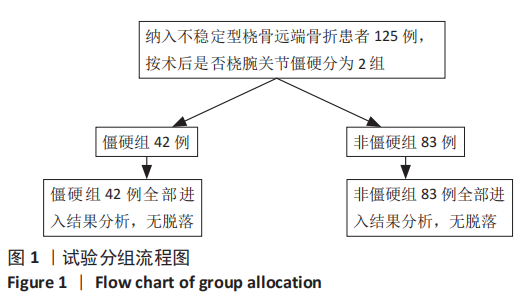
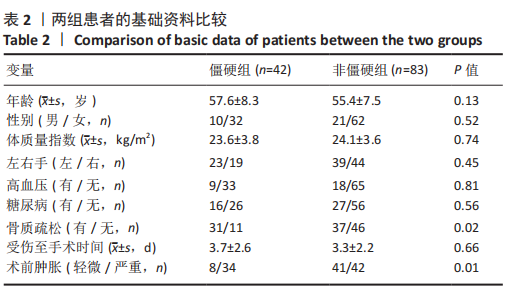
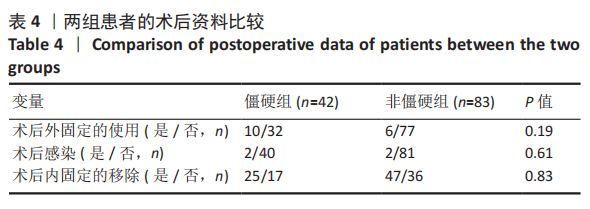
[1] FILER J, SMITH A, GIDDINS G. Assessing distal radius malrotation following fracture using computed tomography. J Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):2309499019862872.
[2] YAO H, ZHANG W, XU W, et al. A new method to predict the outcome of the volar locked plate treatment for distal radius fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):538.
[3] LANDGREN M, TEURNEAU V, ABRAMO A, et al. Intermediate-Term Outcome After Distal Radius Fracture in Patients With Poor Outcome at 1 Year: A Register Study With a 2- to 12-Year Follow-Up. J Hand Surg Am. 2019;44(1):39-45.
[4] 姜保国,张殿英,付中国,等. 桡骨远端骨折的治疗建议[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1053-1056.
[5] TEUNIS T, JUPITER J, SCHASER K, et al. Evaluation of radiographic fracture position 1 year after variable angle locking volar distal radius plating: a prospective multicentre case series. J Hand Surg Eur. 2017;42(5):493-500.
[6] SEKI Y, AOKI T, MAEHARA H, et al. Distal locking screw length for volar locking plate fixation of distal radius fractures: Postoperative stability of full-length unicortical versus shorter screws. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2019;38(1):28-33.
[7] BERGSMA M, DOORNBERG J, DUIT R, et al. Volar plating in distal radius fractures: A prospective clinical study on efficacy of dorsal tangential views to avoid screw penetration. Injury. 2018;49(10):1810-1815.
[8] TANAKA Y, GOTANI H, YANO K, et al. Evaluation of flexor pollicis longus tendon attrition using color Doppler imaging after volar plate fixation for distal radius fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(3):447-452.
[9] KONG L, ZHAI Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Radiocarpal joint stiffness following surgical treatment for distal radius fractures: the incidence and associated factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):313.
[10] THOMAS D, ZANIN D. Hand rehabilitation after distal radius fracture. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2016;35S:S156-S61.
[11] YUAN C, ZHANG H, LIU H, et al. Does concomitant ulnar styloid fracture and distal radius fracture portend poorer outcomes? A meta-analysis of comparative studies. Injury. 2017;48(11):2575-2581.
[12] MCQUEEN M, CASPERS J. Colles’ fractures: does anatomical result affect the final function? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70:649-651.
[13] 姜保国, 张殿英, 傅忠国, 等. 桡骨远端粉碎性骨折及关节内骨折的手术治疗[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2002,22(2):80-83.
[14] GABL M, ARORA R, KLAUSER AS, et al. Characteristics of secondary arthrofibrosis after intra-articular distal radius fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(8): 1181-1188.
[15] KREDER HJ, HANEL DP, AGEL J, et al. Indirect reduction and percutaneous fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87-B:829-836.
[16] FORWARD DP, DAVIS TRC, SITHOLE JS. Do young patients with malunited fractures of the distal radius inevitably develop symptomatic post-traumatic osteoarthritis? J Bone Joint Surg. 2008;90-B:629-637.
[17] 李哲, 孙天祥, 钟易林, 等. 手法复位石膏外固定与切开复位锁定钢板内固定 治疗 AO-B、C 型桡骨远端骨折的比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019, 34(5):534-536.
[18] KHAN M, NOORDIN S, HASHMI P. Intra-articular distal radius fractures: Postoperative roentgenographic and functional outcomes. J Pak Med Assoc. 2016; 66(3):275-279.
[19] LOISEL F, BOURGEOIS M, RONDOT T, et al. Treatment goals for distal radius fractures in 2018: recommendations and practical advice. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(8):1465-1468.
[20] 张兴平. 桡骨远端骨折治疗方法的选择与思考[J]. 中国骨伤,2011,24(11): 887-889.
[21] THELEN S, GRASSMANN JP, JUNGBLUTH P, et al. Distal radius fractures : Current treatment concepts and controversies. Chirurg. 2018;89(10):798-812.
[22] 廉志明, 晶杨, 张太良, 等. 桥接外固定架联合克氏针与掌侧锁定板修复桡骨远端不稳定型骨折的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(44):6590-6598.
[23] MANSURIPUR P, GIL J, CASSIDY D, et al. Fixation Strength in Full and Limited Fixation of Osteoporotic Distal Radius Fractures. Hand (N Y). 2018;13(4):461-465.
[24] WILSON J, HOLZGREFE R, STALEY C, et al. Use of a 5-Item Modified Frailty Index for Risk Stratification in Patients Undergoing Surgical Management of Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg. 2018;43(8):701-709.
[25] ROSENAUER R, PEZZEI C, QUADLBAUER S, et al. Complications after operatively treated distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):665-673.
[26] JOHNSON N, DIAS J, WILDIN C, et al. Comparison of distal radius fracture intra-articular step reduction with volar locking plates and K wires: a retrospective review of quality and maintenance of fracture reduction. J Hand Surg. 2017; 42(2):144-150. |