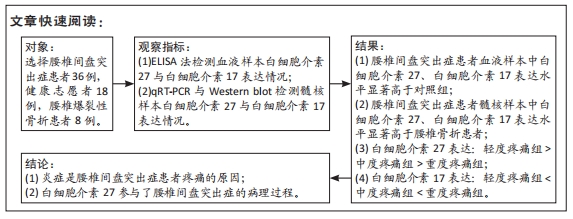
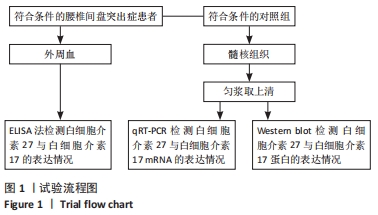
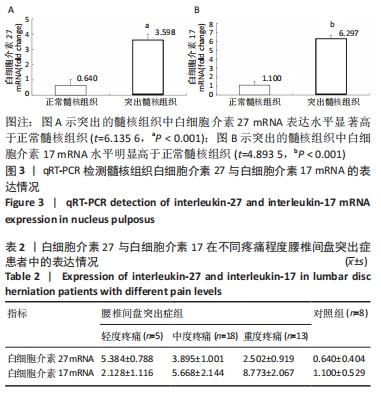
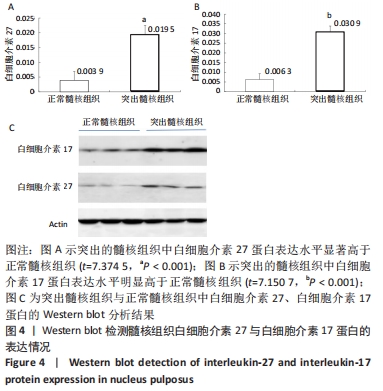
[1] GILBERTSON L, AHN SH, TENG PN, et al. The effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2, recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-12, and adenoviral bone morphogenetic protein-12 on matrix synthesis in human annulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus cells. Spine J. 2008;8(3):449-456.
[2] SCHWARZER AC, APRILL CN, DERBY R, et al. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(17):1878-1883.
[3] DE SOUZA GRAVA AL, FERRARI LF, DEFINO HL. Cytokine inhibition and time-related influence of inflammatory stimuli on the hyperalgesia induced by the nucleus pulposus. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3):537-545.
[4] KIM HJ, YEOM JS, KOH YG, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of platelet-rich plasma on nucleus pulposus cells with response of TNF-α and IL-1. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(4):551-556.
[5] WEILER C, NERLICH AG, BACHMEIER BE, et al. Expression and distribution of tumor necrosis factor alpha in human lumbar intervertebral discs: a study in surgical specimen and autopsy controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):44-53; discussion 54.
[6] KEPLER CK, MARKOVA DZ, DIBRA F, et al. Expresion and relationship of proinflammatory chemokine RANTES/CCL5 and cytokine IL-1β in painful human intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(11):873-880.
[7] SAAL JS, FRANSON RC, DOBROW R, et al. High levels of inflammatory phospholipase A2 activity in lumbar disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(7):674-678.
[8] O’DONNELL JL, O’DONNELL AL. Prostaglandin E2 content in herniated lumbar disc disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(14):1653-1655; discussion 1655-1656.
[9] KARPPINEN J, DAAVITTILA I, NOPONEN N, et al. Is the interleukin-6 haplotype a prognostic factor for sciatica? Eur J Pain. 2008;12(8):1018-1025.
[10] CHENG L, FAN W, LIU B, et al. Th17 lymphocyte levels are higher in patients with ruptured than non-ruptured lumbar discs, and are correlated with pain intensity. Injury. 2013;44(12):1805-1810.
[11] XUE H, YAO Y, WANG X, et al. Interleukin-21 Is Associated with the Pathogenesis of Lumbar Disc Herniation. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;14(5):509-518.
[12] JIANG H, DENG Y, WANG T, et al. Interleukin-23 may contribute to the pathogenesis of lumbar disc herniation through the IL-23/IL-17 pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:12.
[13] PFLANZ S, TIMANS JC, CHEUNG J, et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 2002;16:779-790.
[14] MEKA RR, VENKATESHA SH, DUDICS S, et al. IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential. Autoimmun Rev. 2015; 14(12):1131-1141.
[15] HUBER M, STEINWALD V, GURALNIK A, et al. IL-27 inhibits the development of regulatory T cells via STAT3. Int Immunol. 2008;20: 223-234.
[16] LUCAS S, GHILARDI N, LI J, et al. IL-27 regulates IL-12 responsiveness of naive CD4+ T cells through Stat1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:15047-15052.
[17] FUJIMOTO H, HIRASE T, MIYAZAKI Y, et al. IL-27 inhibits hyperglycemia and pancreatic islet inflammation induced by streptozotocin in mice. Am J Pathol. 2011;179:2327-2336.
[18] TANIDA S, YOSHITOMI H, ISHIKAWA M, et al. IL-27-producing CD14(+) cells infiltrate inflamed joints of rheumatoid arthritis and regulate inflammation and chemotactic migration. Cytokine. 2011;55:237-244.
[19] TANG SC, FAN XH, PAN QM, et al. Decreased expression of IL-27 and its correlation with Th1 and Th17 cells in progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2015;348:174-180.
[20] SASAOKA T, ITO M, YAMASHITA J, et al. Treatment with IL-27 attenuates experimental colitis through the suppression of the development of IL-17-producing T helper cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;300:G568-576.
[21] XIA LP, LI BF, SHEN H, et al. Interleukin-27 and interleukin-23 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: possible role in lupus nephritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44:200-205.
[22] TOJO G, FUJIMURA T, KAMBAYASHI Y, et al. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Psoriasis Induces IL-27-Producing Cells in Both Affected Areas of the Skin. Case Rep Dermatol . 2012;4(2):181-185.
[23] MACNAB I. Cervical spondylosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;(109):69-77.
[24] DI MARTINO A, MERLINI L, FALDINI C. Autoimmunity in intervertebral disc herniation: from bench to bedside. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013; 17(12):1461-1470.
[25] SATOH K, KONNO S, NISHIYAMA K, et al. Presence and distribution of antigen-antibody complexes in the herniated nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(19):1980-1984.
[26] ARAI Y, YASUMA T, SHITOTO K, et al. Immunohistological study of intervertebral disc herniation of lumbar spine. J Orthop Sci. 2000;5(3): 229-231.
[27] GEISS A, LARSSON K, RYDEVIK B, et al. Autoimmune properties of nucleus pulposus: an experimental study in pigs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(2):168-173.
[28] MURAI K, SAKAI D, NAKAMURA Y, et al. Primary immune system responders to nucleus pulposus cells: evidence for immune response in disc herniation. Eur Cell Mater. 2010;19:13-21.
[29] NAYLOR A, HAPPEY F, TURNER RL, et al. Enzymic and immunological activity in the intervertebral disk. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975;6(1):51-58.
[30] JAFARZADEH A, NEMATI M, CHAUHAN P, et al. Interleukin-27 Functional Duality Balances Leishmania Infectivity and Pathogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1573.
[31] JONES GW, HILL DG, CARDUS A, et al. IL-27: a double agent in the IL-6 family. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;193(1):37-46.
[32] YOSHIDA H, HUNTER CA. The immunobiology of interleukin-27. Ann Rev Immunol. 2015;33:417-443.
[33] HALL A, SILVER J, HUNTER C. The immunobiology of IL-27. AdvImmunol. 2012;115:1-44.
[34] HUNTER CA, KASTELEIN R. Interleukin-27: balancing protective and pathological immunity. Immunity. 2012;37:960-969.
[35] KORN T, OUKKA M, KUCHROO V, et al. Th17 cells: effector T cells with inflammatory properties. Semin Immunol. 2007;19(6):362-371.
[36] SASAGURI T, TAGUCHI T, MURATA Y, et al. Interleukin-27 controls basal pain threshold in physiological and pathological conditions. Sci Rep. 2018;8:11022.
[37] OWAKI T, ASAKAWA M, KAMIYA S, et al. IL-27 suppresses CD28-mediated [correction of medicated] IL-2 production through suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. J Immunol. 2006;176:2773-2780.
[38] 冯勇军,王明婧,曾春蓉,等. 变应性鼻炎患者血清Th细胞亚群及相关细胞因子水平变化[J].山东医药,2016,56(9):69-70.
[39] 陈毅斐,高亚东,胡家豪,等. 白细胞介素27在自身免疫性疾病中的功能调控[J]. 医学综述,2017,23(22):4376-4381.
[40] 李阳,夏丽坤. 白细胞介素-27的生物学功能及其抗病毒作用的研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志,2015,38(2):195-198.
[41] 单敏敏,李长安,崔红生. 哮喘宁颗粒对哮喘大鼠Th1/Th2平衡和STAT1通路调节作用的研究[J]. 中国医药导报,2019,16(10):11-15.
[42] 任媛媛,王贵强. 白细胞介素27在抗病毒免疫中的作用及临床应用前景[J]. 国际流行病学传染病学杂志,2011,38(6):425-428.
[43] 冯硕,崔德成. 自拟通窍止咳汤治疗儿童上气道咳嗽综合征疗效观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2020,29(11):1215-1218.
[44] 杨景英,陈学利,吴文钦,等. 白细胞介素-12家族与感染性疾病相关研究进展[J]. 临床检验杂志,2014,32(6):443-446.
|