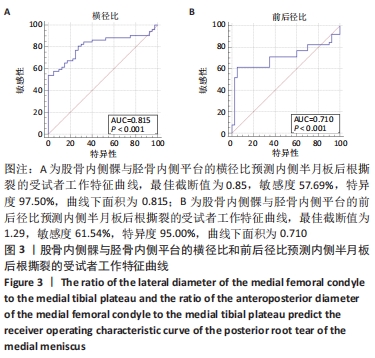
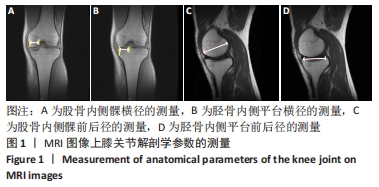
[1] BHATIA S, LAPRADE CM, ELLMAN MB, et al. Meniscal root tears: significance, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(12): 3016-3030.
[2] CALANNA F, DUTHON V, TSCHOLL PM, et al. Classification and treatment of modern traumatic meniscal tears. Rev Med Suisse. 2021; 17(745):1301-1309.
[3] FOX AJ, BEDI A, RODEO SA. The basic science of human knee menisci: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2012;4(4):340-351.
[4] HWANG BY, KIM SJ, LEE SW, et al. Risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tear. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(7):1606-1610.
[5] RODEO SA, MONIBI F, DEHGHANI B, et al. Biological and Mechanical Predictors of Meniscus Function: Basic Science to Clinical Translation. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(5):937-945.
[6] LAPRADE CM, JANSSON KS, DORNAN G, et al. Altered tibiofemoral contact mechanics due to lateral meniscus posterior horn root avulsions and radial tears can be restored with in situ pull-out suture repairs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(6):471-479.
[7] SUNDARARAJAN SR, RAMAKANTH R, SETHURAMAN AS, et al. Correlation of factors affecting correction of meniscal extrusion and outcome after medial meniscus root repair. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03870-8.
[8] MATSUDA S, MIURA H, NAGAMINE R, et al. Anatomical analysis of the femoral condyle in normal and osteoarthritic knees. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(1):104-109.
[9] LAHM A, DABRAVOLSKI D, RÖDIG J, et al. Varying development of femoral and tibial subchondral bone tissue and their interaction with articular cartilage during progressing osteoarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(12):1919-1930.
[10] KWAK YH, LEE S, LEE MC, et al. Large meniscus extrusion ratio is a poor prognostic factor of conservative treatment for medial meniscus posterior root tear. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(3): 781-786.
[11] MUSAHL V, AYENI OR, CITAK M, et al. The influence of bony morphology on the magnitude of the pivot shift. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(9):1232-1238.
[12] KELLGREN JH, LAWRENCE JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-502.
[13] FLANDRY F, HOMMEL G. Normal anatomy and biomechanics of the knee. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2011;19(2):82-92.
[14] NAGHIBI H, JANSSEN D, VAN DEN BOOGAARD T, et al. The implications of non-anatomical positioning of a meniscus prosthesis on predicted human knee joint biomechanics. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020;58(6): 1341-1355.
[15] BOZKURT M, UNLU S, CAY N, et al. The potential effect of anatomic relationship between the femur and the tibia on medial meniscus tears. Surg Radiol Anat. 2014;36(8):741-746.
[16] COX CL, DEANGELIS JP, MAGNUSSEN RA, et al. Meniscal tears in athletes. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2009;18(1):2-8.
[17] GOES RA, CAVALCANTI AS, SIQUEIRA CAMPOS AL, et al. Prediction of reparability of meniscal tears in athletes using magnetic resonance. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(4 Suppl. 3):153-162.
[18] SHRIVE NG, O’CONNOR JJ, GOODFELLOW JW. Load-bearing in the knee joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;(131):279-287.
[19] JONES RS, KEENE GC, LEARMONTH DJ, et al. Direct measurement of hoop strains in the intact and torn human medial meniscus. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1996;11(5):295-300.
[20] OHORI T, MAE T, SHINO K, et al. Different effects of the lateral meniscus complete radial tear on the load distribution and transmission functions depending on the tear site. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021; 29(2):342-351.
[21] REYNOLDS RJ, WALKER PS, BUZA J. Mechanisms of anterior-posterior stability of the knee joint under load-bearing. J Biomech. 2017;57:39-45.
[22] SHEFELBINE SJ, MA CB, LEE KY, et al. MRI analysis of in vivo meniscal and tibiofemoral kinematics in ACL-deficient and normal knees. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(6):1208-1217.
[23] KEDGLEY AE, SAW TH, SEGAL NA, et al. Predicting meniscal tear stability across knee-joint flexion using finite-element analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(1):206-214.
[24] VANDERHAVE KL, MORAVEK JE, SEKIYA JK, et al. Meniscus tears in the young athlete: results of arthroscopic repair. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011; 31(5):496-500.
[25] ZEDDE P, MELA F, DEL PRETE F, et al. Meniscal injuries in basketball players. Joints. 2015;2(4):192-196.
[26] SHI H, DING L, JIANG Y, et al. Comparison Between Soccer and Basketball of Bone Bruise and Meniscal Injury Patterns in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(4):2325967121995844.
[27] ELIAS SG, FREEMAN MA, GOKCAY EI. A correlative study of the geometry and anatomy of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (260):98-103.
[28] LU F, SUN X, WANG W, et al. Anthropometry of the medial femoral condyle in the Chinese population: the morphometric analysis to design unicomparmental knee component. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021; 22(1):95.
[29] BHATIA S, LAPRADE CM, ELLMAN MB, et al. Meniscal root tears: significance, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(12): 3016-3030.
[30] PAPALIA R, VASTA S, FRANCESCHI F, et al. Meniscal root tears: from basic science to ultimate surgery. Br Med Bull. 2013;106:91-115.
[31] WOLF BR, GULBRANDSEN TR. Degenerative Meniscus Tear in Older Athletes. Clin Sports Med. 2020;39(1):197-209.
|