| [1] Mundy GR. Metastasis to bone: Causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(8):584-593.[2] Kumar N, Gupta B. Global incidence of primary malignant bone tumors. Curr Orthop Pract. 2016;27(5):530-534.[3] Redondo A, Bague S, Bernabeu D, et al. Malignant bone tumors (other than Ewing's): clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up by Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas (GEIS). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(6):1113-1131.[4] Saracino R, Luciano R, Battafarano G, et al. Nanoparticles-Based Treatment for Bone Metastasis. Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(3): 303-310.[5] He X, Cao H, Wang H, et al. Inflammatory Monocytes Loading Protease-Sensitive Nanoparticles Enable Lung Metastasis Targeting and Intelligent Drug Release for Anti-Metastasis Therapy. Nano Lett. 2017;17(9):5546-5554.[6] Zhao K, Li D, Xu W, et al. Targeted hydroxyethyl starch prodrug for inhibiting the growth and metastasis of prostate cancer. Biomaterials. 2017;116:82-94.[7] Maeda H. Polymer therapeutics and the EPR effect. J Drug Target. 2017;25(9-10):781-785.[8] Li C, Xu W, Ding J, et al. Micellization of Antineoplastic Agent to Significantly Upregulate Efficacy and Security. Macromol Biosci. 2015; 15(3):328-341[9] Ding J, Li C, Zhang Y, et al. Chirality-mediated polypeptide micelles for regulated drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:346-55[10] Zhang FW, Zhang SY, Pollack SF, et al. Improving Paclitaxel Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of PEGylated Polyphosphoester- Based Nanocarriers. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(5):2056-2066[11] Abrahamse H, Kruger CA, Kadanyo S, et al. Nanoparticles for Advanced Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017;35(11):581-588.[12] Dang J, He H, Chen D, et al. Manipulating tumor hypoxia toward enhanced photodynamic therapy (PDT). Biomater Sci. 2017;5(8): 1500-1511.[13] Wang C, Cai X, Zhang J, et al. Trifolium-like Platinum Nanoparticle- Mediated Photothermal Therapy Inhibits Tumor Growth and Osteolysis in a Bone Metastasis Model. Small.2015;11(17):2080-2086.[14] Duchi S, Sotgiu G, Lucarelli E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as delivery vehicle of porphyrin loaded nanoparticles: Effective photoinduced in vitro killing of osteosarcoma. J Control Release.2013;168(2):225-237.[15] Mura S, Nicolas J, Couvreur P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat Mater. 2013;12(11):991-1003.[16] Li X, Zhao Y, Liu P, et al. Senegenin Inhibits Hypoxia/ Reoxygenation-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis by Upregulating RhoGDIα. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;52(3):1561-1571.[17] Chen J, Ding J, Zhang Y, et al. Polyion complex micelles with gradient pH-sensitivity for adjustable intracellular drug delivery. Polym Chem. 2015;6(3):397-405.[18] Xu W, Ding J, Xiao C, et al. Versatile preparation of intracellular-acidity-sensitive oxime-linked polysaccharide-doxorubicin conjugate for malignancy therapeutic. Biomaterials. 2015;54:72-86.[19] Sun D, Ding J, Xiao C, et al. Preclinical Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Acid-Sensitive PEGylated Doxorubicin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(23):21202-21214.[20] Feron O. Pyruvate into lactate and back: From the Warburg effect to symbiotic energy fuel exchange in cancer cells. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92(3):329-333.[21] Fan XL, Cai GP, Zhu LL, et al. Efficacy and safety of ifosfamide-based chemotherapy for osteosarcoma: a meta-analysis. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2015;9:5925-5932.[22] Chen B, Yang JZ, Wang LF, et al. Ifosfamide-loaded poly (lactic-co- glycolic acid) PLGA-dextran polymeric nanoparticles to improve the antitumor efficacy in Osteosarcoma. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:752.[23] Aluri S,Janib SM, Mackay JA. Environmentally responsive peptides as anticancer drug carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(11):940-52.[24] Maciel D, Figueira P, Xiao S, et al. Redox-responsive alginate nanogels with enhanced anticancer cytotoxicity. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14(9):3140-3146.[25] Fleige E, Quadir MA, Haag R. Stimuli-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for the controlled transport of active compounds: Concepts and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(9):866-884.[26] Han HJ, Valdeperez D, Jin Q, et al. Dual Enzymatic Reaction-Assisted Gemcitabine Delivery Systems for Programmed Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Acs Nano. 2017;11(2):1281-1291.[27] Mu CF, Shen JL, Liang J, et al. Targeted drug delivery for tumor therapy inside the bone marrow. Biomaterials. 2018;155:191-202.[28] Chae YK, Pan AP, Davis AA, et al. Path toward Precision Oncology: Review of Targeted Therapy Studies and Tools to Aid in Defining "Actionability" of a Molecular Lesion and Patient Management Support. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(12):2645-2655.[29] Ryu TK, Kang RH, Jeong KY, et al. Bone-targeted delivery of nanodiamond-based drug carriers conjugated with alendronate for potential osteoporosis treatment. J Control Release. 2016;232: 152-160.[30] Morton SW, Shah NJ, Quadir MA, et al. Osteotropic therapy via targeted layer-by-layer nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(6): 867-75.[31] Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Munshi NC, et al. Focus on multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell. 2004;6(5):439-444.[32] Wu WC, Fernández-Seara M, Detre JA, et al. A theoretical and experimental investigation of the tagging efficiency of pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med. 2007; 58(5):1020-1027.[33] Pan D, Pham CTN, Weilbaecher KN, et al. Contact-facilitated drug delivery with Sn2 lipase labile prodrugs optimize targeted lipid nanoparticle drug delivery. Wires Nanomed Nanobi. 2016;8(1):85-106.[34] Kuehl WM. Mouse models can predict cancer therapy. Blood. 2012; 120(2):238-240.[35] Ashley JD, Stefanick JF, Schroeder VA, et al. Liposomal carfilzomib nanoparticles effectively target multiple myeloma cells and demonstrate enhanced efficacy in vivo. J Control Release. 2014;196:113-121.[36] Hassan SE, Bekarev M, Kim MY, et al. Cell surface receptor expression patterns in osteosarcoma. Cancer. 2012;118(3):740-749.[37] Van Driel M, Van Leeuwen J. Cancer and bone: A complex complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561:159-166.[38] Levine RM, Kokkoli E. Dual-ligand alpha(5)beta(1) and alpha(6)beta(4) integrin targeting enhances gene delivery and selectivity to cancer cells. J Control Release. 2017;251:24-36.[39] Rejinold NS, Baby T, Chennazhi KP, et al. Multi Drug Loaded Thermo-Responsive Fibrinogen-graft-Poly(N-vinyl Caprolactam) Nanogels for Breast Cancer Drug Delivery. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(3):392-402.[40] Kolter M, Ott M, Hauer C, et al. Nanotoxicity of poly(n-butylcyano- acrylate) nanoparticles at the blood–brain barrier, in human whole blood and in vivo. J Control Release. 2015;197:165-179.[41] Oh SS, Lee BF, Leibfarth FA, et al. Synthetic aptamer-polymer hybrid constructs for programmed drug delivery into specific target cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(42):15010-15015.[42] Kanapathipillai M, Brock A, Ingber DE. Nanoparticle targeting of anti-cancer drugs that alter intracellular signaling or influence the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014;79-80:107-118.[43] Wicki A, Witzigmann D, Balasubramanian V, et al. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: Challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J Control Release. 2015;200:138-157.[44] Lorscheidt S, Lamprecht A. Safety assessment of nanoparticles for drug delivery by means of classic in vitro assays and beyond. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(11):1545-1558.[45] Yang Q, Parker CL, Mccallen JD, et al. Addressing challenges of heterogeneous tumor treatment through bispecific protein-mediated pretargeted drug delivery. J Control Release. 2015;220(Pt B):715-726.[46] Cheng Z, Al Zaki A, Hui JZ, et al. Multifunctional nanoparticles: cost versus benefit of adding targeting and imaging capabilities. Science. 2012;338(6109):903-910.[47] Li CY, Zhang YJ, Chen GC, et al. Engineered Multifunctional Nanomedicine for Simultaneous Stereotactic Chemotherapy and Inhibited Osteolysis in an Orthotopic Model of Bone Metastasis. Adv Mater. 2017;29(13).[48] Wang YT, Yang J, Liu HM, et al. Osteotropic peptide-mediated bone targeting for photothermal treatment of bone tumors. Biomaterials. 2017;114:97-105.[49] Tan YF, Chandrasekharan P, Maity D, et al. Multimodal tumor imaging by iron oxides and quantum dots formulated in poly (lactic acid)-D- alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):2969-2978. |
.jpg)
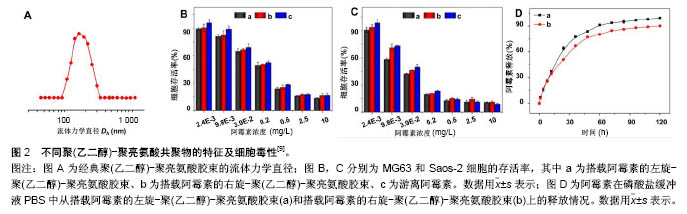
.jpg)
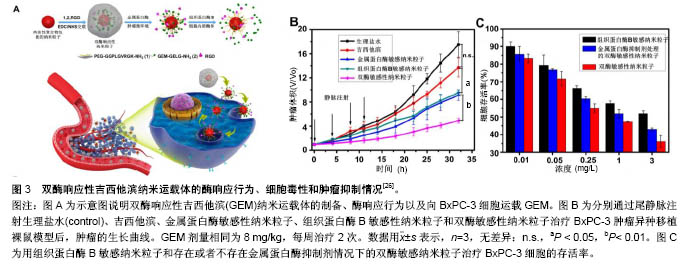
.jpg)