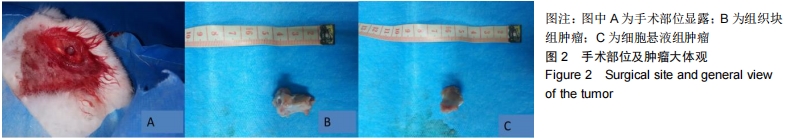
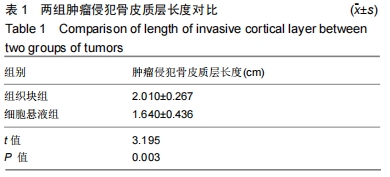
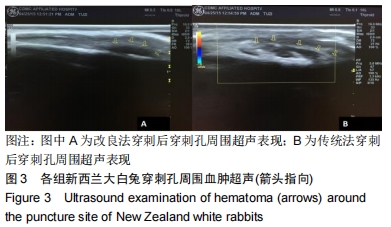
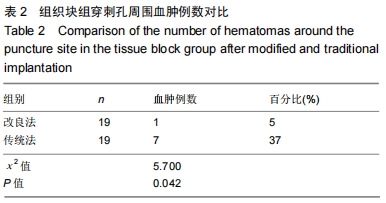
[1]SMITH-GUZMÁN NE, TORETSKY JA, TSAI J, et al. A probable primary malignant bone tumor in a pre-Columbian human humerus from Cerro Brujo, Bocas del Toro, Panamá. Int J Paleopathol. 2018; 21:138-146.
[2]WANG L, LONG NJ, LI L, et al. Multi-functional bismuth-doped bioglasses: combining bioactivity and photothermal response for bone tumor treatment and tissue repair. Light Sci Appl. 2018;7:1.
[3]OGURA K, HOSODA F, NAKAMURA H, et al. Highly recurrent H3F3A mutations with additional epigenetic regulator alterations in giant cell tumor of bone. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2017;56(10):711-718.
[4]OU JY, SPRAKER-PERLMAN H, DIETZ AC, et al. Conditional survival of pediatric, adolescent, and young adult soft tissue sarcoma and bone tumor patients. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017; 50(Pt A):150-157.
[5]WANG LJ, WU HB, ZHOU WL, et al. Gummatous Syphilis Mimicking Malignant Bone Tumor on FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2019;44(4): 313-316.
[6]HIGUCHI T, YAMAMOTO N, HAYASHI K, et al. Calcium Phosphate Cement in the Surgical Management of Benign Bone Tumors. Anticancer Res. 2018;38(5):3031-3035.
[7]VAN BREUGEL JMM, GESCHWIND JF, MIRPOUR S, et al. Theranostic application of lipiodol for transarterial chemoembolization in a VX2 rabbit liver tumor model. Theranostics. 2019;9(13): 3674-3686.
[8]SUN Y, XIONG X, PANDYA D, et al. Enhancing tissue permeability with MRI guided preclinical focused ultrasound system in rabbit muscle: From normal tissue to VX2 tumor. J Control Release. 2017;256:1-8.
[9]DESCHAMPS F, FAROUIL G, GONZALEZ W, et al. Stabilization Improves Theranostic Properties of Lipiodol®-Based Emulsion During Liver Trans-arterial Chemo-embolization in a VX2 Rabbit Model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(6):907-913.
[10]BING C, PATEL P, STARUCH RM, et al. Longer heating duration increases localized doxorubicin deposition and therapeutic index in Vx2 tumors using MR-HIFU mild hyperthermia and thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):196-203.
[11]HUNG SH, JAO JC, TZENG JS, et al. Evaluation of Rabbit VX2 Tumor Model Using Magnetic Resonance T1-Mapping and T2-Mapping Techniques at 1.5 T. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2018; 38(4): 607-617.
[12]PELLERIN O, AMARA I, SAPOVAL M, et al. Hepatic Intra-arterial Delivery of a "Trojan-horses" Gene Therapy: A Pilot Study on Rabbit VX2 Hepatic Tumor Model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018;41(1): 153-162.
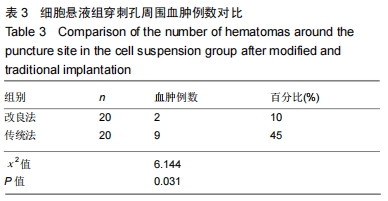
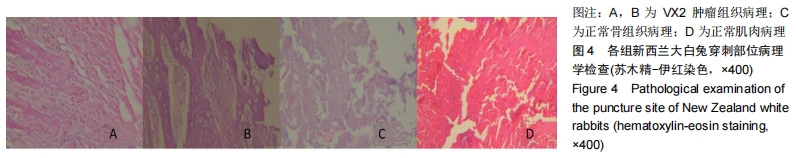
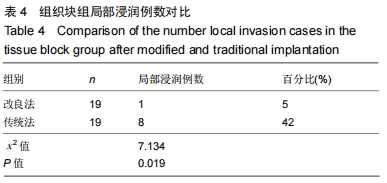
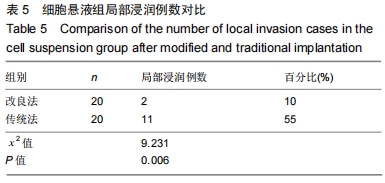
[13]曹海营,金宇,冯震,等.改良穿刺法改善针道肿瘤细胞转移情况的研究[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(1):40-42,45.
[14]曹海营,金宇,赵景新,等.改良穿刺活检技术用于降低 VX2 肌肉肿瘤穿刺并发症的研究[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(5): 560-564.
[15]张猛,魏俊强,段建伟,等.股骨骨折模型兔外固定架稳定性与股四头肌肌腱的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(39): 5834-5839.
[16]张猛,魏俊强,段建伟,等.外固定架制作兔股骨骨折模型[J].中国临床研究, 2016,29(5):685-686.
[17]段建伟,魏俊强,张猛,等.外固定架加压-牵开-再加压治疗非感染性骨折不愈合实验研究[J].新医学,2016,47(5):318-323.
[18]魏然,赵景新,孔庆柱,等.一种新的骨肿瘤穿刺活检器械的研究[J].中国医疗设备,2015,30(11):98-99.
[19]魏然,孔庆柱,赵景新,等.自创封闭穿刺技术应用于骨肿瘤诊断的动物实验研究[J].新医学,2016,47(2):92-96.
[20]LI C, ZHANG Y, CHEN G, et al. Engineered Multifunctional Nanomedicine for Simultaneous Stereotactic Chemotherapy and Inhibited Osteolysis in an Orthotopic Model of Bone Metastasis. Adv Mater. 2017;29(13): 1605754.
[21]HE K, WAN Y, XIAN S. Risk analysis on infection caused by peripherally inserted central catheter for bone tumor patients. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(1):90-93.
[22]AMARY F, BERISHA F, YE H, et al. H3F3A (Histone 3.3) G34W Immunohistochemistry: A Reliable Marker Defining Benign and Malignant Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017;41(8): 1059-1068.
[23]WANG Y, YANG J, LIU H, et al. Osteotropic peptide-mediated bone targeting for photothermal treatment of bone tumors. Biomaterials. 2017;114:97-105.
[24]WU CC, HSIEH PP. Denosumab-Treated Giant Cell Tumor of the Bone Mimicking Low-Grade Central Osteosarcoma. J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):133-135.
[25]MIOLA M, GERBALDO R, LAVIANO F, et al. Multifunctional ferrimagnetic glass–ceramic for the treatment of bone tumor and associated complications. Journal of Materials Science. 2017; 52(15): 9192-9201.
[26]MATSUBARA H, TSUCHIYA H. Treatment of bone tumor using external fixator. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):1-8.
[27]VARTEVAN A, MAY C, BARNES CE. Pediatric bone imaging: Differentiating benign lesions from malignant. Applied Radiology. 2018; 47(7):8-15.
[28]IQBAL T, SHI L, WANG L, et al. Development of finite element model for customized prostheses design for patient with pelvic bone tumor. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(6): 525-533.
[29]ZHANG L, WANG N, MAO J, et al. Dual-Energy CT-Derived Volumetric Iodine Concentration for the Assessment of Therapeutic Response after Microwave Ablation in a Rabbit Model with Intrahepatic VX2 Tumor. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(10):1455-1461.
[30]LI SY, HUANG PT, FANG Y, et al. Ultrasonic Cavitation Ameliorates Antitumor Efficacy of Residual Cancer After Incomplete Radiofrequency Ablation in Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor Model. Transl Oncol. 2019;12(8):1113-1121.
[31]WANG P, TAN H, WANG B, et al. MR lymphography in detecting internal mammary sentinel lymph node for rabbit models of VX2 breast cancer. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging Technology. 2018;34(5): 641-645.
[32]NASS N, STREIT S, WYBRANSKI C, et al. Validation of VX2 as a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model: Comparison of the Molecular Reaction of VX2 and HepG2 Tumor Cells to Sorafenib In Vitro. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(1):87-93.
[33]任葆胜,杨正强,施海彬,等.VX2兔肝门静脉主干癌栓模型建立的实验研究[J].实用放射学杂志,2017,33(9):1454-1457.
[34]FOSNIGHT TR, HOOI FM, KEIL RD, et al. Echo Decorrelation Imaging of Rabbit Liver and VX2 Tumor during In Vivo Ultrasound Ablation. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017;43(1): 176-186.
[35]WU CC, WANG F, RONG S, et al. Enhancement of osteogenesis of rabbit bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by transfection of human BMP-2 and EGFP recombinant adenovirus via Wnt signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):4030-4036.
[36]GALLI S, ANDERSSON M, JINNO Y, et al. Magnesium release from mesoporous carriers on endosseus implants does not influence bone maturation at 6 weeks in rabbit bone. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(7): 2118-2125.
[37]ZHU W, GUO D, PENG L, et al. Repair of rabbit cartilage defect based on the fusion of rabbit bone marrow stromal cells and Nano-HA/PLLA composite material. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(1): 115-119.
[38]QIAN S, WANG Z, ZHENG Z, et al. A Collagen and Silk Scaffold for Improved Healing of the Tendon and Bone Interface in a Rabbit Model. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:269-278.
|