中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 99-105.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1858
釉原蛋白羧基末端肽加速细胞周期促进成釉细胞系ALC细胞增殖
刘 敏1,王睿捷1,宋丹阳1,杨 随1,谭 陶2,王 磊1,王衣祥3
- 北京大学口腔医院,1修复科,3中心实验室,北京市 100081;2北京大学首钢医学院口腔科,北京市 100144
The C-terminus of the amelogenin peptide promotes the proliferation of ALC ameloblasts through accelerating cell cycle
Liu Min1, Wang Ruijie1, Song Danyang1, Yang Sui1, Tan Tao2, Wang Lei1, Wang Yixiang3
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, 3Clinical Laboratory, Peking University Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Peking University Shougang Hospital, Beijing 100144, China
摘要:

文题释义:
釉原蛋白羧基末端肽:是由牙齿发育过程中成釉细胞表达的基质金属蛋白酶20水解全长釉原蛋白产生的,其具有调控骨髓间充质干细胞和牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖和分化的作用。
成釉细胞系ALC细胞:ALC细胞系是由Akira Nakata从新生小鼠牙胚中分离培养建立的成釉细胞系,表达成釉细胞特异性基因釉原蛋白、釉丛蛋白、釉蛋白,用于体外研究成釉上皮细胞分化和功能。
背景:釉原蛋白羧基末端肽(C-terminus of the amelogenin peptide,AMG-CP)作为一种小分子内源性短肽,在物种间的序列高度保守,提示其在牙齿发育过程中参与重要的生理过程。有研究表明AMG-CP对成牙骨质细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、牙周膜成纤维细胞的增殖分化有调控作用,但是AMG-CP对成釉细胞生物学功能的影响尚未见报道。
目的:探究不同质量浓度AMG-CP对成釉细胞系ALC细胞增殖的影响及相关机制。
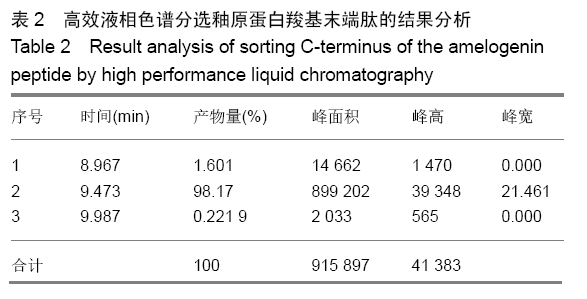
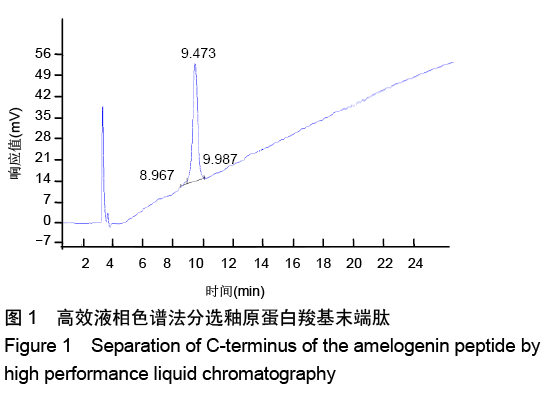
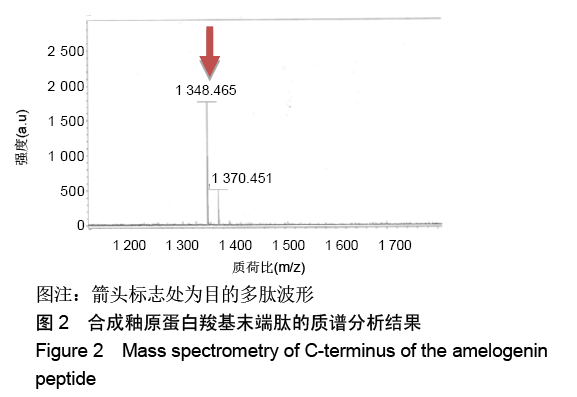
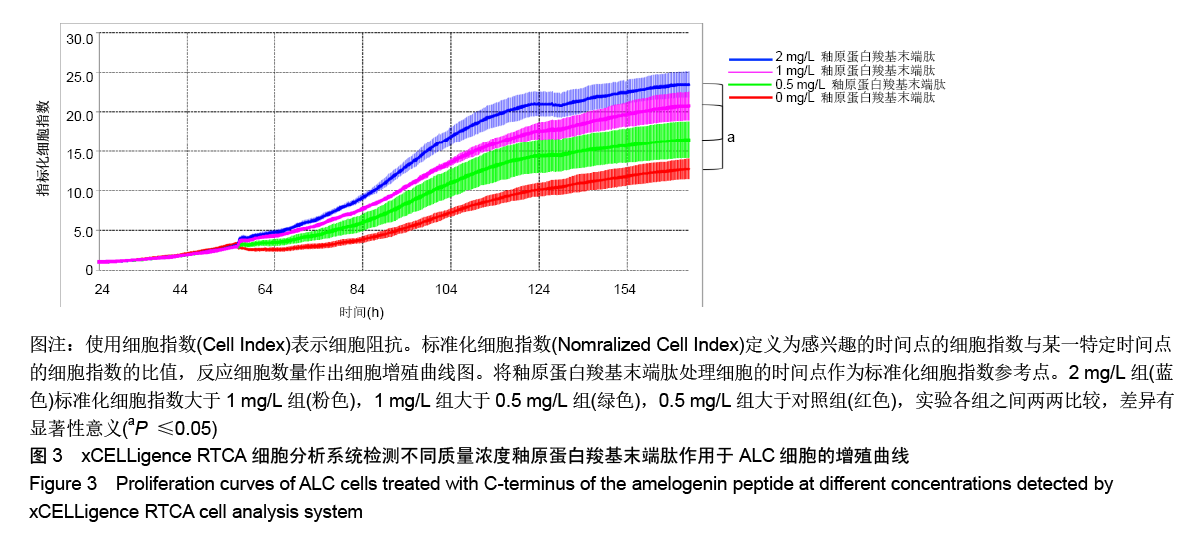
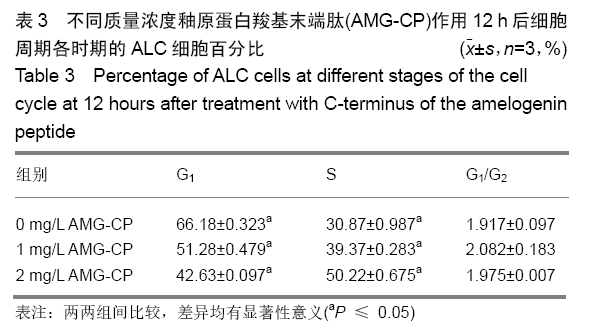
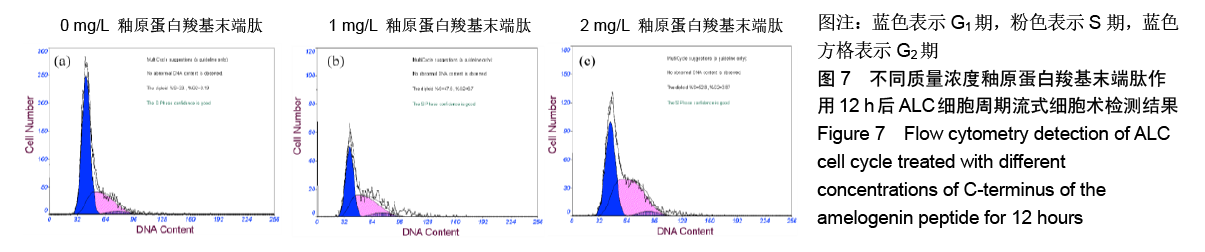
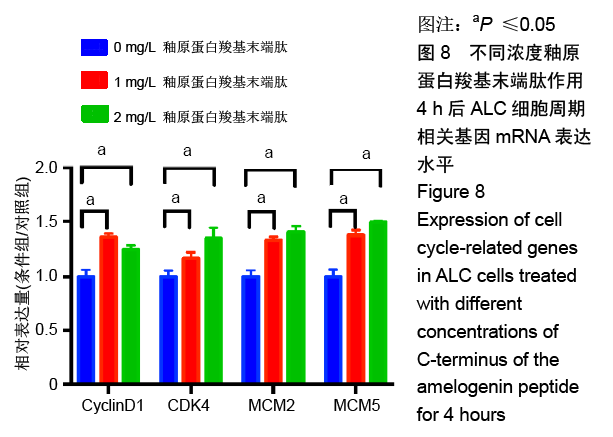
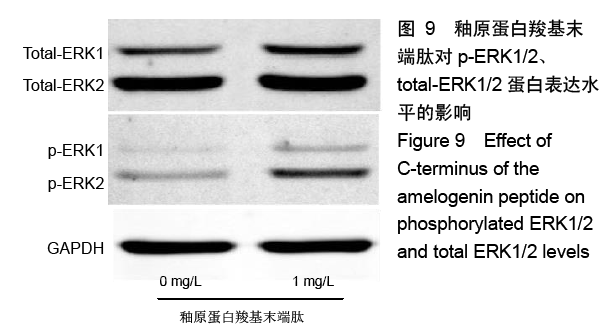
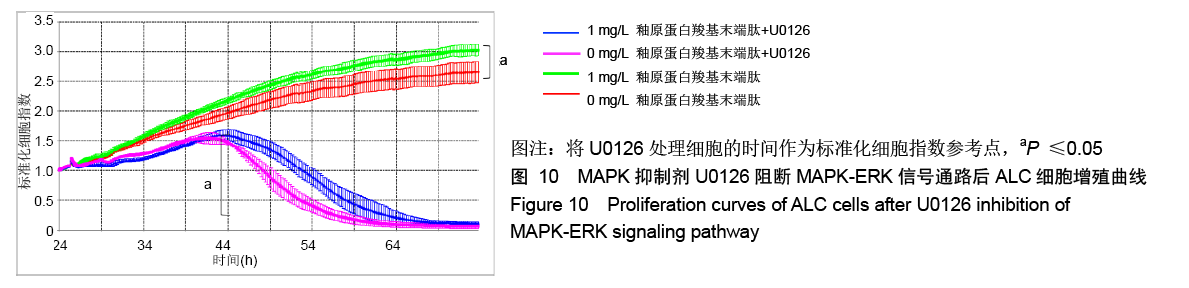
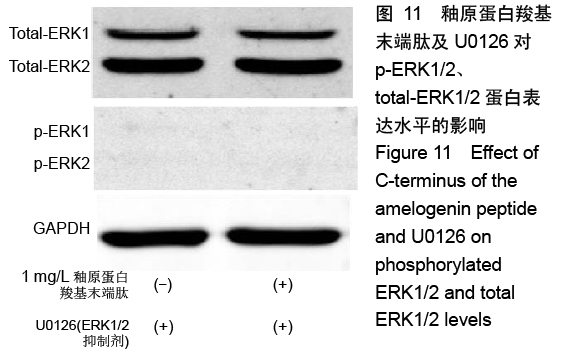
方法:人工合成并通过液相色谱和质谱检测AMG-CP合成情况。使用xCELLigence RTCA实时细胞分析系统观察0,0.5,1,2 mg/L AMG-CP对ALC细胞增殖的影响。流式细胞仪检测0,1,2 mg/L AMG-CP对ALC细胞周期的影响。Real-time PCR检测0,1,2 mg/L AMG-CP对ALC细胞的细胞周期蛋白Cyclin D1、CDK4、MCM2、MCM5 mRNA表达水平的影响。Western blot检测0,1 mg/L AMG-CP对ALC细胞表达细胞增殖相关通路中p-ERK1/2、total-ERK1/2表达水平的影响。利用MAPK-ERK1/2通路抑制实验,在ERK阻断剂U0126作用下阻断ERK1/2磷酸化,检测AMG-CP对ALC细胞增殖能力的影响。
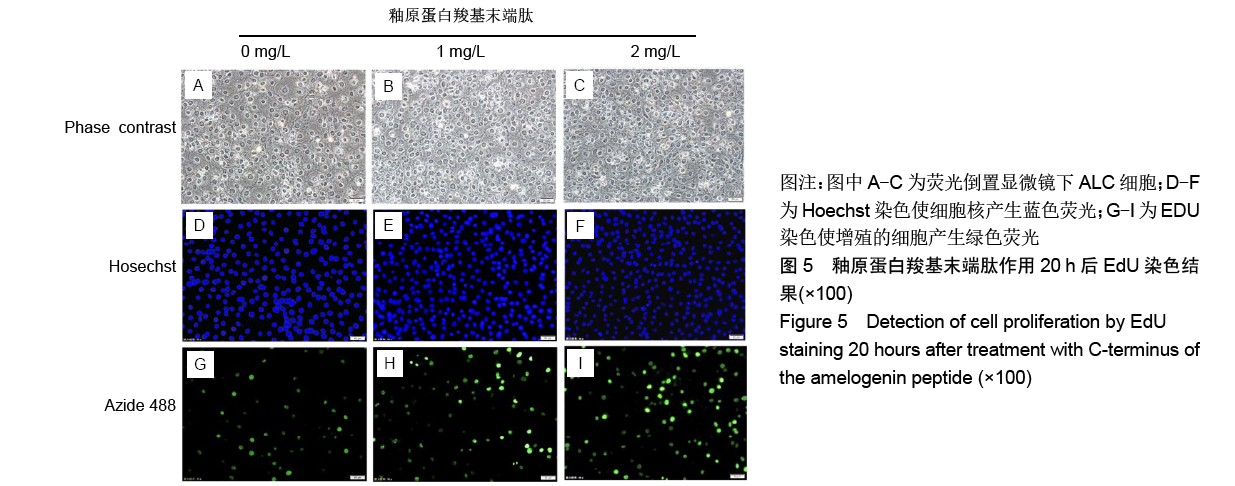
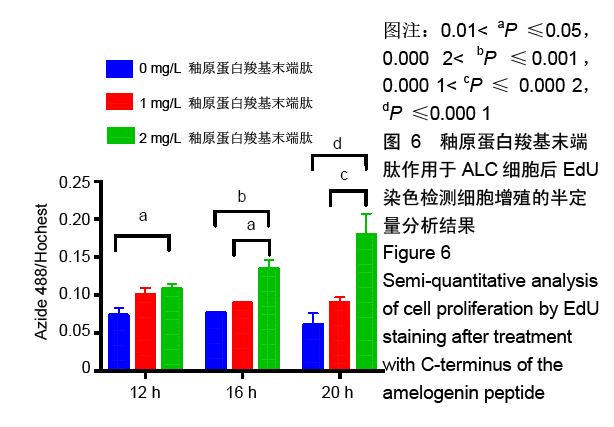
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,AMG-CP促进ALC细胞增殖,群体倍增时间降低,并存在浓度梯度依赖性;②与对照组比较,AMG-CP具有加速细胞周期的作用;③与对照组比较,AMG-CP可以上调细胞周期相关基因Cyclin D1、CDK4、MCM2、MCM5的表达;④与对照组比较,AMG-CP可以上调p-ERK1/2表达,激活MAPK-ERK1/2信号通路;⑤U0126抑制MAPK-ERK1/2通路激活后,AMG-CP失去对ALC细胞促增殖作用;⑥以上结果证实AMG-CP可以激活MAPK-ERK1/2通路,加速细胞周期,进而促进ALC细胞增殖,提示AMG-CP具有促进成釉细胞增殖的潜能。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4338-4123(刘敏)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: