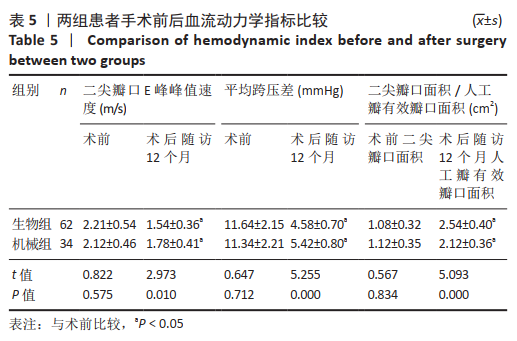
[1] CETINKAYA A, POGGENPOHL J, BRAMLAGE K, et al. Long-term outcome after mitral valve replacement using biological versus mechanical valves. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;14(1):120.
[2] NISHMURA RA, OTTO CM, BONOW RO, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart didease: a report of the American College of Cardiology / American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practive gudiellined. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(2):252-289.
[3] 于振坤,樊红光,郑哲,等.老年瓣膜性心脏病患者生物瓣与机械瓣置换术早期和中期预后的对比研究[J].中国循环杂志,2018, 33(11):1098-1101.
[4] OKOH AK, SHAH A, KANG N, et al. Outcomes After Transcatheter Mitral Valve-in-Valve Replacement in Patients With Degenerated Bioprosthesis: A Single-Center Experience. J Invasivee Cardiol. 2020;32(2):49-54.
[5] 高建秋.老年钙化性心脏瓣膜病发病机制及超声诊断研究进展[J].海南医学院学报,2018,24(6):734-736.
[6] GENTRY 3RD JL, PARIKH PK, ASASHI A, et al. Characteristics and Outcomes in a Contemporary Group of Patients With Suspected Significant Mitral Stenosis Undergoing Treadmill Stress Echocardiography. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12(6):e009062.
[7] 邹佳桐,徐薇,黄艳.衰弱评估在老年瓣膜病微创治疗中的研究进展[J].实用老年医学,2020,34(9):960-962.
[8] BAUMGARTENR H, FAKL V, BAX JJ, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2017 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease . Eur Heart J. 2017;38(36):2739-2791.
[9] EDMUNDS LH JR, CLARK RE, COHN LH, et al. Guidelines for reporting morbidity and mortality after cardiac valvular operations. Ad Hoc Liaison Committee for Standardizing Definitions of Prosthetic Heart Valve Morbidity of The American Association for Thoracic Surgery and The Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;112(3):708-711.
[10] 齐喜玲,许海燕,刘庆荣,等.中国老年退行性心脏瓣膜病住院患者诊疗现状分析[J].中国循环杂志,2019,34(8):771-776.
[11] STULAK JM, TCHANTCHALEISHVILI V, DALY RC, et al. Conventional redo biological valve replacement over 20 years: Surgical benchmarks should guide patient selection for transcatheter valve-in-valve therapy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;156(4):1380-1390.e1.
[12] 王建德,权欣,孟红,等.术中经食管超声心动图对心脏瓣膜置换术后即刻人工瓣膜功能异常的诊断价值[J].中国循环杂志,2019, 34(7):703-707.
[13] 黄健,刘一涵.妊娠期机械心脏瓣膜置换术非华法林抗凝患者出现血栓卡瓣2例并文献复习[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2021,46(2): 207-211.
[14] SCHAEFER A, CONRADI L. Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement for Degenerated Bioprosthetic Valves and Failed Annuloplasty Rings. Surg Technol Int. 2020;37:185-190.
[15] 朱思明,姜胜利.60-70岁患者二尖瓣机械瓣与生物瓣置换术后疗效的对比观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2017,42(5):468-471.
[16] HAMERMEISTER K, SETHI GK, HENDERSION WG, et al. Outcomes 15 years after valve replacement with a mechanical versus a bioprosthetic valve: final report of the veterans affairs randomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36(4):1152-1158.
[17] FUKUNAGA N, MIYAKOSHI C, SAKATA R, et al. Impact of valve type on outcomes after redo mitral valve replacement in patients aged 50 to 69 years . Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;27(3):322-327.
[18] 赵伟,郑哲.50至70岁心脏瓣膜置换患者瓣膜选择与长期预后[J].中国心血管病杂志,2020,18(4):330-333.
[19] 王栋.生物与机械瓣膜置换术对心脏瓣膜病患者心功能及并发症的影响[J].华夏医学,2018,31(4):46-49.
[20] NTARI L, SAKKOU M, CHOUVARDAS P, et al. Comorbid TNF-mediated heart valve disease and chronic polyarthritis share common mesenchymal cell-mediated aetiopathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(6):926-934.
[21] 王叶宝, 刘玲,李建民.老龄退行性心脏瓣膜病合并房颤患者血清炎症因子表达水平变化[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(24):2646-2649.
[22] 梁丽梅,刘燕,黄达,等.心脏瓣膜术联合冠状动脉旁路移植术对老年冠心病合并心脏瓣膜病患者炎症因子及用心脏功能的影响[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2018,10(8):929-931.
[23] JIAN YP, YUAN HX, HU KH, et al. Protein Compositions Changes of Circulating Microparticles in Patients With Valvular Heart Disease Subjected to Cardiac Surgery Contribute to Systemic Inflammatory Response and Disorder of Coagulation. Shock. 2019;52(5):487-496.
[24] 俞瑾,詹海婷,李帆,等.改良超滤与零平衡超滤对高风险心脏瓣膜置换术患者术后肺功能的影响[J].中国体外循环杂志,2017,15(3): 144-147.
[25] 魏凯,王晶,王期峰.米力农注射液对心脏瓣膜病置换术患者急性
组织炎性反应及心功能的影响[J].检验医学与临床,2018,15(21):
3281-3283.
[26] 周子凡,王龙飞,董松坡,等.生物瓣膜置换术联合托拉塞米治疗心脏瓣膜病的效果及对B型脑钠肽和脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A水平的影响[J].中国医药,2019,14(1):45-49.
[27] SARAN N, GREASON K, SCHAFF HV, et al. Does Mitral Valve Calcium in Patients Undergoing Mitral Valve Replacement Portend Worse Survival? Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;107(2):444-452.
[28] 郭梦霞,马永熊,董怡帆,等.壳聚糖/二氧化硅/羟基磷灰石杂化材料的体内反应性研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2018,36(1):33-37.
[29] 马超,王辉山,韩劲松,等.心脏瓣膜假体植入和外科消融迷宫手
术治疗瓣膜病合并心房颤动[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(28):
4580-4587.
[30] 刘成林.风湿性心脏瓣膜病的彩色多普勒超声心动图观察[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,2(18):198-199.
[31] 覃祖光,罗业春,陈永福.主动脉瓣及二尖瓣机械瓣联合置换术后人工心脏瓣膜-患者不匹配(VP-PM)现象的发生率及其与术前患者情况及预后的关系[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2017,4(12): 2230-2231.
[32] 刘晨,杨理践,张兴.人工生物瓣膜血流动力学行为的有限元分析[J].材料研究学报(中文版),2018,32(1):51-57.
[33] AZARI S, REZAPOUR A, OMIDI N, et al. A systematic review of the cost-effectiveness of heart valve replacement with a mechanical versus biological prosthesis in patients with heart valvular disease. Heart Fail Rev. 2020;25(3):495-503.
[34] 张浒,张桂敏,王钰,等.全瓣下结构保留下不同人工瓣膜下游血流动力指标的比较[J].重庆医学,2014,43(6):696-698.
|
 文题释义:
文题释义: