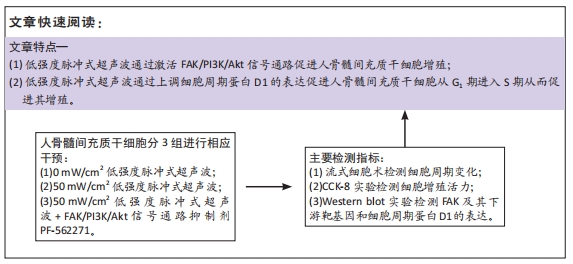
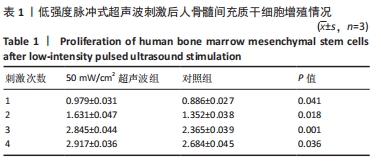
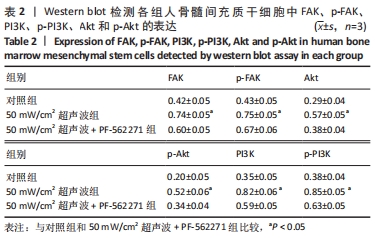
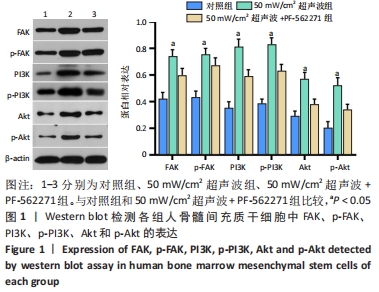
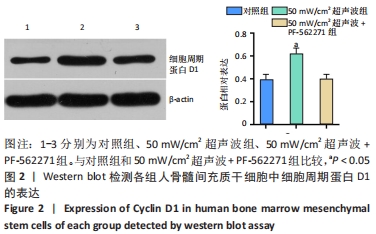
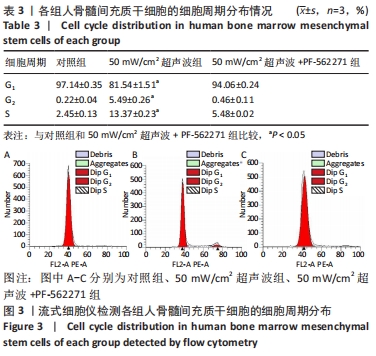
[1] 谢树才,张剑权,蒋锡丽,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导分化为肝细胞的方法及机制研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(50): 7586-7593.
[2] Fleming MM, Liu F, Zhang Y, et al. Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Underestimates Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Ascites Undergoing Colectomy. World J Surg. 2018;42(10):3390-3397.
[3] Hatzistergos KE, Quevedo H, Oskouei BN, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulate cardiac stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Circ Res. 2010;107(7):913-922.
[4] Wu Y, Gao Q, Zhu S, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells through notch signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(3):793-798.
[5] Doan N, Reher P, Meghji S, et al. In vitro effects of therapeutic ultrasound on cell proliferation, protein synthesis, and cytokine production by human fibroblasts, osteoblasts, and monocytes. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57(4):409-419.
[6] Miyasaka M, Nakata H, Hao J, et al. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation Enhances Heat-Shock Protein 90 and Mineralized Nodule Formation in Mouse Calvaria-Derived Osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(23-24):2829-2839.
[7] Huang D, Gao Y, Wang S, et al. Impact of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on transcription and metabolite compositions in proliferation and functionalization of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13690.
[8] Gao Q, Walmsley AD, Cooper PR, et al. Ultrasound Stimulation of Different Dental Stem Cell Populations: Role of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling. J Endod. 2016;42(3):425-431.
[9] Korstjens CM, van der Rijt RH, Albers GH, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2008;46(12):1263-1270.
[10] Ishihara Y, Ueki K, Sotobori M, et al. Bone regeneration by statin and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in rabbit nasal bone. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(3):185-193.
[11] Sato M, Motoyoshi M, Shinoda M, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates nerve regeneration following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats. Eur J Oral Sci. 2016;124(3):246-250.
[12] 李志,谢树才,张剑权,等.低强度超声波对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖影响的体外研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(11):2006-2009.
[13] Ren C, Chen X, Du N, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes Schwann cell viability and proliferation via the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(5):497-507.
[14] Xu T, Gu J, Li C, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis via p38 MAPK signaling in rat visceral preadipocytes. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(3):948-956.
[15] Wu S, Xu X, Sun J, et al. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Accelerates Traumatic Vertebral Fracture Healing by Coupling Proliferation of Type H Microvessels. J Ultrasound Med. 2018;37(7):1733-1742.
[16] Coskun ME, Coskun KA, Tutar Y. Determination of Optimum Operation Parameters for Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound and Low-Level Laser Based Treatment to Induce Proliferation of Osteoblast and Fibroblast Cells. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018;36(5):246-252.
[17] Akca H, Demiray A, Tokgun O, et al. Invasiveness and anchorage independent growth ability augmented by PTEN inactivation through the PI3K/AKT/NFkB pathway in lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2011; 73(3):302-309.
[18] Xu R, Chen J, Cong X, et al. Lovastatin protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2. J Cell Biochem. 2008;103(1): 256-269.
[19] Aliabouzar M, Lee SJ, Zhou X, et al. Effects of scaffold microstructure and low intensity pulsed ultrasound on chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018;115(2):495-506.
[20] Bayat M, Virdi A, Rezaei F, et al. Comparison of the in vitro effects of low-level laser therapy and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy on bony cells and stem cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018;133:36-48.
[21] Bruder SP, Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE. Growth kinetics, self-renewal, and the osteogenic potential of purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive subcultivation and following cryopreservation. J Cell Biochem. 1997;64(2):278-294.
[22] Baker N, Sohn J, Tuan RS. Promotion of human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis by PI3-kinase/Akt signaling, and the influence of caveolin-1/cholesterol homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:238.
[23] Liu Y, Zhang Y, Lin L, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the axonal outgrowth through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling in primary cortical neurons followed oxygen-glucose deprivation injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78514.
[24] Xu P, Gul-Uludag H, Ang WT, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-mediated stimulation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell viability, proliferation and differentiation in vitro. Biotechnol Lett. 2012;34(10):1965-1973.
[25] Zhang J, Guan J, Qi X, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine Promotes the Angiogenic Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from iPSCs via Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway for Bone Regeneration. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(6):639-652.
[26] Presneau N, Shalaby A, Idowu B, et al. Potential therapeutic targets for chordoma: PI3K/AKT/TSC1/TSC2/mTOR pathway. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(9):1406-1414.
[27] Liu H, Xu J, Zhou L, et al. Hepatitis B virus large surface antigen promotes liver carcinogenesis by activating the Src/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Res. 2011;71(24):7547-7557.
[28] Cheng K, Xia P, Lin Q, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on integrin-FAK-PI3K/Akt mechanochemical transduction in rabbit osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014;40(7):1609-1618.
[29] Liu XB, Jiang J, Gui C, et al. Angiopoietin-1 protects mesenchymal stem cells against serum deprivation and hypoxia-induced apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008;29(7):815-822.
[30] Matsuo T, Sato K, Matsui T, et al. Inhibitory effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound sonication on the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(3):3071-3076.
[31] Jung YJ, Kim R, Ham HJ, et al. Focused low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defect through enhancement of cell proliferation. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015; 41(4):999-1007.
[32] Uddin SM, Richbourgh B, Ding Y, et al. Chondro-protective effects of low intensity pulsed ultrasound. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(11):1989-1998.
[33] Puts R, Rikeit P, Ruschke K, et al. Functional regulation of YAP mechanosensitive transcriptional coactivator by Focused Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound (FLIPUS) enhances proliferation of murine mesenchymal precursors. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0206041.
[34] Li L, Yang Z, Zhang H, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through osteocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418(2):296-300.
[35] Go MJ, Takenaka C, Ohgushi H. Effect of forced expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. J Biochem. 2007;142(6):741-748.
[36] Jäger M, Feser T, Denck H, et al. Proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured onto three different polymers in vitro. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33(10):1319-1332.
[37] Song G, Ju Y, Soyama H, et al. Regulation of cyclic longitudinal mechanical stretch on proliferation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Biomech. 2007;4(4):201-210.
[38] Zhong C, Zhang X, Xu Z, et al. Effects of low-intensity electromagnetic fields on the proliferation and differentiation of cultured mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Phys Ther. 2012;92(9): 1208-1219.
[39] Tsai MT, Li WJ, Tuan RS, et al. Modulation of osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells by specific pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(9):1169-1174.
[40] 蒋柳宏,郑有华,张志光,等.bFGF基因转染对兔骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2009,30(S2): 41-46.
[41] 朱磊,沈洪,刘丽,等.健脾补肾、清肠化湿方对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖迁移的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2016,36(2):191-195.
|