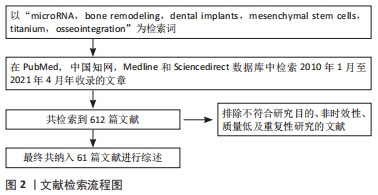
[1] DE-UGARTE L, SERRA-VINARDELL J, NONELL L, et al. Expression profiling of microRNAs in human bone tissue from postmenopausal women. Hum Cell. 2018;31(1):33-41.
[2] CAKOUROS D, GRONTHOS S. Epigenetic regulators of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell lineage determination. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020; 18(5):597-605.
[3] LANZILLOTTI C, DE MATTEI M, MAZZIOTTA C, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs interplay in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:646032.
[4] PETERS LJF, FLOEGE J, BIESSEN EAL, et al. MicroRNAs in chronic kidney disease: four candidates for clinical application. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(18):6547.
[5] FRÖHLICH LF. Micrornas at the interface between osteogenesis and angiogenesis as targets for bone regeneration. Cells. 2019;8(2):121.
[6] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854.
[7] LI Y, ZENG Q, QIU J, et al. MiR-183-5p Promotes proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells through negatively regulating four and a half LIM protein 1. J Breast Cancer. 2020;23(4): 355-372.
[8] SAHA S, AIN R. MicroRNA regulation of murine trophoblast stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Life Sci Alliance. 2020;3(11): e202000674.
[9] EZHILARASAN D. MicroRNA interplay between hepatic stellate cell quiescence and activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173507.
[10] LI R, WU H, JIANG H, et al. FBLN5 is targeted by microRNA‑27a‑3p and suppresses tumorigenesis and progression in high‑grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2020;44(5):2143-2151.
[11] FENG Q, ZHENG S, ZHENG J. The emerging role of microRNAs in bone remodeling and its therapeutic implications for osteoporosis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(3):BSR20180453.
[12] ZHA JP, WANG X Q, DI J. MiR-920 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by targeting HOXA7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):254.
[13] FENG L, ZHANG JF, SHI L, et al. MicroRNA-378 suppressed osteogenesis of MSCs and impaired bone formation via inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:1017-1028.
[14] MÖHLHENRICH SC, HEUSSEN N, MODABBER A, et al. Influence of bone density, screw size and surgical procedure on orthodontic mini-implant placement - part B: implant stability. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;50(4):565-572.
[15] GÓMEZ-POLO M, ORTEGA R, GÓMEZ-POLO C, et al. Does length, diameter, or bone quality affect primary and secondary stability in self-tapping dental implants? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(7): 1344-1353.
[16] GEHRKE SA, GUIRADO JLC, BETTACH R, et al. Evaluation of the insertion torque, implant stability quotient and drilled hole quality for different drill design: an in vitro Investigation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29(6):656-662.
[17] MEREDITH N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11(5):491-501.
[18] SHU T, HE L, WANG X, et al. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via miRNA-145-5p/SMAD5 and miRNA-124-3p/SMAD4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;514(1):316-322.
[19] KOMORI T. Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):313-323.
[20] DONG M, JIAO G, LIU H, et al. Biological silicon stimulates collagen type 1 and osteocalcin synthesis in human osteoblast-like cells through the BMP-2/Smad/RUNX2 signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016; 173(2):306-315.
[21] CHENG F, YANG MM, YANG RH. miRNA-365a-3p promotes the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting osteogenic differentiation via targeting RUNX2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(18):7766-7774.
[22] ZHANG W, WU Y, SHIOZAKI Y, et al. miRNA-133a-5p inhibits the expression of osteoblast differentiation-associated markers by targeting the 3’ UTR of RUNX2. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37(3):199-209.
[23] KIDWAI F, EDWARDS J, ZOU L, et al. Fibrinogen induces RUNX2 activity and osteogenic development from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2016;34(8):2079-2089.
[24] ZUO B, ZHU J, LI J, et al. microRNA-103a functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit bone formation through targeting Runx2. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):330-345.
[25] ITO K, TOMOKI R, OGURA N, et al. MicroRNA-204 regulates osteogenic induction in dental follicle cells. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(4):457-465.
[26] MELNIK S, GABLER J, DREHER SI, et al. MiR-218 affects hypertrophic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells during chondrogenesis via targeting RUNX2, MEF2C, and COL10A1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):532.
[27] CHEN H, JI X, SHE F, et al. miR-628-3p regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting RUNX2: Possible role in atrophic non-union. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(2):279-286.
[28] GAO Y, XIAO F, WANG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes osterix expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation by targeting miRNA-143 in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):6986-6996.
[29] WANG C, LIAO H, CAO Z. Role of osterix and microRNAs in bone formation and tooth development. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2934-2942.
[30] ZHANG SY, GAO F, PENG CG, et al. miR-485-5p promotes osteoporosis via targeting Osterix. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(15):4792-4799.
[31] LIU H, LIU Q, WU XP, et al. MiR-96 regulates bone metabolism by targeting osterix. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018;45(6):602-613.
[32] GAN S, HUANG Z, LIU N, et al. MicroRNA-140-5p impairs zebrafish embryonic bone development via targeting BMP-2. FEBS Lett. 2016; 590(10):1438-1446.
[33] KUREEL J, DIXIT M, TYAGI AM, et al. miR-542-3p suppresses osteoblast cell proliferation and differentiation, targets BMP-7 signaling and inhibits bone formation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(2):e1050.
[34] CHANG M, LIN H, FU H, et al. MicroRNA-195-5p regulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells under mechanical loading. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3762-3774.
[35] DUAN L, ZHAO H, XIONG Y, et al. miR-16-2* Interferes with WNT5A to regulate osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1087-1102.
[36] LONG H, ZHU Y, LIN Z, et al. miR-381 modulates human bone mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) osteogenesis via suppressing Wnt signaling pathway during atrophic nonunion development. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):470.
[37] SU X, LIAO L, SHUAI Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015; 6(8):e1851.
[38] HU H, ZHAO C, ZHANG P, et al. miR-26b modulates OA induced BMSC osteogenesis through regulating GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;107:158-164.
[39] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, BERG ME, et al. Osteoblast lineage cells can discriminate microscale topographic features on titanium-aluminum-vanadium surfaces. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(12):2551-2561.
[40] VISAVADIYA N P, KEASEY M P, RAZSKAZOVSKIY V, et al. Erratum to: integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):11.
[41] WU D, MA L. Downregulating microRNA-152-3p promotes the viability and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via targeting integrin alpha 5. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;120:104930.
[42] LIU X, XU H, KOU J, et al. MiR-9 promotes osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting DKK1 gene expression. Mol Biol Rep. 2016;43(9):939-946.
[43] YANG M, LI CJ, SUN X, et al. MiR-497-195 cluster regulates angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis by maintaining endothelial Notch and HIF-1α activity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:16003.
[44] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507 (7492):376-380.
[45] YAN J, CHANG B, HU X, et al. Titanium implant functionalized with antimiR-138 delivered cell sheet for enhanced peri-implant bone formation and vascularization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 89:52-64.
[46] WU X, GU Q, CHEN X, et al. MiR-27a targets DKK2 and SFRP1 to promote reosseointegration in the regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(1):123-134.
[47] WU T, XIE M, WANG X, et al. miR-155 modulates TNF-α-inhibited osteogenic differentiation by targeting SOCS1 expression. Bone. 2012; 51(3):498-505.
[48] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328.
[49] HUANG Y, CRAWFORD M, HIGUITA-CASTRO N, et al. miR-146a regulates mechanotransduction and pressure-induced inflammation in small airway epithelium. FASEB J. 2012;26(8):3351-3364.
[50] WANG H, SUN Z, WANG Y, et al. miR-33-5p, a novel mechano-sensitive microRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting Hmga2. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23170.
[51] NAQVI AR, ZHONG S, DANG H, et al. Expression profiling of LPS responsive miRNA in primary human macrophages. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2016;8(2):136-143.
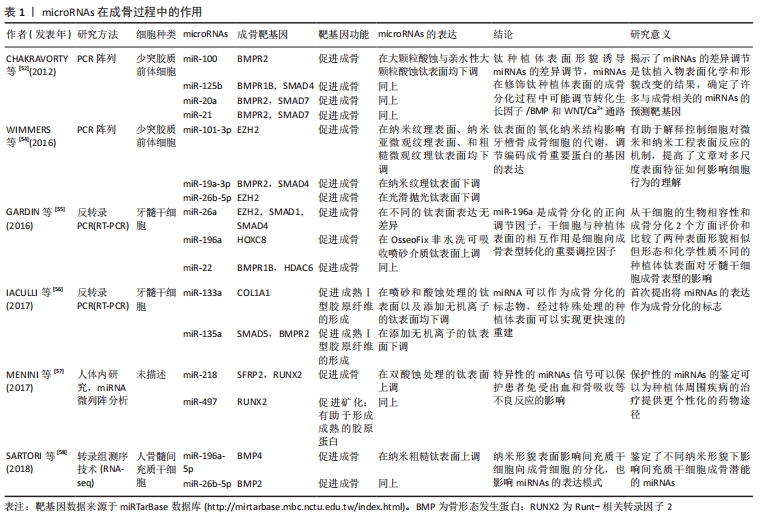
[52] CHAKRAVORTY N, IVANOVSKI S, PRASADAM I, et al. The microRNA expression signature on modified titanium implant surfaces influences genetic mechanisms leading to osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(9):3516-3523.
[53] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, HUTTON DL, et al. Role of non-canonical Wnt signaling in osteoblast maturation on microstructured titanium surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2740-2750.
[54] WIMMERS FERREIRA MR, RODRIGO FERNANDES R, FREIRE ASSIS A, et al. Oxidative nanopatterning of titanium surface influences mRNA and microRNA expression in human alveolar bone osteoblastic cells. Int J Biomater. 2016;2016:9169371.
[55] GARDIN C, FERRONI L, PIATTELLI A, et al. Non-washed resorbable blasting media (NWRBM) on Titanium Surfaces could Enhance Osteogenic Properties of MSCs through increase of miRNA-196a and VCAM1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):543-552.
[56] IACULLI F, DI FILIPPO ES, PIATTELLI A, et al. Dental pulp stem cells grown on dental implant titanium surfaces: an in vitro evaluation of differentiation and microRNAs expression. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(5):953-965.
[57] MENINI M, DELLEPIANE E, BALDI D, et al. Microarray expression in peri-implant tissue next to different titanium implant surfaces predicts clinical outcomes: a split-mouth study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017; 28(9):e121-e134.
[58] SARTORI EM, MAGRO-FILHO O, SILVEIRA MENDONÇA DB, et al. Modulation of micro RNA expression and osteoblast differentiation by nanotopography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(2):269-280.
[59] WU K, SONG W, ZHAO L, et al. MicroRNA functionalized microporous titanium oxide surface by lyophilization with enhanced osteogenic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(7):2733-2744.
[60] SHAO D, WANG C, SUN Y, et al. Effects of oral implants with miR‑122‑modified cell sheets on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1537-1544.
[61] LIU L, ZENG D, CHEN Y, et al. Microarc oxidation surface of titanium implants promote osteogenic differentiation by activating ERK1/2-miR-1827-Osterix. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(4):296-306.
|