[1] WANG RM, CHRISTMAN KL. Decellularized myocardial matrix hydrogels: In basic research and preclinical studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;96:77-82.
[2] WASSENAAR JW, GAETANI R, GARCIA JJ, et al. Evidence for Mechanisms Underlying theFunctional Benefits of a Myocardial Matrix Hydrogel for Post-MI Treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(9):1074-1086.
[3] JIANG J, ZHANG C, ZHANG T, et al. Research progress of decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogel in regenerative medicine. J Biomed Eng. 2020;37(1):179-184.
[4] VENTURA RD, PADALHIN AR, PARK CM, Et al. Enhanced decellularization technique of porcine dermal ECM for tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109841.
[5] WON JY, LEE MH, KIM MJ, et al. A potential dermal substitute using decellularized dermis extracellular matrix derived bio-ink. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019; 47(1):644-649.
[6] ZHANG Z, LV L, MAMAT M, et al. Xenogenic (porcine) acellular dermal matrix promotes growth of granulation tissues in the wound healing of Fournier gangrene. Am Surg. 2015;81(1):92-95.
[7] REING JE, BROWN BN, DALY KA, et al. The effects of processing methods upon mechanical and biologic properties of porcine dermal extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010;31(33):8626-8633.
[8] ZHANG Y, HE Y, BHARADWAJ S, et al. Tissue-specific extracellular matrix coatings for the promotion of cell proliferation and maintenance of cell phenotype. Biomaterials. 2009;30(23-24):4021-4028.
[9] LIN CY, LIU TY, CHEN MH, et al. An injectable extracellular matrix for the reconstruction of epidural fat and the prevention of epidural fibrosis. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(3):035010.
[10] HAO D, LIU R, GAO K, et al. Developing an Injectable Nanofibrous Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel With an Integrin αvβ3 Ligand to Improve Endothelial Cell Survival, Engraftment and Vascularization. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:890.
[11] NARANJO JD, SALDIN LT, SOBIESKI E, et al. Esophageal extracellular matrix hydrogel mitigates metaplastic change in a dog model of Barrett’s esophagus. Sci Adv. 2020;6(27):eaba4526.
[12] WOLF MT, DALY KA, BRENNAN-PIERCE EP, et al. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012;33( 29):7028-7038.
[13] 吴鹏飞,施光清,范贤明,等.肺细胞外基质水凝胶治疗大鼠放射性肺损伤的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2019,29(12):1-6.
[14] 赵京禹,付小兵,雷永红,等.大鼠小面积全层皮肤缺损创面模型的制备[J].感染·炎症·修复,2008,9(1):64-64.
[15] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321.
[16] CHEN X, SHI Y, SHU B, et al. The effect of porcine ADM to improve the burn wound healing. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(11):2280-2291.
[17] 井刚,潘云川,王君.异种脱细胞真皮结合封闭负压引流技术临时重建巨大Ⅲ型腹壁缺损[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2020,16(1):43-45.
[18] BORDBAR S, BAKHSHAIESH NL, KHANMOHAMMADI M, et al. Production and evaluation of decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogel for cartilage regeneration derived from knee cartilage. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(4):938-946.
[19] TRAVERSE JH, HENRY TD, DIB N, et al. First-in-Man Study of a Cardiac Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel in Early and Late Myocardial Infarction Patients. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2019;4(6):659-669.
[20] CHEN G, YU Y, WU X, et al. Bioinspired Multifunctional Hybrid Hydrogel Promotes Wound Healing. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(33):1801386.
[21] BONDIOLI E, PURPURA V, ORLANDI C, et al. The use of an acellular matrix derived from human dermis for the treatment of full-thickness skin wounds. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):183-192.
[22] 杨维,崔占峰.组织工程皮肤发展现状[J].中国科学:生命科学,2015,45(5): 460-470.
[23] 杜烨,冯自波,李恭驰,等.猪脱细胞真皮基质对小鼠创面毛囊再生中基质细胞衍生因子-1及Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路表达的影响[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2019,14(1):26-33.
[24] 施恩,刘英芹.组织工程皮肤及其附属器再生修复机制与生物学行为的研究进展[J].中国保健营养,2017,13(27):93-95.
[25] HONG JY, SEO Y, DAVAA G, et al. Decellularized Brain Matrix Enhances Macrophage Polarization and Functional Improvements in Rat Spinal Cord Injury. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:357-371.
[26] HE C, YANG Z, JIN Y, et al. ADM Scaffolds Generate a Pro-regenerative Microenvironment During Full-Thickness Cutaneous Wound Healing Through M2 Macrophage Polarization via Lamtor1. Front Physiol. 2018;9:657.
[27] JIANG K, CHAIMOV D, PATEL SN, et al.3-D physiomimetic extracellular matrix hydrogels provide a supportive microenvironment for rodent and human islet culture. Biomaterials. 2019;198:37-48.
[28] ZHAO Y, FAN J, BAI S. Biocompatibility of injectable hydrogel from decellularized human adipose tissue in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(5):1684-1694.
[29] LEE JS, SHIN J, PARK HM, et al. Liver extracellular matrix providing dual functions of two-dimensional substrate coating and three-dimensional injectable hydrogel platform for liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1):206. |
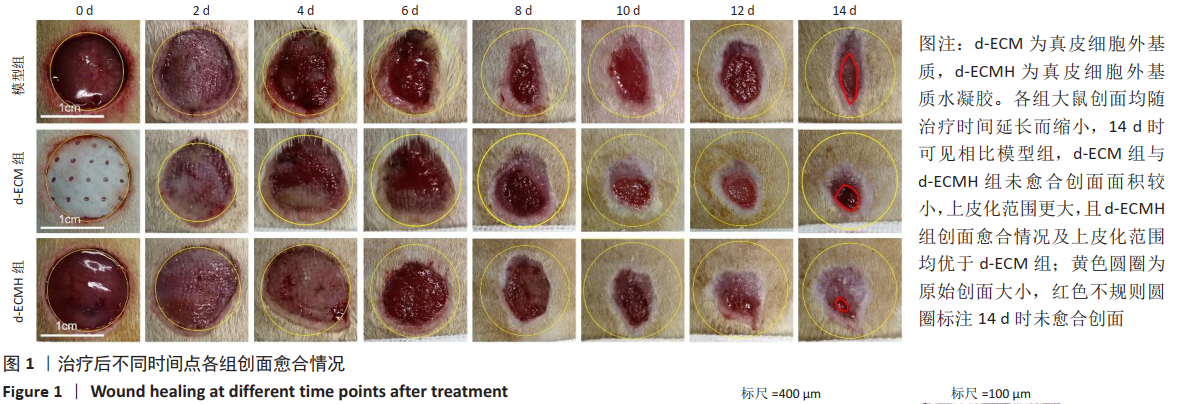
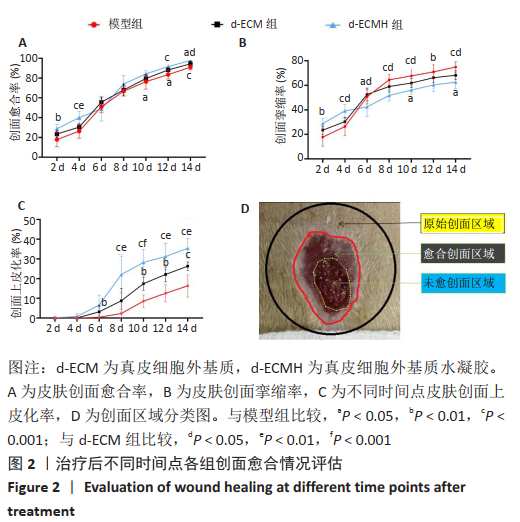
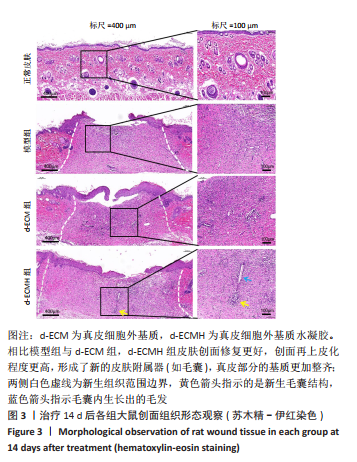
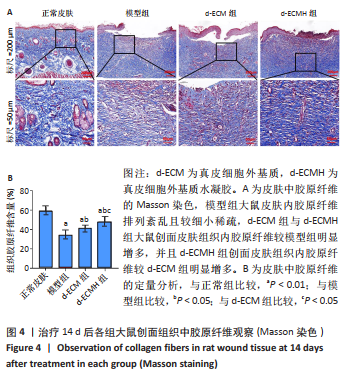
 文题释义:
文题释义: