Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 447-452.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0595
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide
Gao Hua1,2, Li Yanxia1, Wang Dan1, Yang Xinling1
- (1Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Neurology, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
-
Received:2018-08-07Online:2019-01-28Published:2021-04-28 -
Contact:Yang Xinling, MD, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Gao Hua, MD, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Neurology, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U1503222 (to YXL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Hua, Li Yanxia, Wang Dan, Yang Xinling. Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 447-452.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
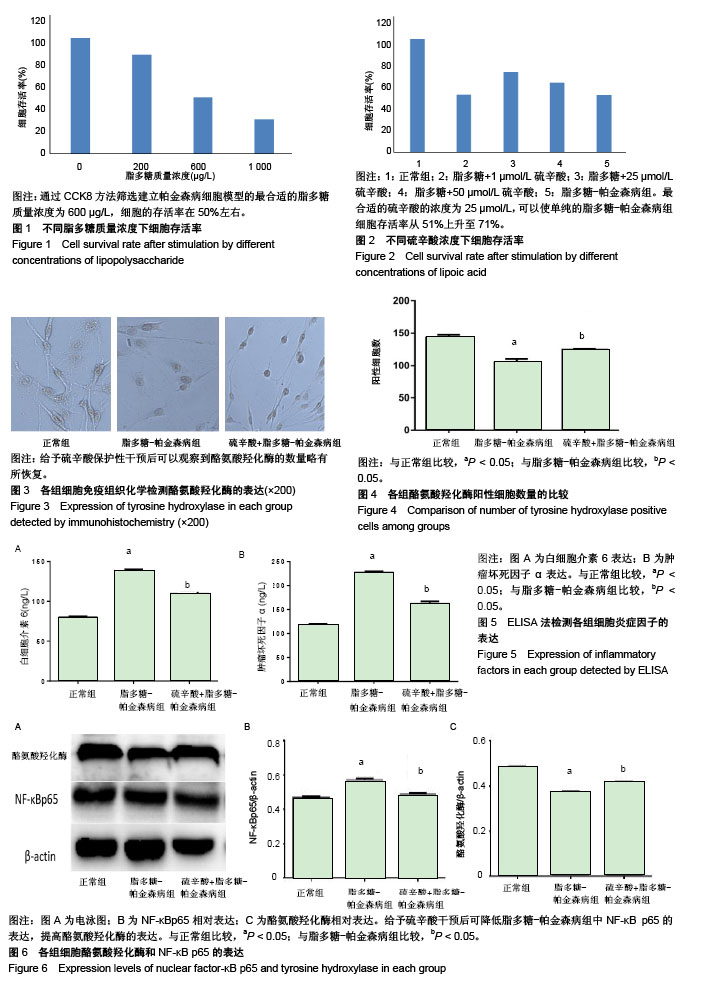
2.1 脂多糖诱导的帕金森病细胞模型的建立 在200,600,1 000μg/L不同脂多糖质量浓度下,其细胞存活率分别为85%,49%,30%,相对于未进行干预的细胞组为基准(100%,单纯加入CCK8检测)。通过CCK8方法筛选建立帕金森病细胞模型的最合适的脂多糖质量浓度为 600 μg/L,见图1,在此质量浓度下细胞的存活率在50%左右,故作为后续实验研究条件。 2.2 硫辛酸干预细胞模型的最佳浓度的测定 在确定了合适的脂多糖(600 μg/L)建造帕金森细胞模型的质量浓度后,在脂多糖-帕金森病模型之前给予硫辛酸进行保护性干预2 h后,在不同浓度(1,25和 50 μmol/L)采用CCK8方法检测其细胞存活率分别为51%,71%,61%,以未进行干预的细胞组为基准(100%,单纯加入CCK8检测),最合适的硫辛酸的浓度为25 μmol/L,在此浓度下,相对于 1 μmol/L和50 μmol/L,对细胞存活率有很好的保护作用,可以使单纯的脂多糖-帕金森病组细胞存活率从51%上升至71%,以此为最佳浓度,见图2。 2.3 各组细胞酪氨酸羟化酶的表达 可以看到表现胞浆为棕黄色的酪氨酸羟化酶的表达,细胞胞体略有缩小,突触更明显。PC12的细胞正常组中,酪氨酸羟化酶的阳性细胞数表现最为多。在给予脂多糖(600μg/L)建造的帕金森病细胞模型中,可以发现细胞活性部分被损害,脂多糖-帕金森病组中酪氨酸羟化酶的阳性细胞数减少,给予硫辛酸(25 μmol)保护性干预后可以观察到酪氨酸羟化酶的数量略有所恢复,将3组(每组包含有15个视野)的酪氨酸羟化酶阳性细胞数进行比较[(143±4),105±5),(124±1)个],差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3,4。 2.4 ELISA法检测各组细胞炎症因子表达 在正常细胞组、脂多糖-帕金森病组和硫辛酸+脂多糖-帕金森病组的3组细胞中,白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平在脂多糖-帕金森病组相对于正常细胞组明显增加,加入硫辛酸后可以抑制两者的产生,从而使其表达有所下降。即白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平在脂多糖+硫辛酸组中,相比较脂多糖-帕金森病组有所减少,但较正常细胞组仍有较高表达[白细胞介素6:(80.02±1.25),(138.10±2.11),(109.60±1.30) ng/L;肿瘤坏死因子α:(116.60±3.55),(228.00±2.12),(162.00±5.08) ng/L],3组间比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.5 Western blot检测各组NF-KBP65和酪氨酸羟化酶的表达 正常细胞的对照组中,酪氨酸羟化酶和NF-κB p65均有表达。以此为对照基线,在脂多糖-帕金森病组中NF-κB p65表达含量增加,同时促使酪氨酸羟化酶表达含量减少。给予硫辛酸干预后可降低脂多糖-帕金森病组中NF-κB p65的表达含量,提高的酪氨酸羟化酶的表达。但硫辛酸-脂多糖-帕金森病组中两者相对于正常细胞的对照组中,不能恢复正常状态。其两者的含量在3组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图6。"
| [1] Muldoon LL, Alvarez JI, Begley DJ, et al. Immunologic privilege in the central nervous system and the blood. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(1):13-21. [2] Jha MK, Suk K, G1ia. based biomarkers and their functional role in the CNS. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2013;10:43-63.[3] Gonz61ez H, Elgueta D, Montoya A, et al. Neuroimmune regulation of mieroglial activity involved in neuro-inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol. 2014;274:1-13. [4] Sveinbjornsdottir S. The clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2016;139:318. [5] He H, Wang S, Tian J, et al. Protective effects of 2, 3, 5, 4-tetra-hydroxystilbene-2-O-B-dglucoside in the MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of reactive of oxygen species mediated JNK, P38 and mitochondrial pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;767:175-182.[6] Benskey MJ, Perez RG, Manfredsson FP. The contribution of alpha synuclein to neuronal survival and function-implications for parkinson′s disease. J Neurochem. 2016;137(3):331-359. [7] Gallagher DA, Schapira AH. Etiopathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson′s disease. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(10):860-868. [8] Giordano S, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J. Autophagy as an essential cellular antioxidant pathway in neurodegenerative disease. Redox Biol. 2014;2(1):82-90. [9] Labandeira-Garcia JL, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Dominguez-Meijide A, et al. opamine-angiotensin interactions in the basal ganglia and their relevance for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2013;28(10): 1337-1342. [10] Borrajo A, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Diaz-Ruiz C, et al. Microglial TNF-alpha mediates enhancement of dopaminergic degeneration by brain angiotensin. Glia. 2014;62(1):145-157. [11] Hirsch EC, Vyas S, Hunot S. Neuroinflanunation in Parkinson's Disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011;18:85-64. [12] 杨丽娟,董军,陆大祥,等.姜黄素对脂多糖激活小胶质细胞条件培养基诱导损伤的海马神经元保护作用及机制[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010, 26(4):742-747.[13] 和青.LPS经鼻小鼠帕金森病模型的建立及Rho激酶靶点干预探讨[D].上海:复旦大学,2013.[14] Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, et al. Lipoicacid as a potential therapy for chronicdisease associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11(9):1135-1146. [15] 李艳花,和青,尉杰忠,等.硫辛酸对 脂多糖 诱导的帕金森病小鼠黑质多巴胺能神经元损伤的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2015,31(2): 201-206.[16] Zaitone SA, Abo-Eimatty DM, Shaalan AA. Acety1-L-carnitine and a-lipoicacid affect rotenone-induced damage in nigral dopaminergic neurons of rat brain implication for Parkinson’ s disease therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012;100(3): 347-360. [17] Müller U, Krieglstein J. Prolonged pretreatment with alpha-lipoic acid protects cultured neurons against hypoxic, glutamate-, or iron-induced injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995;15(4): 624-630. [18] Perez-Matos MC, Morales-Alvarez MC, Mendivil CO. Lipids: A Suitable Therapeutic Target in Diabetic Neuropathy? . J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:6943851. [19] Dong Y, Wang H, Chen Z. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Insulin Receptor and PI3K/Akt-Dependent Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015, 903186. [20] Kamarudin MN, Mohd Raflee NA, Hussein SS, et al. (R)-(+)-α-lipoic acid protected NG108-15 cells against H?O?-induced cell death through PI3K-Akt/GSK-3β pathway and suppression of NF-κβ-cytokines. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8: 1765-1780. [21] Kones R. Mitochondfial therapy for Parkinson’s disease: neuroprotective pharmaconutrition may be disease-modifying. Clin Pharmacol. 2010;2:185-198. [22] 马玲,周勇,王莉,等.硫辛酸减轻高尿酸血症大鼠氧化应激损伤[J].基础医学与临床,2015,35(8):1037-1041. [23] Rochette L, Ghibu S, Richard C, et al. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of alpha-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(1):114-125. [24] Kleinkauf-Rocha J, Bobermin LD, Machado PM, et al. Lipoicacid increases glutamate uptake, glutamine symhetase activity and glutathione content in C6 astrocyte cell line. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013;31(3):165-170. [25] [Papanas N, Ziegler D. Efficacy of α-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014;15(18):2721-2731. [26] Zhao L, Hu FX. Alpha-Lipoic acid treatment of aged type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with acute cerebral infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(23):3715-3719. [27] Saygin M, Asci H, Cankara FN, et al. The impact of high fructose on cardiovascular system: Role of alpha-lipoicacid. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015;35(2):194-204. [28] Hegazy SK, Tolba OA, Mostafa TM, et al. Alpha•lipoicacid improves subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatie patients with type 1 diabetes. Rev Diabet Stud. 2013;10(1):58-67. [29] Koriyama Y, Nakayama Y, Matsugo S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of lipoic acid through inhibition of GSK-3β in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells. Neurosci Res. 2013;77(1-2):87-96. [30] Jiang S, Zhu W, Li C, et al. α-Lipoic acid attenuates 脂多糖-induced cardiac dysfunction through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;16(1):100-107. [31] Ying Z, Xie X, Chen M, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid activates eNOS through activation of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015;64:28-35. [32] Liu SF, Malik AB. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol, Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(1):L622-L645. [33] Wu DC, Teismann P, Tieu K, et al. NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson′s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(10):6145-6150. [34] Zhang F, Qian L, Flood PM, et al. Inhibition of IkappaB kinase-beta protectsdopamine neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333(3):822-833. [35] Li Y, Ma QG, Zhao LH, et al. Effects of lipoic acid on immune function, the antioxidant defense system, and inflammation-related genes expression of broiler chickens fed aflatoxin contaminated diets. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5649-5662. [36] Kim HS, Kim HJ, Park KG, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits matrix metallop-roteinase-9 expression by inhibiting NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Exp Mol Med. 2001;39(1):106-113. [37] Li G, Fu J, Zhao Y, Ji K, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid exerts anti-inflammatory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat mesangial cells via inhibition of nuclear factor kappa b(NF-kappab) signaling pathway. Inflammation. 2015;38(2):510-519. [38] Koriyama Y, Nakayama Y, Matsugo S. et al Anti-inflammatory effects of lipoic acid through inhibition of GSK-3β in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells. Neurosci Res. 2013;77(1/2):87-96. [39] Li YH, He Q, Yu JZ, et al. Lipoic acid protects dopaminergic neurons in lps-induced parkinson′s disease model. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30(5):1-10. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||