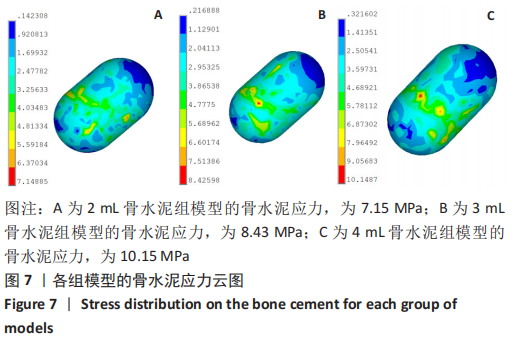
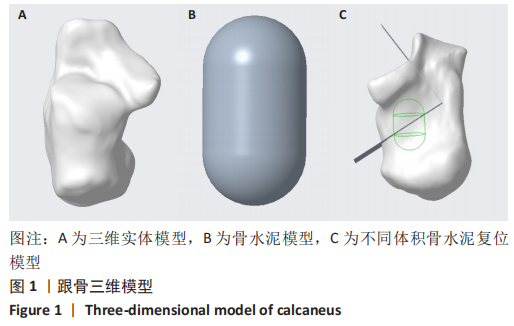
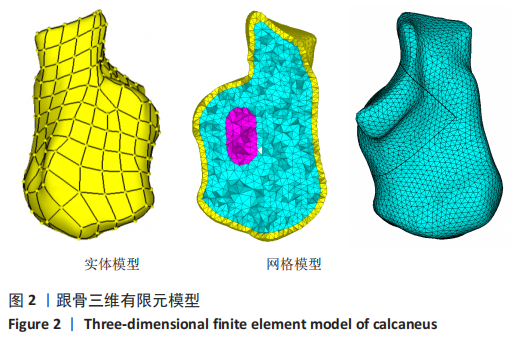
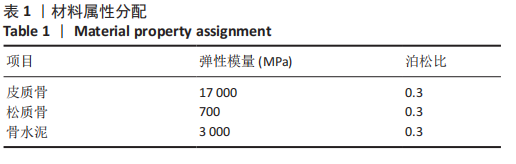
[1] TALARICO LM, VITO GR, ZYRYANOV SY. Management of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures by using external ring fixation, minimally invasive open reduction, and early weightbearing. Foot Ankle Surg. 2004;43(1):43.
[2] 张柏,祁琇,韩作峰,等.钛板联合植骨内固定修复跟骨骨折:外侧L形切口愈合的影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26): 3876-3882.
[3] RAUSCH S, KLOS K, WOLF U, et al. A biomechanical comparison of fixed angle locking compression plate osteosynthesis and cement augmented screw osteosynthesis in the management of intra articular calcaneal fractures. Int Orthop. 2014;38(8):1705-1710.
[4] 管志海,王勤业,常小波,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥注射治疗跟骨Sanders Ⅲ型骨折的生物力学测试[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(2):178-182.
[5] BANO A, PASKU D, KARANTANAS A, et al. Intra-articular calcaneal fracture: closed reduction and balloon-assisted augmentation with calcium phosphate cement: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2(1):9290.
[6] JACQUOTF, ATCHABAHIAN A.Balloon reduction and cement fixation in intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a percutaneous approach to intra-articular calcaneal fracture. Int Orthop. 2011;35(7):1007-1014.
[7] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[8] 田丰德,赵德伟,郭林,等.步幅大小及髋关节外展角度对坏死股骨头影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17): 3052-3055.
[9] 宋作成,闫小龙.踝关节胫骨远端关节面缺损生物力学特征的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(48):7212-7218.
[10] SABRY FF, EBRAHEIM NA, MEHALIK JN, et al. Internal architecture of the calcaneus: implications for calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2000;21(2):114-119.
[11] NI M, WONG DW, MEI J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of locking plate and crossing metallic and absorbable screws fixations for intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59(9):958-964.
[12] 李维新,袁斌云.跟骨骨折锁定钢板内固定与普通钢板内固定的有限元分析[J].中医正骨,2013,25(4):10-11.
[13] GALLOWAY F, KAHNT M, RAMM H, et al. A Large scale finite element study of a cementless ossointegrated tibial tray. J Biomech. 2013;46(11):1900-1906.
[14] CHEN F, HUANG X, YA Y, et al. Finite element analysis of intramedullary nailing and double locking plate for treating extra-articular proximal tibial fractures.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):12.
[15] ATMACA H, ÖZKAN A, MUTLU I, et al. The effect of proximal tibial corrective osteotomy on menisci tibia and tarsal bones: a finit element model study of tibia vara. Int J Med Robot. 2014; 10(1):93-97.
[16] NI M, W ONG DWC, NIU W, et al. Biomechanical comparison of modified Calcanail system with plating fixation in intra-articular calcaneal fracture: A finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2019;70: 55-61.
[17] NI M, MEI J, LI K, et al. The primary stability of different implants for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: an in vitro study. Biomed Eng Online. 2018;17(1):50.
[18] 李赞罡,陈为坚,李贵涛.不同运动步态下锁定加压钢板固定胫骨干骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):612-619.
[19] 朱雪松.椎体成形填充材料:应用现状与未来前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53):8644.
[20] 徐峰,蔡贤华,张志文,等.可注射性磷酸钙骨水泥对骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,28(10): 8-10.
[21] 谭斌,刘雄文,刘刚,等.经皮椎体后凸与经皮椎体成形术修复骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折:随机分组比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(4):539-543.
[22] CHEN L, ZHANG G, LI S, et al. Percutaneous treatment of calcaneus fractures associated with underlying bone cysts. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(5):424-429.
[23] LABBE JL, PERES O, LECLAIR O, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures using the balloon kyphoplasty technique: preliminary study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):829-836.
[24] 刘易军,宫赫,刘百奇,等.胫骨上端外部形状及内部结构的模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学,2006,25(5):563-579.
[25] 贾军锋,唐承杰,乐劲涛,等.胫骨远端骨折3种不同固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5188-5194
[26] 陈超,关宏刚,区杏枝,等.直入式注入PMMA骨水泥强化椎弓根钉内固定生物力学研究[J].岭南现代临床外科,2016,16(1):63-66.
[27] 许红生,赵志江.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2016,19(1):127.
(责任编辑:GW,ZN,SX)
|