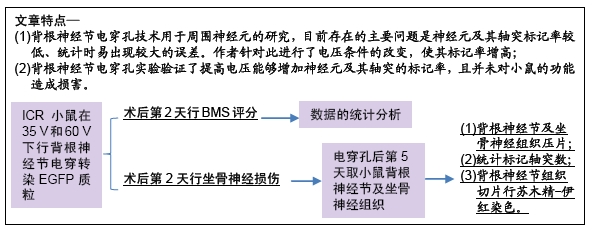
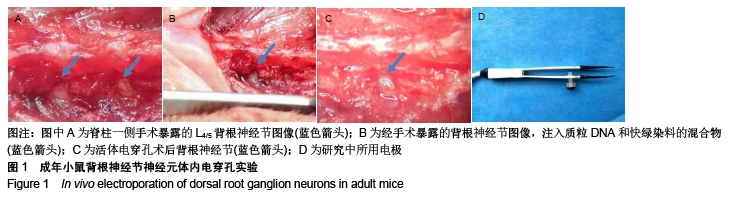
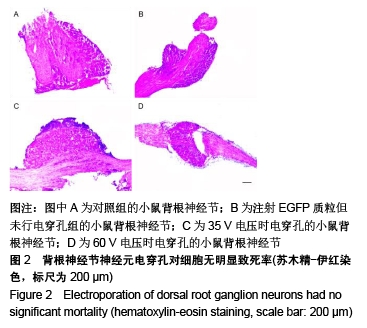
[1] NOBLE J, MUNRO CA, PRASAD VS, et al. Analysis of upper and lower extremity peripheral nerve injuries in a population of patients with multiple injuries. J Trauma. 1998;45(1): 116-122.
[2] 陈明伟,袁晓华,潘敏,等.从道路交通事故统计分析对比谈预防措施[J].中国安全科学学报, 2004,14(8):59-63.
[3] 韦正超,蔡道章,徐柜如,等.医源性外周神经损伤临床治疗分析[J].中华显微外科杂志,2002,25(2):152-153.
[4] 李志杰,高伟阳,廖孔荣,等.医源性周围神经损伤及显微外科治疗[J].温州医学院学报,2002,32(2): 115-116.
[5] 张国亮,蔡启卿,冯明录.医源性周围神经损伤的治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000,7(5):503.
[6] MOKARRAM N, BELLAMKONDA RV. Overcoming endogenous constraints on neuronal regeneration. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2011;58(7):1900-1906.
[7] JACOB HE, FÖRSTER W, BERG H. Microbiological implications of electric field effects. II. Inactivation of yeast cells and repair of their cell envelope. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1981; 21(3):225-233.
[8] SAIJILAFU, ZHANG BY, ZHOU FQ. In vivo electroporation of adult mouse sensory neurons for studying peripheral axon regeneration. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1162:167-175.
[9] LI Q, QIAN C, ZHOU FQ. Investigating Mammalian Axon Regeneration: In Vivo Electroporation of Adult Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglion. J Vis Exp. 2018;(139):58171.
[10] BASSO DM, FISHER LC, ANDERSON AJ, et al. Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(5):635-659.
[11] FILBIN MT. Myelin-associated inhibitors of axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(9):703-713.
[12] SAIJILAFU, HUR EM, LIU CM, et al. PI3K-GSK3 signalling regulates mammalian axon regeneration by inducing the expression of Smad1. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2690.
[13] ABE N, CAVALLI V. Nerve injury signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008;18(3):276-283.
[14] CHOI J, KIM JH, JANG JW, et al. Decellularized sciatic nerve matrix as a biodegradable conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(10):1796-1803.
[15] CARLÉN M, MELETIS K, BARNABÉ-HEIDER F, et al. Genetic visualization of neurogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006; 312(15):2851-2859.
[16] CONSIGLIO A, GRITTI A, DOLCETTA D, et al. Robust in vivo gene transfer into adult mammalian neural stem cells by lentiviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(41): 14835-14840.
[17] TASHIRO A, ZHAO C, GAGE FH. Retrovirus-mediated single-cell gene knockout technique in adult newborn neurons in vivo. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(6):3049-3055.
[18] LIU K, LU Y, LEE JK, et al. PTEN deletion enhances the regenerative ability of adult corticospinal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(9):1075-1081.
[19] XI F, XU RJ, XU JH, et al. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulates mammalian axon growth by affecting F-actin length in growth cone. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23053-23065.
[20] HIRAKAWA M, MCCABE JT, KAWATA M. et al. Time-related changes in the labeling pattern of motor and sensory neurons innervating the gastrocnemius muscle, as revealed by the retrograde transport of the cholera toxin B subunit. Cell Tissue Res. 1992;267(3):419-427.
[21] BARNABÉ-HEIDER F, MELETIS K, ERIKSSON M, et al. Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by in vivo electroporation. Nat Methods. 2008;5(2):189-196.
[22] WEAVER JC. Electroporation in cells and tissues: A biophysical phenomenon due to electromagnetic fields. Radio Science.1995;30(1):205-221.
[23] TAMURA T, NISHI T, GOTO T, et al. Intratumoral delivery of interleukin 12 expression plasmids with in vivo electroporation is effective for colon and renal cancer. Hum Gene Ther. 2001; 12(10):1265-1276.
[24] KISHIDA T, ASADA H, SATOH E, et al. In vivo electroporation-mediated transfer of interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 genes induces significant antitumor effects against melanoma in mice. Gene Ther. 2001;8(16): 1234-1240.
[25] PAVSELJ N, BREGAR Z, CUKJATI D, et al. The course of tissue permeabilization studied on a mathematical model of a subcutaneous tumor in small animals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2005;52(8):1373-1381.
[26] LOTURCO J, MANENT JB, SIDIQI F. New and improved tools for in utero electroporation studies of developing cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19 Suppl 1:i120-125.
[27] DUAN RS, LIU PP, XI F, et al. Wnt3 and Gata4 regulate axon regeneration in adult mouse DRG neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(2):246-252.
[28] MA JJ, XU RJ, QI SB, et al. Regulation of adult mammalian intrinsic axonal regeneration by NF-κB/STAT3 signaling cascade. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):22517-22528.
[29] 刘颖,周玮,熊正爱,等.不可逆性电穿孔致山羊肝脏组织凋亡与坏死的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志, 2011,36(4): 356-360.
[30] 姚陈果,孙才新,米彦,等.陡脉冲对恶性肿瘤细胞不可逆性电击穿的实验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2004,23(1): 92-97.
[31] 梁冰,牛立志,曾健滢,等.不可逆电穿孔消融兔胆囊侧肝脏病理学观察[J].介入放射学杂志,2014,23(4):320-324.
[32] 俞允.基于电穿孔技术的活细胞表面增强拉曼光谱研究[D].福州:福建师范大学,2011.
[33] STEWARD O, ZHENG B, BANOS K, et al. Response to: Kim et al. "axon regeneration in young adult mice lacking Nogo-A/B." Neuron 38, 187-199. Neuron. 2007;54(2): 191-195.
[34] SAIJILAFU, HUR EM, ZHOU FQ. Genetic dissection of axon regeneration via in vivo electroporation of adult mouse sensory neurons. Nat Commun. 2011;2:543.
|