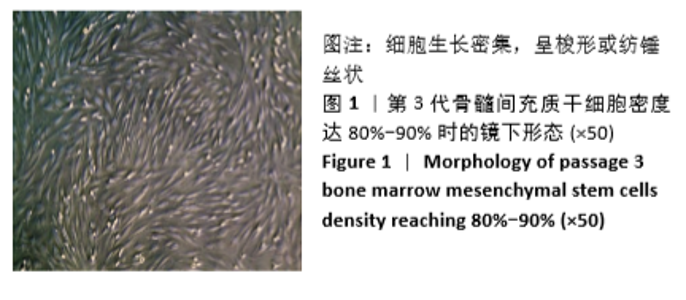
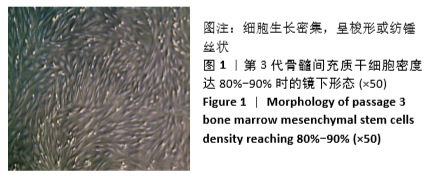
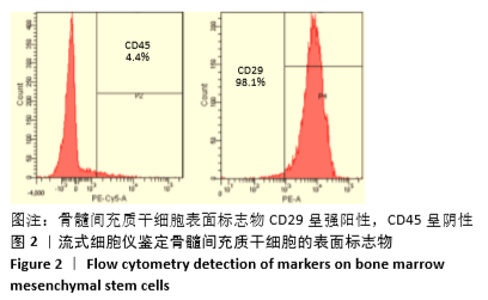
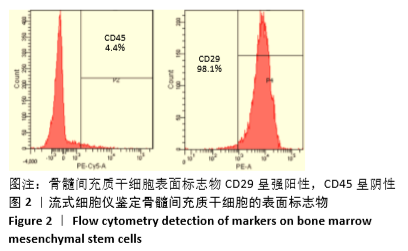
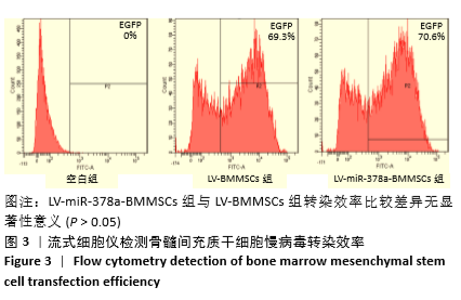
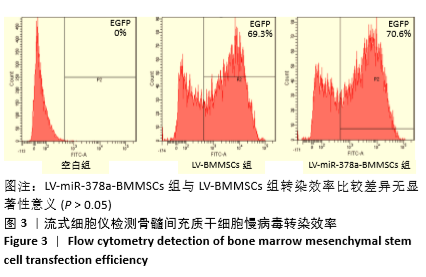
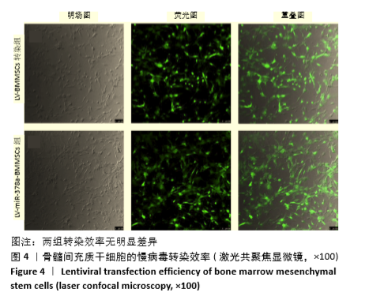
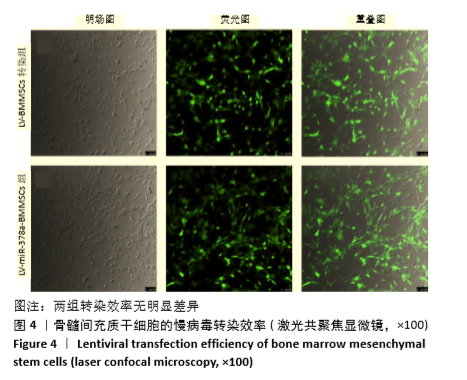
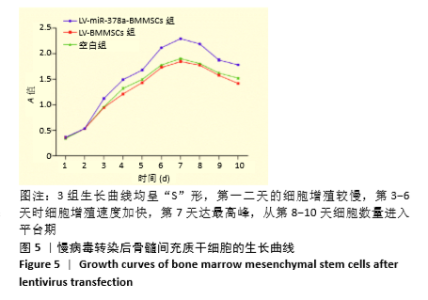
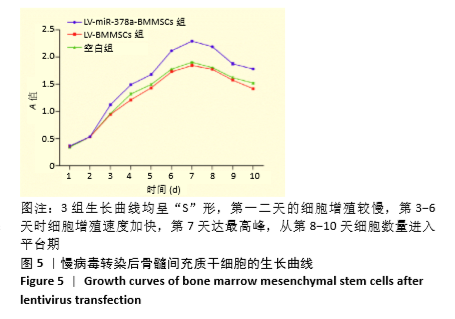
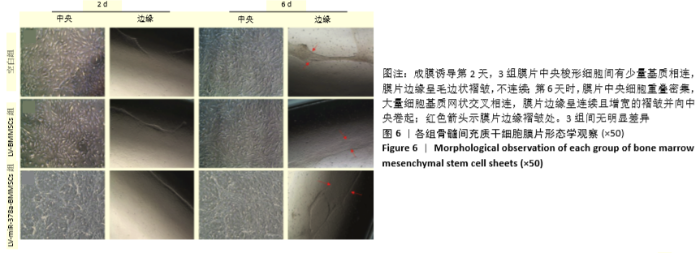
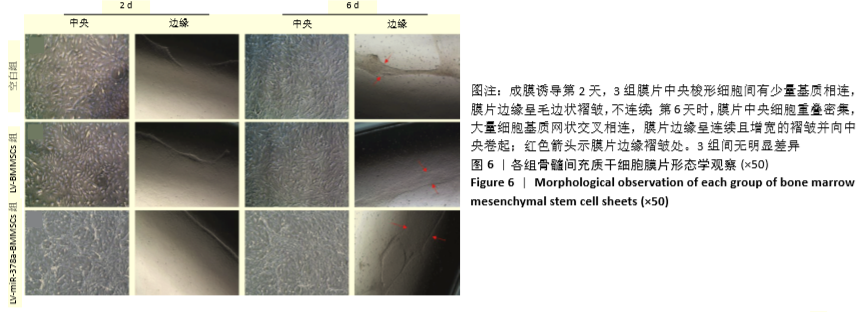
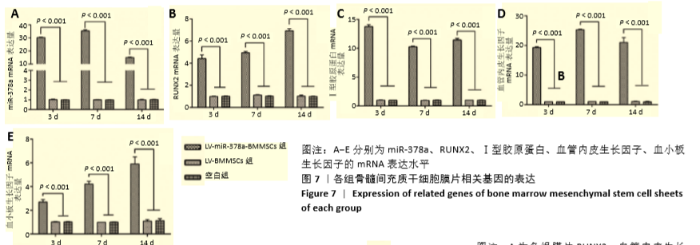
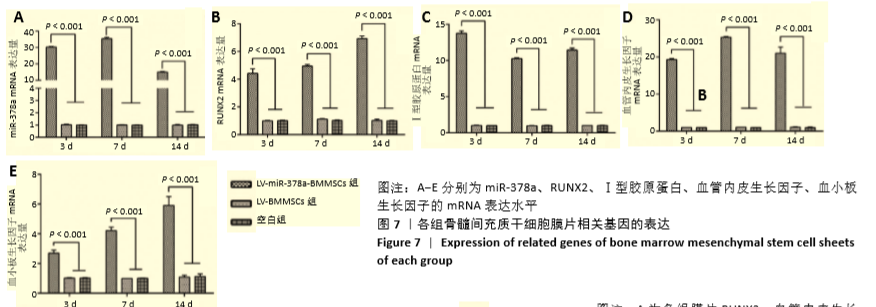
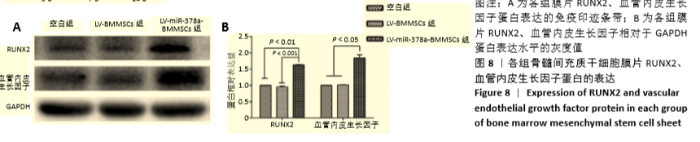
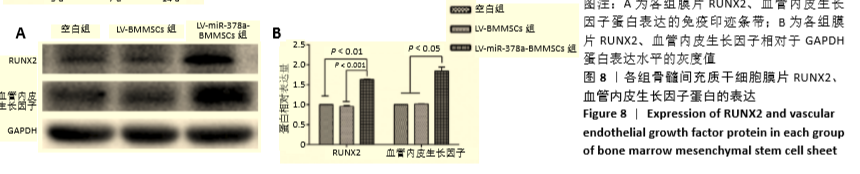
[1] 周思佳,姜文学,尤佳,等.骨缺损修复材料:现状与需求和未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(14):2251-2258.
[2] 谭志军,陈艳,张翠萍,等.微小RNA调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(6):1389-1390.
[3] 郭海林,贾智明,鲍星奇,等.细胞膜片技术在组织工程中的应用[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2017,7(6):351-355.
[4] TAKEUCHI R, KURUMA Y, SEKINE H, et al. In vivo vascularization of cell sheets provided better long‐term tissue survival than injection of cell suspension. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(8):700-710.
[5] 张文静.BMP-2及FGF-2诱导BMSCs膜片复合马鹿角粉支架构建组织工程骨的实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2020.
[6] HUPKES M, SOTOCA AM, HENDRIKS JM, et al. MicroRNA miR-378 promotes BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. BMC Mol Biol. 2014;15(1):1-1.
[7] AGARWAL V, BELL GW, NAM JW, et al. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife. 2015;4:e05005.
[8] BO Z, YALI L, YANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-378 Promotes Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling in BMMSCs for Potential Bone Regeneration. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018;2018:8402390.
[9] Verma IM. Gene therapy that works. Science. 2013;341(6148):853-555.
[10] AAGAARD L, ROSSI JJ. RNAi therapeutics: principles, prospects and challenges. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(2-3):75-86.
[11] YAN J, ZHANG C, ZHAO Y, et al. Non-viral oligonucleotide antimiR-138 delivery to mesenchymal stem cell sheets and the effect on osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2014;35(27):7734-7749.
[12] 吴镭,夏茜,毛久凤,等.成骨细胞膜片在不同钛表面骨桥蛋白基因和蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(10):1501-1507.
[13] KARALASHVILI L, KAKABADZE A, UHRYN M, et al. Bone grafts for reconstruction of bone defects. Georgian Med News. 2018;(282):44-49.
[14] 张文静,王佳,田梦婷,等.骨形态发生蛋白2及碱性成纤维生长因子2对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞膜片增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(1):65-71.
[15] WANG J, LIU S, LI J, et al. Roles for miRNAs in osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):197.
[16] GROL MW, LEE BH. Gene therapy for repair and regeneration of bone and cartilage. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;40:59-66.
[17] TAIPALEENMÄKI H. Regulation of Bone Metabolism by microRNAs. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(1):1-12.
[18] HOSSEINPOUR S, HE Y, NANDA A, et al. MicroRNAs Involved in the Regulation of Angiogenesis in Bone Regeneration. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;105(3):223-238.
[19] BENSKEY MJ, MANFREDSSON FP. Lentivirus Production and Purification. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1382:107-114.
[20] ANNONI A, GREGORI S, NALDINI L, et al. Modulation of immune responses in lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer. Cell Immunol. 2019;342:103802.
[21] KOMORI T. Regulation of proliferation, differentiation and functions of osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694.
[22] BAI Y, BAI L, ZHOU J, et al. Sequential delivery of VEGF, FGF-2 and PDGF from the polymeric system enhance HUVECs angiogenesis in vitro and CAM angiogenesis. Cell Immunol. 2018;323:19-32.
[23] YOU L, GU W, CHEN L, et al. MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10):7249-7261.
[24] GANESAN J, RAMANUJAM D, SASSI Y, et al. MiR-378 controls cardiac hypertrophy by combined repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation. 2013;127(21):2097-2106.
[25] SUN M, MA X, TU C, et al. MicroRNA-378 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis of melanoma by inhibiting FOXN3 expression through the Wnt/β‐catenin pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(10):1113-1124.
[26] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOUSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2937-2948.
[27] ZHANG M, YU W, NIIBE K, et al. The effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on bone marrow stromal cell-mediated vascularized bone regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:1-16.
|