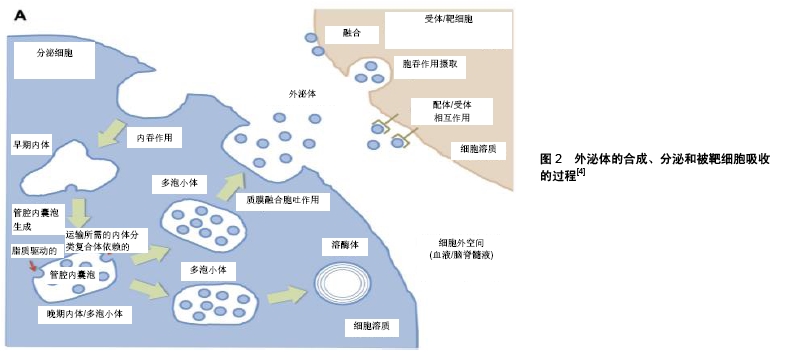
2.1 外泌体的来源及生物学特征 外泌体是由多泡体分泌的直径在30-120 nm的封闭脂质囊泡[1-3](不同文献报道外泌体特征有所差别),属于细胞外囊泡的一种。细胞外囊泡主要由凋亡小体、细胞微体(泡)和外泌体组成,其中对外泌体的研究最为广泛。外泌体最初起源于细胞内吞途径,形成早期内体,早期内体逐步形成晚期内体或多泡体,在此过程中成熟的早期内体膜向内通过ESCRT依赖性机制或者非ESCRT依赖性机制(脂质驱动机制)完成出芽运动,形成内囊泡,随后一部分多泡体与细胞膜融合,内囊泡被释放到细胞外[4-5],释放过程受到p53和细胞骨架运动的调控[6],释放到细胞外的外泌体被微环境中的靶细胞摄取或者通过体液运送到身体其他部位[7]。外泌体通过3种主要机制被靶细胞摄取,即膜融合摄取、细胞内吞作用摄取和配体受体介导摄取途径[4]。外泌体的合成、分泌和被靶细胞吸收的过程见图2。很多组织器官的细胞,如T细胞、树突状细胞、肥大细胞、肿瘤细胞、间充质干细胞等均可分泌外泌体[8],外泌体作为3种主要的细胞外囊泡之一,发挥着重要的细胞通讯功能[2,9]。外泌体最早被发现于红细胞的成熟过程中,被认为具有清除细胞废物的功能[1],随后发现外泌体内容物中含有mRNA和miRNA并且可与其他细胞发生融合,这证明了外泌体还具有细胞间信号传导的功能[1,9]。外泌体拥有丰富的脂质、蛋白、核酸,这些内容物在外泌体形成过程、外泌体被靶细胞摄取过程以及细胞间物质信息传递中发挥重要作用,见表1[7-8,10]。外泌体具有许多标志物,例如四次跨膜蛋白(CD81、CD63和CD9)、热休克蛋白(HSP60、HSP70和HSP90)、ALIX、瘤易感基因101蛋白(tumor susceptibility gene 101,sg101)和不同组织来源的特异性外泌体标志物[7]。

2.2 间充质干细胞的特点及其外泌体的应用 间充质干细胞是一种多能干细胞,具有自我更新、分化的能力,最初在骨髓中被发现[11]。2006年国际细胞治疗协会定义并阐述了间充质干细胞的特征:①间充质干细胞必须在标准培养下黏附在塑料上;②间充质干细胞还有基质抗原表达,CD105、CD73、CD90呈阳性且CD45、CD34、CD14(CD11b)、CD79a(CD19)和HLA-DR呈阴性;③具有分化潜能[12]。
近些年间充质干细胞一直成为干细胞领域的研究重点,其在组织工程和再生医学领域具有明显优势:①较为广泛的组织分化能力:间充质干细胞除了具有基本的中胚层分化能力,还有研究表明间充质干细胞具有转分化为外胚层和内胚层细胞的能力,如神经胶质细胞、神经元、肝细胞等;②免疫原性较低:其缺乏主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ(MHCⅡ)并抑制免疫细胞发挥功能[13],同时利用自体间充质干细胞治疗可降低细胞排斥反应;③获取来源广泛:间充质干细胞可以从骨髓、脂肪组织、牙髓、月经及妊娠组织(胎盘、羊水、脐带胶质、脐血、绒毛膜)等获取[13-14]。间充质干细胞应用于组织修复过程中还存在很多缺陷,如多次传代后细胞增殖能力下降、细胞排斥、对细胞表型要求高等,并且会造成心率失常、肿瘤发生、组织内骨化和(或)钙化、肺栓塞等不良反应[8,10]。更为重要的是,人为注射的间充质干细胞只有10%到达并植入受损组织,其余90%细胞在体内运输过程中丢失,因此组织修复效果无法用细胞移植理论解释[15],单纯的利用间充质干细胞分化功能无法达到理想的组织修复效果,需要替代的治疗方法。
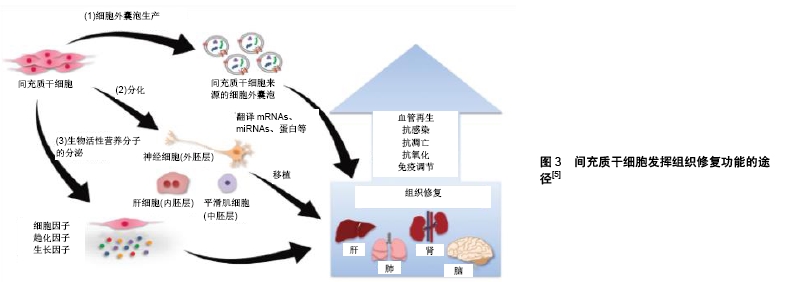
间充质干细胞主要通过3种途径发挥组织修复功能,见图3:①细胞外囊泡途径:间充质干细胞通过分泌细胞外囊泡将mRNAs、miRNAs、蛋白质等物质运输到受损组织细胞;②分化途径:间充质干细胞分化成相应细胞,植入到受损组织区域;③活性营养因子途径:间充质干细胞通过分泌活性因子、趋化因子、生长因子等促进组织修复[5]。大量的调节因子并不是通过胞吐方式直接释放到细胞外,而是通过细胞外囊泡实现细胞间信息传递[15]。外泌体以其易生产、易储存、可大量制备、低免疫原性与间充质干细胞拥有相同治疗效果等优点,被广泛应用于癌症、心血管疾病、骨关节炎等领域[8]。尤其在神经系统疾病治疗中,由于血脑屏障的存在,很多药物无法到达中枢神经系统发挥药效,使得相关疾病缺乏有效的治疗[16]。间充质干细胞外泌体治疗的步骤:①从组织中分离出间充质干细胞;②修改间充质干细胞使其携带治疗分子或使其接受特殊环境刺激;③分离、纯化、鉴定并量产带有治疗分子的间充质干细胞外泌体;④通过静脉注射等方式给药[7]。由于脂质外膜的保护,外泌体内容物不容易被降解,通过归巢能力到达受损组织并被细胞吸收[17]。外泌体更是以其体积小易穿透血脑屏障的特点为阿尔茨海默症、帕金森综合征等神经退行性疾病的治疗带来曙光。
2.3 间充质干细胞外泌体在神经系统疾病中发挥的生物学功能
2.3.1 间充质干细胞外泌体在宏观上改善神经系统功能
(1)维护神经元数量,减少神经元损失:足够的神经元数量是维持复杂神经系统正常功能的重要前提之一。间充质干细胞外泌体可通过维持受损神经组织周围的神经元数量、减少神经元损失来降低神经系统的损伤程度,并且经过修饰的特定外泌体具有更好的疗效。在成年雄性SD大鼠T10胸椎用动脉瘤夹施以35 g闭合力并持续60 s诱发脊髓损伤,经大鼠尾静脉注射0.5 mL含 100 μg
miRNA-133b改造的间充质干细胞外泌体,大鼠的NeuN+神经元较普通间充质细胞外泌体有明显增 多[18]。0.5 U Ⅶ型细菌胶原酶诱导雄性Wistar大鼠脑出血模型,经脑部注射miRNA-21过表达的间充质干细胞,TUNEL检测大鼠脑部阳性凋亡细胞明显减少并且NeuN+神经元增多,随后研究者又将miRNA-21过表达的间充质干细胞外泌体与PC12细胞培养,发现外泌体可与PC12细胞发生融合并且miRNA-21在PC12细胞和缺血周围组织细胞中表达量大幅增加,证实了外泌体在保护脑缺血细胞中的作用[19]。在另一项实验中,miRNA-133b过表达的间充质干细胞外泌体显著降低TUNEL阳性和FJB染色阳性神经细胞,表明该外泌体抑制神经元细胞凋亡和神经组织的退行性病变[20]。从骨髓间充质干细胞提取A1外泌体(在脾中有抗感染性的细胞外囊泡)治疗毛果芸香碱诱导的癫痫持续状态小鼠,结果显示小鼠海马齿状回和CA1细胞层的神经元丢失数量减少,并且抑制了海马中一些抑制性神经元的丢失,如钙结合蛋白小白蛋白(PV)阳性神经元、神经肽生长抑素(SS)阳性神经元和神经肽Y(NPY)阳性神经元。在脑血管病大鼠模型中,经过富含miRNA-17-92簇间充质干细胞外泌体处理后的小鼠缺血边界区域的新生神经元、少突胶质祖细胞和成熟少突胶质细胞明显增加[21]。上述研究还表明经过修饰的富含某种miRNA的间充质干细胞外泌体拥有较未经修饰的间充质干细胞外泌体更强的保护神经元或少突胶质细胞的能力,可能与miRNA特定的蛋白调控机制有关。
(2)促进神经突重塑和神经突的生长:研究发现,间充质干细胞外泌体对脑血管病大鼠的神经突重塑有重要作用。用Bielshowsky silver和Luxol fast blue染色发现外泌体治疗显著增加缺血周围区域的神经-髓鞘束的密度。通过免疫组织化学染色法发现外泌体治疗后缺血周围的免疫活性区域明显增加,该结果表明经外泌体治疗的大鼠轴突和突触的可塑性增强。通过高尔基银浸渍分析发现外泌体治疗后树突的可塑性增强[21]。另一项实验证明人月经血间充质干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞可促进皮质神经元和感觉神经元的神经突增长且人月经血间充质干细胞外泌体可增加神经突分支数量[14]。
(3)神经系统疾病病变腔的萎缩:组织学方法检测神经系统病变腔大小是较为直接地检测神经系统疾病严重程度的方法,病变腔的萎缩在一定程度上反映疾病的恢复情况。苏木精-伊红染色显示,miRNA-133b改造的间充质干细胞外泌体能有效降低脊髓损伤面积[18]。在脑出血大鼠模型中,间充质干细胞外泌体有效降低脑血肿面积,其中miRNA-21改造的间充质干细胞外泌体比正常外泌体改善脑血肿的效果更好[19]。
(4)改善神经系统行为评估结果:根据不同的实验需求选取相应的行为测验,检测实验动物的运动、学习、记忆等能力,直观反映间充质干细胞外泌体对神经系统的修复能力。用BBB运动评定量表发现,富含miRNA-133b的间充质干细胞外泌体提高了脊髓损伤大鼠的BBB分数,脊髓损伤小鼠的后肢运动功能得到提 高[18]。另一项实验用运动功能缺失指数(MDI)来评估暂时性脊髓缺血大鼠的运动功能,通过大鼠的移动和放置/踩踏反射结果得出骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体提高大鼠的运动功能,且富含miRNA-25外泌体的效果更好[22]。在脑血管病大鼠模型中应用间充质干细胞外泌体有效降低mNSS分数并且脚误实验显示大鼠踏空水平梯子的数量降低,其中富含miRNA-17-92簇外泌体对大鼠神经元功能恢复比普通外泌体更好[21]。XIN等[21]研究通过分析mNSS分数和前肢脚误实验得到相同的结果,证实骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体促进创伤性脑损伤大鼠的感觉运动功能恢复。
学习和记忆能力是评判大脑功能的另一项重要指标,尤其对于像海马区域功能受损的阿尔茨海默症等神经退行性疾病。Morris水迷宫实验用于检测脑学习和记忆功能,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体治疗的创伤性脑损伤大鼠较对照组在寻找隐秘平台的时间更短、在正确象限逗留时间更长、游泳的路径更短,这些结果表明经外泌体治疗对大鼠空间识别和记忆的恢复有效果[23]。另一实验通过Morris水迷宫实验证明人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体有效改善阿尔茨海默症小鼠模型(AβPP/PS1转基因小鼠)空间学习和记忆力功能[24]。通过对象位置测试(object location test,OLT)、新对象识别测试(novel object recognition test,NORT)和模式分离测试(pattern separation test,PST),人骨髓间充质细胞A1外泌体可长期逆转癫痫状态小鼠的认知和记忆损伤[25]。
(5)通过调节小胶质细胞种类和数量直接减轻炎症反应:组织的稳态受到免疫系统的调节,由疾病或者损伤造成的长期炎症反应会导致组织的进一步损伤[26]。小胶质细胞是神经系统的重要免疫细胞,其数量的多少直接反映局部炎症情况。小胶质细胞分为促炎症发生的M1型小胶质细胞和抗炎症发生的M2型小胶质细胞[24]。向实验性自身免疫脑脊髓炎大鼠尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体,发现M1型小胶质细胞标志物肿瘤坏死因子α和诱导型一氧化氮合酶的mRNA水平较对照组明显降低,M2型小胶质细胞标志物白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β明显升高,并且通过免疫荧光染色分析CD68+(M1小胶质细胞标志物)细胞明显减少,CD206+(M2型小胶质细胞标志物)细胞明显增加[3]。从骨髓间充质干细胞提取A1外泌体(在脾中有抗感染性的细胞外囊泡)治疗毛果芸香碱诱导的癫痫持续状态小鼠,发现ED-1+(CD68+)小胶质细胞在海马齿状回、CA1、CA3子区域及整个海马区域均明显减少[25]。另一项实验中用骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体能显著降低创伤性脑损伤大鼠脑部GFAP+星形胶质细胞和CD68+小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞[23]。人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体可以有效降低阿尔茨海默症小鼠Iba-1+小胶质细胞数量,表明小鼠脑部活化小胶质细胞数量降低。经外泌体治疗后,小鼠M2型小胶质细胞标志物:YM-1(Chitinase 3-like 3)、Arg-1(arginase-1)、 MRC1(mannose receptors C type 1)、FIZZ1(found in inflammatory zone 1)和CD163(the haptoglobin/hemoglobin scavenger
receptor)均较对照组有明显增加。该研究还通过检测分子标志Arg1和Ym1表明外泌体能在体外诱导BV2细胞向M2型小胶质细胞选择性激活[24]。
2.3.2 间充质干细胞外泌体在微观上改善神经系统功能
(1)通过调节酶的含量发挥调控细胞的功能:间充质干细胞外泌体内富含有催化活性的酶,通过酶的种类、数量的调节,改变细胞内生化反应的种类和速度,进而减少对细胞的损伤反应,并且通过酶快速调节组织的稳态[26],在脊髓缺血前经鞘内注射富含miRNA-25的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体,能降低脊髓细胞内的NADPH氧化酶4(NADPH oxidase 4,NOX4)的含量。NADPH氧化酶是一类能产生活性氧的酶类,经富含miRNA-25的外泌体治疗后NOX4含量下降,表明细胞内活性氧的生成量下降,其对细胞的损伤程度降低[22]。Aβ沉淀是导致阿尔茨海默症的主要原因,有2种途径可以降低Aβ沉淀在细胞内的累计,即减少Aβ沉淀的生成和提升沉淀的清除能力[5],两种途径都与相应的酶有关。Aβ前身是淀粉样蛋白前体蛋白(amyloid precursor protein,APP),依次经过β-分泌酶和γ-分泌酶的分解最终生成成熟Aβ[27]。研究表明,转化的含有β位点APP切割酶1(β-site APP-cleaving Enzyme 1,BACE-1)树突状细胞外泌体能敲除动物体内60%的BACE-1基因并降低55%Aβ含 量[5,28]。因此推测,间充质干细胞外泌体也可发挥相同的功能。研究表明,人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体能增加阿尔茨海默症小鼠脑细胞中Aβ沉淀降解酶如脑啡肽酶(neprilysin,NEP)和胰岛素降解酶(insulin-degrading enzyme,IDE)的含量,提高细胞对Aβ淀粉样沉淀的清除能力,从而达到缓解细胞受损程度[24]。
(2)通过调节炎症因子间接减轻炎症反应:炎症因子是调节细胞免疫反应的一类重要分子,可参与到多种免疫反应中。向实验性自身免疫脑脊髓炎大鼠尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体,通过ELISA分析小鼠血清中的炎症因子水平,结果发现经外泌体治疗后促炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素12明显降低,抗炎症因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β明显增高。体外实验得到相同的结果,将骨髓间充质干细胞和大鼠小胶质细胞系放入透孔系统(Transwell system)共培养,体系中加入脂多糖模拟炎症环境,发现促炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素12明显降低,抗炎症因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β明显增高[3]。通过鞘内注射骨髓间充质干细胞的普通外泌体和富含miRNA-25外泌体均发现暂时性脊髓缺血大鼠的白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α水平明显降低[22]。向L5/6脊神经结扎术大鼠模型经鞘内注入人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体,发现外泌体显著抑制由于脊神经节扎导致的肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的升高并且增加了白细胞介素10的表达[29]。从骨髓间充质干细胞提取A1外泌体(在脾中有抗感染性的细胞外囊泡)治疗毛果芸香碱诱导的癫痫持续状态的小鼠,分析治疗后小鼠海马组织裂解液中的炎症因子成分,结果显示有7种促炎症因子水平明显降低,分别是肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、单核细胞趋化蛋白1、干细胞因子、巨噬细胞炎症蛋白1α、粒细胞巨噬细胞刺激因子和白细胞介素12;5种抗炎症因子水平明显降低,分别是白细胞介素10、粒细胞集落刺激因子、血小板源生长因子β、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素2[25]。另一项实验表明人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体能有效改善阿尔茨海默症小鼠模型的神经性炎症,结果显示外泌体对小鼠体内脑部、外周血液以及体外BV2细胞(Aβ25-35预处理)培养基中的炎症因子有调节作用,其中促炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β明显降低,抗炎症因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β明显增高[24]。
(3)通过miRNA及信号通路调节神经系统功能:miRNA是由22-26个核苷酸组成的小的单链非编码RNA,其在转录后的基因表达中发挥着重要功能。miRNA通过结合mRNA的3'非翻译区使mRNA稳定性降低和沉默转录。有研究表明miRNA在干细胞分裂分化和细胞衰老中发挥重要作用[10]。miRNA的发生过程:首先以DNA为模板转录成为由200个核苷酸组成的拥有发卡环、5'帽和3'多聚核苷酸尾的pri-miRNA(primary miRNA),经Drosha和DiGeorge综合征关键区域基因8(Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8,DGRC8)处理形成pre-miRNA(precursor miRNA)。pre-miRNA在exportin5和RanGTP中组装成复合物并运输到细胞质。经Dicer分裂并与Argonaute蛋白(Ago)结合组装成miRNA诱导沉默复合体,阻止mRNA的翻译或将mRNA降解[9-10]。miRNA和Ago2复合体有对核酸酶和蛋白酶很高的抗性,所以在胞外可以很长时间不被降解[30]。
间充质干细胞外泌体能够抑制细胞死亡信号通路和促进细胞存活信号通路,来促进神经细胞在疾病条件下的存活,其可通过miRNA实现调节功能。①抑制细胞死亡信号通路:RhoA是Rho家族的一种蛋白质,其可直接激活下游的Rho相关激酶(Rho-associated kinase, ROCK)。Rho/ROCK信号通路在脊髓损伤后神经元死亡过程中发挥重要作用。经过富含miRNA-133b的间充质干细胞治疗后,脊髓损伤大鼠体内高表达的Rho得到抑制[18]。在另一项实验中向脑出血大鼠注射富含miRNA-21的间充质干细胞外泌体,研究人员发现miRNA-21可直接作用于靶目标TRPM7 mRNA。TRPM7是神经元凋亡基因,可以表达高钙离子非选择性渗透阳离子通道,参与细胞凋亡。经外泌体治疗后TRPM7表达量显著降低,同时NF-κB凋亡信号通路中的IκB-α磷酸化程度下降且p56转移到细胞核含量降低,NF-κB凋亡信号通路被抑制[19]。②促进细胞存活信号通路:大鼠脊髓损伤后,miRNA-133b外泌体可促进ERK1/2磷酸化,进而促进脊髓损伤后ERK细胞生存通路[18]。另一项实验也表明富含miRNA-133b的间充质干细胞外泌体显著降低脑出血大鼠RhoA的表达并增加磷酸化的ERK1/2和磷酸化的CREB的比率,激活了细胞ERK1/2-CREB信号通路[20]。人牙髓干细胞/人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可增加红藻氨酸兴奋性中毒的海马细胞的PI3K磷酸化水平,表明其外泌体可激活AKT/PI3K信号通路[31]。另一项实验得出类似结论,富含miRNA-17-92的间充质干细胞外泌体显著降低脑血管病大鼠PTEN水平,促进了Akt、mTOR、GSK-3β的磷酸化,该实验表明miRNA-17-92靶向PTEN并激活下游PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路从而抑制GSK-3β在神经元的活性,促进轴突生长和恢复[21]。






