fixed-point at lateral decubitus position under different pushing modes collected using multi-point membrane pressure test system
Liu Peina1, Li Yuanming2, Fan Zhiyong2
- 1Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Massage, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
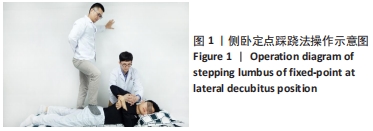
侧卧定点踩跷法:是广东省中医院名中医吴山教授在多年跟师广东省名老中医、岭南林氏正骨推拿流派创始人林应强教授的基础上,结合林氏正骨手法中立体定位斜扳法的特点,将传统踩跷进行创新的一种新型正骨手法。这套手法既有立体定位斜扳的特点,即能使病变节段从立体上位于旋转中心,又结合了踩跷法比徒手正骨力量更大的特点,在常规斜扳法或传统踩跷法治疗效果达不到预期的情况下,运用该手法往往能取得很好的疗效。
扳动方式:林氏正骨推拿手法在扳动时有快扳法及缓扳法之分。快扳操作时,治疗者足跟贴实、压紧目标关节,当关节处于被动活动的终末端时快速发力,小幅度扳动关节使其超过关节活动的允许范围,主要针对年轻或身体壮实的患者。缓扳操作时,治疗者足跟贴实、压紧目标关节,当关节处于被动活动的终末端时小幅度、缓慢扳动关节,每次活动要使关节临近关节活动范围的终末端,并能感觉到关节周围软组织的弹性及抵抗感,主要针对不耐疼痛的年轻患者、身材瘦小女性及老年患者。
背景:目前对侧卧定点踩跷法的研究较少,缺少对手法力学特征的分析,亦无关于快扳法及缓扳法的相关研究。
目的:利用数字化方式分析不同扳动方式下侧卧定点踩跷法的各项力学参数异同。
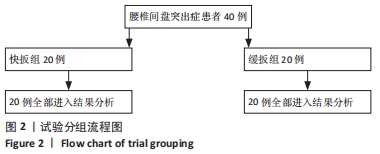
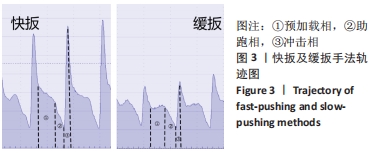
方法:选择2020年6月在广东省中医院大德路总院推拿科就诊的腰椎间盘突出症患者40例,随机分为2组,分别进行快扳方式下的侧卧定点踩跷治疗与缓扳方式下的侧卧定点踩跷治疗,每组20例,通过多点薄膜压力测试系统采集操作者在两种扳动方式下运用侧卧定点踩跷法时的手法轨迹图及相关力学参数。评估治疗前后患者的目测类比评分。
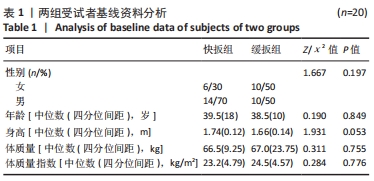
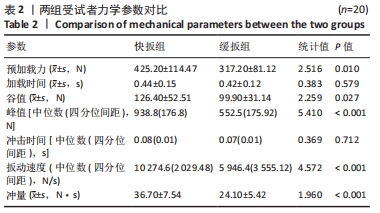
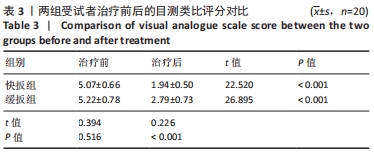
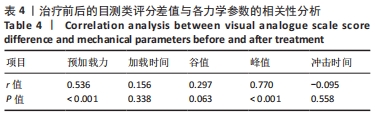
结果与结论:①两种扳动方式均存在预加载相、助跑相及冲击相,快扳组预加载力、谷值、峰值、扳动速度及冲量均大于缓扳组(P < 0.05),两组间加载时间、冲击时间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②两组治疗后的目测类比评分均低于治疗前(P < 0.05),快扳组治疗后的目测类比评分低于缓扳组(P < 0.05);③Pearson及Spearman相关性分析显示,治疗前后的目测类比评分差值与预加载力、峰值(即冲击力)的大小存在显著相关性(r=0.536,P < 0.001;r=0.740,P < 0.001);④结果显示,两种扳动方式下侧卧定点踩跷法单次治疗后腰椎间盘突出症患者的腰痛症状均得到明显改善,其中以快扳方式下的镇痛效果更佳;治疗前后的目测类比评分差值与预加载力及峰值大小存在显著相关性。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5474-9645 (刘沛娜)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: