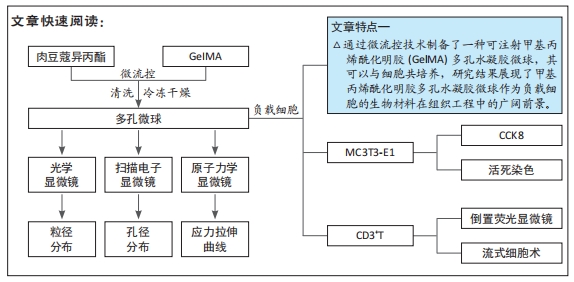
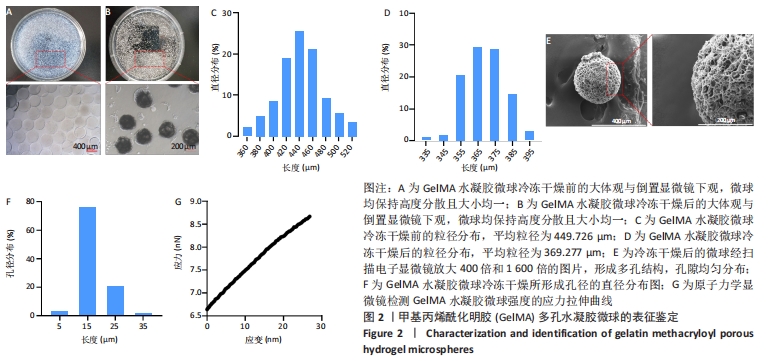
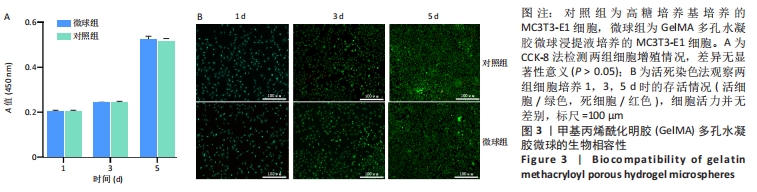
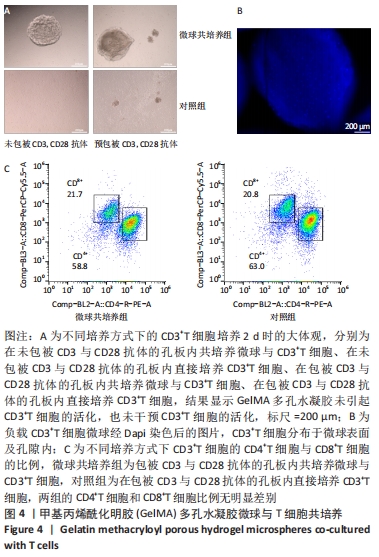
[1] BUZHOR E, LESHANSKY L, BLUMENTHAL J, et al. Cell-based therapy approaches: the hope for incurable diseases. Regen Med. 2014;9(5): 649-672.
[2] UCCELLI A, MORETTA L, PISTOIA V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):726-36.
[3] EL-BADAWY A, EL-BADRI N. Clinical Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0151938.
[4] FACKLAM AL, VOLPATTI LR, ANDERSON DG. Biomaterials for Personalized Cell Therapy. Adv Mater. 2020;32(13):e1902005.
[5] SHAH NJ, MAO AS, SHIH TY, et al. An injectable bone marrow-like scaffold enhances T cell immunity after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(3):293-302.
[6] HUANG G, LI F, ZHAO X, et al. Functional and Biomimetic Materials for Engineering of the Three-Dimensional Cell Microenvironment. Chem Rev. 2017;117(20):1276412-1276850.
[7] LI W, ZHANG L, GE X, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of microparticles for biomedical applications. Chem Soc rev. 2018;47(15):5646-5683.
[8] JO YK, LEE D. Biopolymer Microparticles Prepared by Microfluidics for Biomedical Applications. Small. 2020;16(9):e1903736.
[9] LIU X, ZHANG H, CHENG R, et al. An immunological electrospun scaffold for tumor cell killing and healthy tissue regeneration. Mater Horiz. 2018;5(6):1082-1091.
[10] YANG J, HAN Y, LIN J, et al. Superlubricated Microspheres: Ball-Bearing-Inspired Polyampholyte-Modified Microspheres as Bio-Lubricants Attenuate Osteoarthritis (Small 44/2020). Small. 2020;16(44):2070238.
[11] YANG J, HAN Y, LIN J, et al. Ball-Bearing-Inspired Polyampholyte-Modified Microspheres as Bio-Lubricants Attenuate Osteoarthritis. Small. 2020;16(44):2004519.
[12] LI L, DU Y, XIONG Y, et al. Injectable negatively charged gelatin microsphere-based gels as hemostatic agents for intracavitary and deep wound bleeding in surgery. J Biomater Appl. 2018;33(5):647-661.
[13] XU Y, GU Y, CAI F, et al. Metabolism Balance Regulation via Antagonist-Functionalized Injectable Microsphere for Nucleus Pulposus Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(52):2006333.
[14] ZHAO X, LIU Y, SHAO C, et al. Photoresponsive Delivery Microcarriers for Tissue Defects Repair. Adv Sci. 2019;6(20):1901280.
[15] ZHANG L, XIANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. A Biomimetic 3D-Self-Forming Approach for Microvascular Scaffolds. Adv Sci. 2020;7(9):1903553.
[16] CHEN W, CHEN H, ZHENG D, et al. Gene-Hydrogel Microenvironment Regulates Extracellular Matrix Metabolism Balance in Nucleus Pulposus. Adv Sci. 2020;7(1):1902099.
[17] SUN X, LANG Q, ZHANG H, et al. Cell Scaffolds: Electrospun Photocrosslinkable Hydrogel Fibrous Scaffolds for Rapid In Vivo Vascularized Skin Flap Regeneration (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2/2017). Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(2).DOI:10.1002/adfm.201770008
[18] MAO X, CHENG R, ZHANG H, et al. Self-Healing and Injectable Hydrogel for Matching Skin Flap Regeneration. Adv Sci. 2019;6(3):1801555.
[19] CHENG Y, YU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Cold-Responsive Nanocapsules Enable the Sole-Cryoprotectant-Trehalose Cryopreservation of β Cell–Laden Hydrogels for Diabetes Treatment. Small. 2019;15(50):1904290.
[20] LIU Y, ZHAO X, ZHAO C, et al. Responsive Porous Microcarriers With Controllable Oxygen Delivery for Wound Healing. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany). 2019;15(21):1901254.
[21] KANKALA RK, ZHAO J, LIU CG, et al. Highly Porous Microcarriers for Minimally Invasive In Situ Skeletal Muscle Cell Delivery. Small. 2019; 15(25):e1901397.
[22] BIAN J, CAI F, CHEN H, et al. Modulation of Local Overactive Inflammation via Injectable Hydrogel Microspheres. Nano Lett. 2021; 21(6):2690-2698.
[23] MARTINS C, SOUSA F, ARAúJO F, et al. Functionalizing PLGA and PLGA Derivatives for Drug Delivery and Tissue Regeneration Applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(1). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201701035.
[24] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[25] HERSEL U, DAHMEN C, KESSLER H. RGD modified polymers: biomaterials for stimulated cell adhesion and beyond. Biomaterials. 2003;24(24):4385-4415.
[26] ZULU S, KENYON M. Principles of Conditioning Therapy and Cell Infusion//KENYON M, BABIC A. The European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Textbook for Nurses: Under the Auspices of EBMT. Cham (CH); Springer Copyright 2018, EBMT and the Author(s). 2018: 89-96.
[27] WU D, YU Y, ZHAO C, et al. NK-Cell-Encapsulated Porous Microspheres via Microfluidic Electrospray for Tumor Immunotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(37):33716-33724.
[28] PRAKADAN SM, SHALEK AK, WEITZ DA. Scaling by shrinking: empowering single-cell ‘omics’ with microfluidic devices . Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(6):345-361.
[29] JACKSON JM, WITEK MA, KAMANDE JW, et al. Materials and microfluidics: enabling the efficient isolation and analysis of circulating tumour cells. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(14):4245-4280.
[30] PHUENGKHAM H, SONG C, LIM YT. A Designer Scaffold with Immune Nanoconverters for Reverting Immunosuppression and Enhancing Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Adv Mater. 2019;31(42): e1903242.
|