Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (14): 2200-2205.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.14.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transplantation of embryonic neuroepithelial stem cells into the brain of Parkinson disease rats
Wang Jia-zeng
- Shandong Medical Collage, Linyi 276002, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2014-01-23Online:2014-04-02Published:2014-04-02 -
About author:Wang Jia-zeng, Master, Associate professor, Shandong Medical Collage, Linyi 276002, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:A Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program, No. J10LF58
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jia-zeng. Transplantation of embryonic neuroepithelial stem cells into the brain of Parkinson disease rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(14): 2200-2205.
share this article
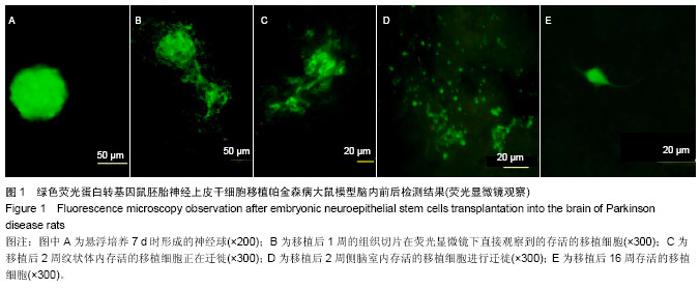
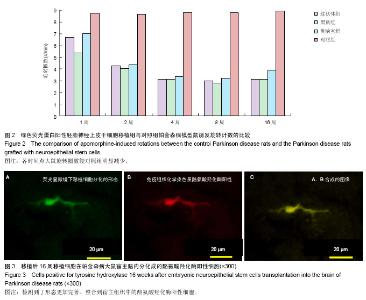
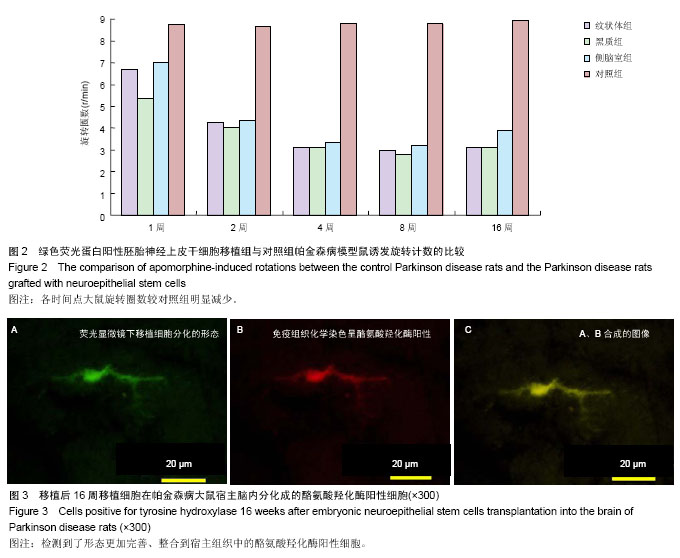
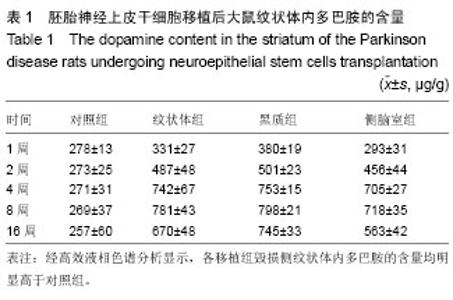
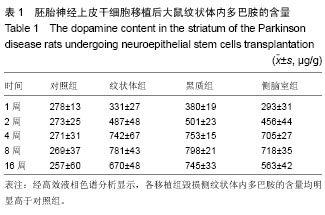
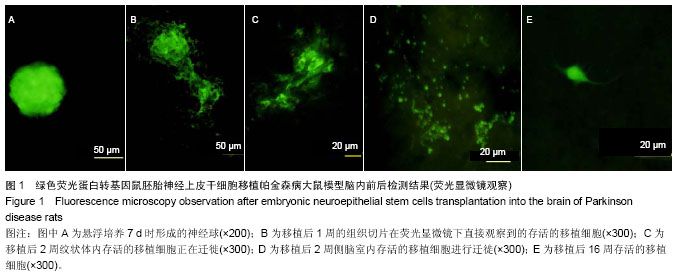
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠80只,分为4组,实验过程无脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 大鼠旋转行为检测结果 移植后1,2,4,8,16周的旋转行为检测结果显示,移植后1周,3个细胞移植组动物的旋转行为即有改善,以黑质内移植组的改善最为明显;2周时改善效果明显,4周时实验组动物的旋转圈数明显减少,移植后8,16周时,移植组动物的旋转行为都明显低于对照组动物,3个移植组动物间的旋转圈数也有差异(图2)。方差分析显示实验组与对照组间的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。 2.3 移植细胞检测结果 荧光显微镜直接观察:绿色荧光蛋白转基因鼠胚胎神经上皮干细胞移植到帕金森病大鼠模型的脑内,在移植后1周的组织切片上,大部分的移植细胞在移植区内成团分布,这些细胞均可激发出明亮的绿色荧光(图1B)。移植后2周移植细胞已经开始从移植区向周围扩散,纹状体内的移植细胞主要向黑质方向迁徙(图1C),植入侧脑室的供体细胞或贴附在侧脑室壁上,或沿室管膜分布,少量细胞已迁徙至邻近的脑实质中(图1D);而移植到黑质内的供体细胞则多向周边尤其是纹状体方向扩散,且距离较小。移植后4周的移植区内,有些移植细胞已具备成熟细胞的形态特征,胞体呈椭圆形,突起较长,与其他细胞间形成了密切接触。移植后8周组织切片中的移植细胞形态更加完善,突起更长;在移植后16周组织切片的移植区以外可见到迁移出的成熟细胞(图1E),表明移植细胞已整合到宿主脑内。 免疫组织化学染色:经免疫组织化学染色,在移植后4周以后的组织切片中均检测到了既能激发出绿色荧光,又呈酪氨酸羟化酶阳性的细胞,这些细胞的数量随术后时间的延长逐渐增多,在移植后16周的组织切片中检测到了形态更加完善、整合到宿主组织中的酪氨酸羟化酶阳性细胞(图3)。"
| [1] Bower JH, Maraganore DM, McDonnell SK, et al.Incidence and distribution of parkinsonism in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-1990. Neurology.1999;52: 1214-1220. [2] de Rijk MC, Breteler MM, Graveland GA, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the elderly: the Rotterdam Study. Neurology.1995;45: 2143-46. [3] Doty RL, Bromley SM, Stern MB.Olfactory testing as an aid in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: development of optimal discrimination criteria. Neurodegeneration.1995;4: 93-97. [4] Iranzo A, Santamaría J, Rye DB, et al. Characteristics of idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder and that associated with MSA and PD. Neurology.2005;65: 247-252. [5] Andrew JL, John H,Tamas R. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2009;373: 2055-2066. [6] Paísan-Ruíz C, Jain S, Evans EW, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron.2004;44: 595-600. [7] Healy DG, Falchi M, O-Sullivan SS, et al. Phenotype, genotype, and worldwide genetic penetrance of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol.2008;7: 583-590. [8] Ozansoy M, Ba?ak AN.The Central Theme of Parkinson’s Disease: α-Synuclein.Mol Neurobiol.2013;47:460-465. [9] Tanner CM.Is the cause of Parkinson’s disease environmental or hereditary? Evidence from twin studies. Adv Neurol.2003; 91:133-142. [10] Taylor KS, Counsell CE, Gordon JC, et al. Screening for undiagnosed parkinsonism among older people in general practice. Age Ageing.2005;34: 501-504. [11] Dick FD, De PG, Ahmadi A, et al.Environmental risk factors for Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: the Geoparkinson study. Occup Environ Med.2007; 64: 666-672. [12] [Clark IE,Dodson MW,Jiang C,et al.Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature.2006; 441: 1162-1166. [13] Park J, Lee SB, Lee S, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature.2006; 441: 1157-1161. [14] Olanow CW, McNaught KS. Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord.2006; 21: 1806-1823. [15] Allam, MF,Campbell MJ,Hofman A,et al.Smoking and Parkinson’s disease: systematic review of prospective studies. Mov Disord, 2004; 19: 614-621. [16] Hernán MA,Zhang SM,Rueda-deCastro AM,et al. Cigarette smoking and the incidence of Parkinson’s disease in two prospective studies. Ann Neurol.2001; 50: 780-786. [17] Ascherio A, Weisskopf MG, O’Reilly EJ.Co?ee consumption, gender, and Parkinson’s disease mortality in the cancer prevention study II cohort: the modifying e? ects of estrogen. Am J Epidemiol.2004; 160: 977-984.. [18] Ascherio A, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA, et al. Ca?eine, postmenopausal estrogen, and risk of Parkinson‘s disease. Neurology.2003; 60: 790-795. [19] Evans AH, Lawrence AD,Potts J.Relationship between impulsive sensation seeking traits, smoking, alcohol and ca? eine intake, and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.2006; 77: 317-321. [20] Sundberg, Bogetofte, Lawson et al.Improved Cell Therapy Protocols for Parkinson’s Disease Based on Differentiation Ef?ciency and Safety of hESC-, hiPSC-, and Non-Human Primate iPSC-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons. stem cells. 2013;31:1548-1562. [21] Yan Z, Maosheng S, Hongjun L,et al.Recovery of behavioral symptoms in hemi-parkinsonian rhesus monkeys through combined gene and stem cell therapy. Cytotherapy. 2013; 15(4):467-480. [22] Katzenschlager R, Head J, Schraq A, et al.Fourteen-year ? nal report of the randomized PDRG-UK trial comparing three initial treatments in PD. Neurology. 2008;71: 474-480. [23] Fahn S, Oakes D, Shoulson I, et al. Levodopa and the progression of Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med.2004;351: 2498-508. [24] Hely MA, Reid WG, Adena MA, et al. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord.2008; 23: 837-844. [25] Kim JH, Auerbach JM, Rodríguez-Gómez JA, et al.Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature. 2002; 418: 50-56. [26] Ben-Hur T, Idelson M, Khaner H, et al.Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors improves behavioral deficit in Parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells.2004; 22: 1246-1255. [27] Kurowska Z, Englund E, Widner H, et al. Signs of Degeneration in 12–22-Year Old Grafts of Mesencephalic Dopamine Neurons in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2011;1(1):83-92. [28] Pawitan JA. Prospect of cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Anat Cell Biol. 2011;44:256-264. [29] Anders B, Kordower JH. Cell Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: What Next?. Movement Disorders.2013;28(1):110-115. [30] Duke CM, Taylor HS.Stem cells and the reproductive system: Historical perspective and future directions. Maturitas. 2013; 6036(10):1-6. [31] Seung UK, Hong JL, Yun BK. Neural stem cell-based treatment for neurodegenerative diseases. Neuropathology. 2013;33: 491–504. [32] Sun J, Gao Y, Yang L, et al. Neural-tube-derived neuroepithelial stem cells: a new transplant resource for Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport. 2007;18(6):543-547. [33] 王家增.GFP转基因鼠胚胎神经上皮干细胞的体外培养[J]. 山东大学学报:医学版, 2009,47(9):49-53. [34] 郑敏,王亚平,裴雪涛,等.神经干细胞移植对帕金森病模型大鼠的治疗作用[J].基础医学与临床,2007,27(8):841-845. [35] Serra PA, Esposito G, Enrico P, et al. Manganese increases L-DOPA autooxidation in the striatum of the freelymoving rat: potential implications to L-DOPA long-term therapy of Parkinson’s disease.Br J Pharmacol.2000; 130(4): 937-945. [36] 王家增. 携带绿色荧光蛋白基因的神经上皮干细胞移植治疗帕金森病[J].中国组织工程研究,2012;16(6):1080-1084. [37] Jinhao S, Qing G, Katherine M, et al.Dopaminergic differentiation of grafted GFP transgenic neuroepithelial stem cells in the brain of a rat model of parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2007;420(5): 23-28. [38] 王普清,孙圣刚,张允健,等黑质内注射脂多糖对多巴胺能神经元和小胶质细胞活性的影响[J].中国康复,2008;23(6):380-382. [39] Caplan AI.Why are MSCs therapeutic? New data: new insight. J Pathol.2009;217(2): 318-324. [40] Hegarty SV, Sullivan AM, O'Keeffe GW. Midbrain dopaminergic neurons: A review of the molecular circuitry that regulates their development. Dev Biol. 2013;379(2):123-38. [41] Shan X,Chi L,Bishop M,et al.Enhanced de novo neurogenesis and dopaminergic neurogenesis in the substantia nigra of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson's disease-like mice. Stem Cells.2006;24(5) : 1280-1287. [42] van den Berge SA, van Strien ME, Hol EM. Resident adult neural stem cells in Parkinson’s disease-The brain’s own repair system?.Eur J Pharmacol.2013;4:058-069. [43] Nishino H, Hida H, Takei N, et al. Mesencephalic neural stem (progenitor) cells develop to dopaminergic neurons more strongly in dopamine-depleted striatum than in intact striatum. Exp Neurol.2000;164(1):209-214. [44] Hurelbrink CB, Armstrong RJ, Dunnett SB, et al. Neural cells from primary human striatal xenografts migrate extensively in the adult rat CNS. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15(7):1255-1266. [45] Tamaki S, Eckert K, He D, et al. Engraftment for sorted/expanded human central nervous system stem cells from fetal brain. J Neurosci Res.2002;69(6):976-986. [46] Fei L, Jiang CC, Feng LY, et al.Transplantation of primary cultured embryonic mesencephalic neural precursor cells for treating Parkinsonian rats.Neural Regen Res.2006;1(1):6-9. |
| [1] | He Lin, Wu Xi, He Song, Yang Sen. Hydrophilicity and cell adhesion of hydroxyapatite bioceramics after the coating of polydopamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3540-3544. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiaobo, Zhang Jie, Sun Yu. Future hot spots for cartilage repair: laminin promotes stem cell proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 141-145. |
| [3] | Wei Renyue, Li Xuechun, Li Yan, Yu Yang, Zhang Yu, Liu Zhonghua. A serum-free monolayer method for differentiation of porcine induced pluripotent stem cells into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4971-4978. |
| [4] |
Cao Sucheng, Xu Xiaofeng, Chen Qi, Lu Hao, Wang Zhe, Zhang Rui, Wang Yao, Zhang Zhijian, Yang Wenjing.
Sonic hedgehog-polydopamine-fibrin scaffold promotes recovery of spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4567-4572. |
| [5] | Ma Jingyi, Yang Wenjiang, Li Yuandi, Huang Youjiao, Gao Jie, Li Hong, Hu Rong, Su Min. Expression of autoimmune regulator during differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into thymic epithelial progenitor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3994-3999. |
| [6] | Zhao Jing. Effects of Tai Chi Chuan on the changes of bone mineral density of perimenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 176-180. |
| [7] | Liu Zu, Han Shen, Li Yaxiong, Li Kunlin, Zhang Yayong, Jiang Lihong. Applications, roles and problems of exosomes derived from different stem cells in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3063-3070. |
| [8] | Sun Li, Zong Yanyan, Wei Jianfeng. Comparison of two passage methods affecting the transfection efficiency of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 72-76. |
| [9] | Gao Hua1, 2, Li Yanxia1, Wang Dan1, Yang Xinling1 . Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 447-452. |
| [10] | Shen Mengjie, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Application potential of different origin stem cells in oral bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 4068-4074. |
| [11] | Ren Chao1, Ji Yongqiang2, Guan Lina3. Cerebrospinal fluid promotes neuron-like differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2770-2775. |
| [12] | Chen Li, Hu Lan, Peng Yanan, Yang Liu, Shen Hui, Wang Tan, Zhao Zhenqiang. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into dopaminergic neurons: security risk for heterogeneity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 118-124. |
| [13] | Wei Han-qing, Pei Yi-jin, Wang Dan-dan, Jiang Yang, Wang Chun, Li Hong-mei. Effects of sustained hypoxia on proliferation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts and preparation of feeder layers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1450-1456. |
| [14] | Ke Min-xia, Ji Meng, Wang Hao, Hong Dan-ping, Wu Yue-hong, Qi Nian-min. Stem cell models for commercialization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 766-773. |
| [15] | Zhou Li, Tian Bin, Ji Yuan-hong, Zhou Zheng, Wei Xiao-dan. Stem cells for ophthalmic diseases: recovery from damage and functional reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4743-4748. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||