中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3147-3151.doi: 10.12307/2022.612
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡与组蛋白去乙酰化酶4含量的降低
顾晓东1,李 飞2,车先达2,李鹏翠2
- 1山西白求恩医院,山西省太原市 030032;2山西医科大学第二医院骨与软组织损伤修复山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001
Relationship between apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and reduction of histone deacetylase 4 content
Gu Xiaodong1, Li Fei2, Che Xianda2, Li Pengcui2
- 1Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
ATF4/CHOP信号通路:内质网应激介导的细胞凋亡主要通过ATF4/CHOP信号通路发挥作用。发生内质网应激时,激活转录因子4的表达上调,上调的激活转录因子4激活其下游CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白的表达,从而触发细胞凋亡。
组蛋白去乙酰化酶:是一类催化核心组蛋白N-末端尾部区域赖氨酸残基去乙酰化的蛋白酶,可通过去乙酰化修饰使组蛋白带正电荷,与带负电荷的DNA紧密结合,染色质呈致密卷曲的阻抑结构,进而抑制基因转录,与细胞增殖、细胞肥大分化及细胞凋亡等诸多过程密切相关。组蛋白去乙酰化酶4的分布具有组织特异性,主要分布于脑、肌肉和软骨中。
背景:内质网应激介导的软骨细胞凋亡在骨关节炎的发病中起重要作用,而内质网应激介导的细胞凋亡主要受ATF4/CHOP信号通路调节,但该信号通路在骨关节炎中的作用及其调控仍不清楚。
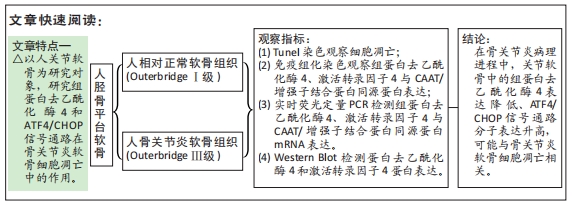
目的:探讨组蛋白去乙酰化酶4和ATF4/CHOP信号通路在骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡中的作用。
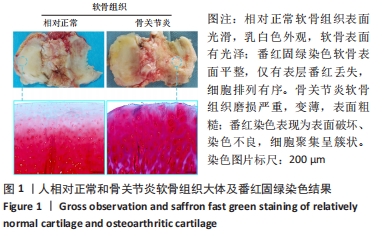
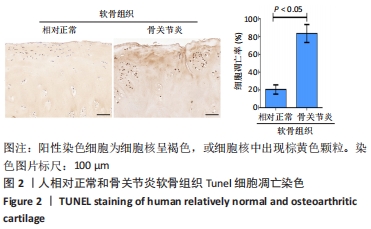
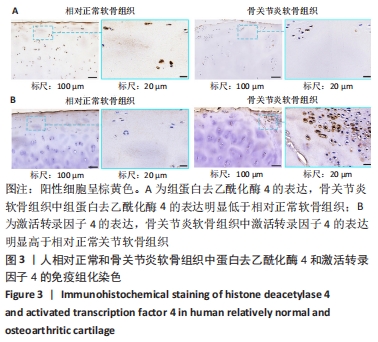
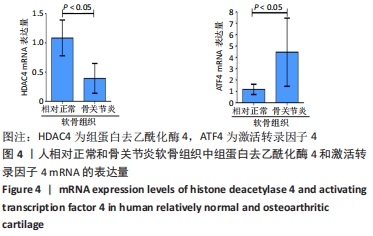
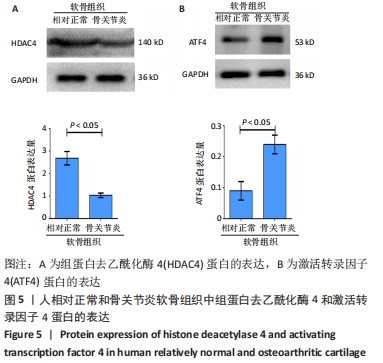
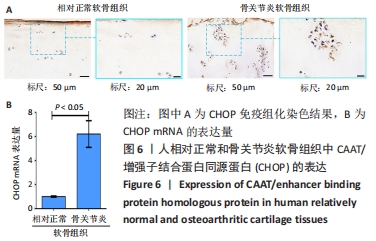
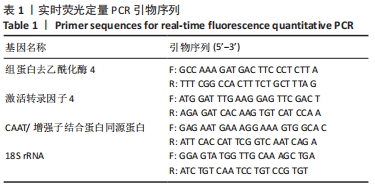
方法:按照Outerbridge分级,将从膝关节置换切取的胫骨平台软骨分为相对正常软骨(OuterbridgeⅠ级)和骨关节炎软骨(Outerbridge Ⅲ级),通过Tunel染色观察软骨细胞凋亡情况,免疫组化染色检测组蛋白去乙酰化酶4、激活转录因子4(ATF4)与CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白(CHOP)表达,实时荧光定量PCR检测CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白mRNA表达,Western Blot与实时荧光定量PCR检测组蛋白去乙酰化酶4、激活转录因子4的表达。
结果与结论:①Tunel染色显示,骨关节炎软骨中软骨细胞的凋亡率高于相对正常软骨[(83.5±10.1)%,(20.5±5.2)%,P < 0.05];②免疫组化染色显示,骨关节炎软骨中激活转录因子4的表达高于相对正常软骨,组蛋白去乙酰化酶4的表达低于相对正常软骨;骨关节炎关节软骨中CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白的表达高于相对正常软骨;③骨关节炎软骨中激活转录因子4与CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白的mRNA表达均高于相对正常软骨(P < 0.05),组蛋白去乙酰化酶4的mRNA表达低于相对正常软骨(P < 0.05);④骨关节炎软骨中组蛋白去乙酰化酶4的蛋白表达低于相对正常软骨(P < 0.05),激活转录因子4的蛋白表达高于相对正常软骨(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,在骨关节炎病理进程中,关节软骨中的组蛋白去乙酰化酶4表达降低、ATF4/CHOP信号通路分子表达升高,可能与骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡相关。
缩略语:CAAT/增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白:CAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein,CHOP
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1432-6389 (顾晓东)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: