Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 905-910.doi: 10.12307/2023.764
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty
Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan
- Department of Joint Surgery, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-15Accepted:2022-12-26Online:2024-02-28Published:2023-07-12 -
Contact:Wang Xu, Chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Wang Tihui, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:Fujian Natural Science Foundation, No. 2019J01618 (to WTH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
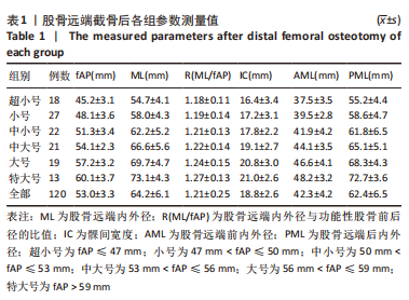
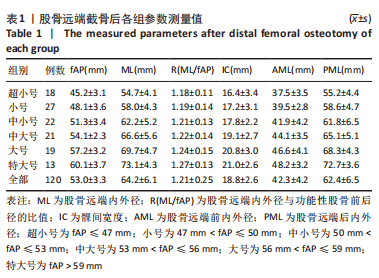
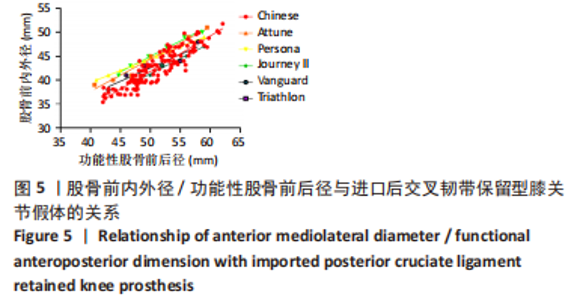
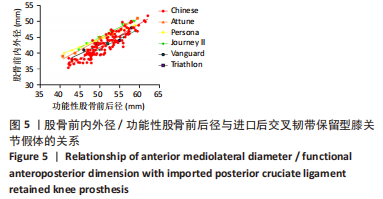
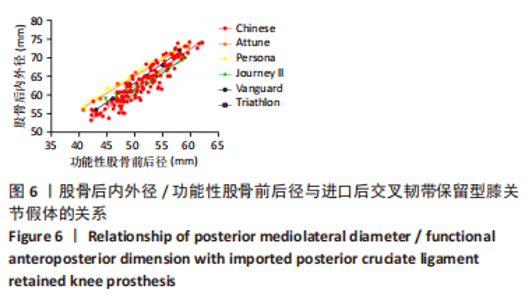
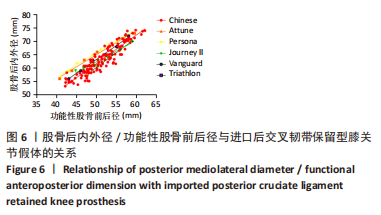
2.2 fAP、股骨远端内外径/fAP比值的测量结果与分析 研究中股骨远端截骨后股骨远端内外径、fAP、股骨远端内外径/fAP比值分别为(64.2±6.1) mm,(53.0±3.3) mm,1.21±0.25,见表1。与5种假体比对研究关系见图3;中国南方女性股骨远端股骨远端内外径、fAP值与进口5种关节假体一样均呈线性分布,该研究中国人股骨远端内外径/fAP比值为1.21±0.25,是这几种关节假体中最小的,进口假体中股骨远端曲面率最大的是Persona(1.38),最小的是Triathlon(1.25),其余Journey II、Vanguard、Triathlon介于两者之间。统计学分析发现,6个分组的股骨远端内外径/fAP比值均与Persona CR假体存在显著性差异(P < 0.05)。而Journey II、Vanguard、Triathlon、Attune假体与超小号、小号组假体存在显著性差异(P < 0.05)。"
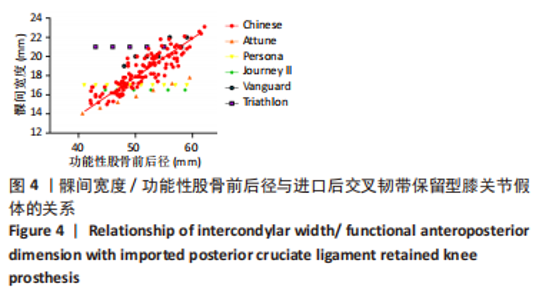
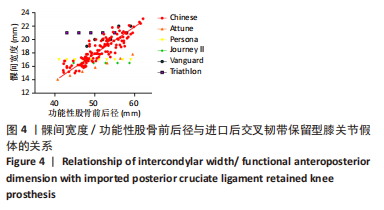
为了提高研究结果的差异性,选择Persona匹配假体悬出率,Triathlon匹配覆盖不良率。Persona假体总的假体悬出率为25%(30/120),按fAP值由小至大假体悬出率分别为11.2%(14/120),4.8%(6/120),4.0%(5/120),3.2%(4/120),1.6%(2/120),0.8%(1/120)。因此fAP≤47 mm组比其余各组更容易出现假体悬出(P < 0.05)。Triathlon假体总的覆盖不良率为12.5%(15/120),fAP > 53 mm组为9.2%(11/120),fAP≤53 mm组为3.3%(4/120);因此fAP > 53 mm组比fAP≤53 mm组更容易出现假体覆盖不良(P < 0.05)。 2.3 髁间宽度的测量结果与分析 股骨远端截骨后髁间宽度为(18.8±2.6) mm (16-22 mm)。髁间宽度值与型号呈线性递增模式,fAP≤53 mm和fAP > 53 mm两组比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 股骨髁间宽度与常用进口膝关节假体髁间大小的比较见图4;根据进口假体髁间宽度数值特点,选择Triathlon匹配假体覆盖不良率,Journey II匹配假体悬出率。Triathlon总的覆盖不良率为27.5%(33/120);按fAP值由小至大假体悬出率分别为12%(15/120),4.8%(6/120),3.2%(4/120),2.4%(3/120),2.6%(2/120),2.4%(3/120);因此fAP≤47 mm组比其余各组更容易出现股骨远端中央区骨面覆盖不良(P < 0.05)。Journey II假体总的假体悬出率为21.6%(26/120),按fAP值由大至小假体悬出率分别为7.2%(9/120),6.4%(5/120),3.2%(5/120),3.2%(4/120),2.4%(3/120),0%(0/120)。fAP > 53 mm组为15.8%(19/120),fAP≤53 mm组为5.8%(7/120);因此Journey II假体在fAP > 53 mm组比fAP≤53 mm组更容易出现假体悬出(P < 0.05)。"

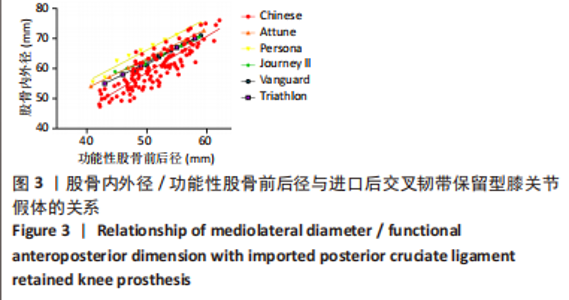
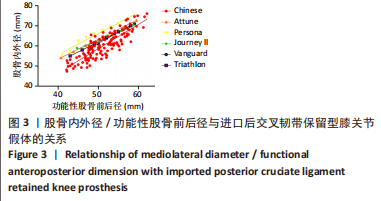
与股骨前内外径差异最大的是Journey II CR假体,容易在股骨假体前外侧悬出;与股骨后内外径差异最大的是Persona CR假体,容易在假体后内侧覆盖不良。股骨前内外径在与Journey II匹配中发现总的假体悬出率为23.3%(29/120),按fAP值由小至大假体悬出率分别为10.4%(13/120),4.8% (6/120),3.2%(4/120),2.4%(3/120),1.6%(2/120),0%(0/120);fAP≤53 mm组18.4%(23/120)相比fAP > 53 mm组4% (5/120),fAP≤47 mm组相比其余5组均有显著性差异(P < 0.05);因此fAP≤53 mm组尤其是fAP≤47 mm组更容易在股骨前外侧发生悬出。 股骨后内外径在与Persona 匹配中发现总的假体覆盖不良率为12%(15/120),多数覆盖不良位于股骨假体内后方。按fAP值由小至大覆盖不良率分别为1.6%(2/120),2.4%(3/120),1.6%(2/120),2.4%(3/120),1.6%(2/120),2.4%(3/120);按fAP≤53 mm组和fAP > 53 mm组统计分别为6.4%(8/120),5.6%(7/120),各组间比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"

| [1] ABHARI S, HSING TM, MALKANI MM, et al. Patient satisfaction following total knee arthroplasty using restricted kinematic alignment. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(6 Supple A):59-66. [2] SMITH AF, ECCLES CJ, BHIMANI SJ, et al. Improved Patient Satisfaction following Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2021; 34(7):730-738. [3] 李大地,朱梁,郑力,等.全膝关节置换疗效及患者满意度与人格特征的关联性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1346-1350. [4] MA QL, LIPMAN JD, CHENG CK, et al. A Comparison Between Chinese and Caucasian 3-Dimensional Bony Morphometry in Presimulated and Postsimulated Osteotomy for Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2878-2886. [5] FAN L, XU T, LI X, et al. Morphologic features of the distal femur and tibia plateau in Southeastern Chinese population: A cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(46):e8524. [6] CAVAIGNAC E, SAVALL F, FARUCH M, et al. Geometric morphometric analysis reveals sexual dimorphism in the distal femur. Forensic Sci Int. 2016;259:246.e1-5. [7] KIM JB, LYU SJ, KANG HW. Are Western Knee Designs Dimensionally Correct for Korean Women? A Morphometric Study of Resected Femoral Surfaces during Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):254-261. [8] BOZKURT M, TAHTA M, GURSOY S, et al. Total and intercondylar notch bone resection in posterior stabilized knee arthroplasty: analysis of five manufacturer designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25(6):1731-1735. [9] ASSELN M, GROTHUES SAGA, RADERMACHER K. Relationship between the form and function of implant design in total knee replacement. J Biomech. 2021;119:110296. [10] LEE JA, KOH YG, KANG KT. Effect of post-cam design on the kinematics and contact stress of posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(6):323-332. [11] GUY SP, FARNDON MA, SIDHOM S, et al. Gender differences in distal femoral morphology and the role of gender specific implants in total knee replacement: a prospective clinical study. Knee. 2012;19(1):28-31. [12] BONNIN MP, SAFFARINI M, BOSSARD N, et al. Morphometric analysis of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty and native knees. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1):49-57. [13] KIM YH, CHOI Y, KIM JS. Comparison of standard and gender-specific posterior-cruciate-retaining high-flexion total knee replacements: a prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(5):639-645. [14] KIM YH, CHOI Y, KIM JS. Comparison of a standard and a gender-specific posterior cruciate-substituting high-flexion knee prosthesis: a prospective, randomized, short-term outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(10):1911-1920. [15] 龚恒,黄斌,付立功,等.中国汉族人与美国局加索白人膝关节几何形态的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(33): 5366-5370. [16] KIM TK, PHILLIPS M, BHANDARI M, et al. What Differences in Morphologic Features of the Knee Exist Among Patients of Various Races? A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(1):170-182. [17] 陈小明,杨五洲,张洁.股骨远端解剖学参数在TKA假体设计中的意义[J].中南医学科学杂志,2018,46(1):48-51. [18] 章晓云,陈跃平,夏天,等.广西地区壮族人群正常膝关节形态学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(20):3141-3146. [19] 顾景范.《中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2015)》解读[J].营养学报,2016,38(6):525-529. [20] CLARKE HD, HENTZ JG. Restoration of femoral anatomy in TKA with unisex and gender-specific components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(11):2711-2716. [21] SHERMAN WF, MANSOUR A, SANCHEZ FL, et al. Increased Intercondylar Femoral Box Cut-to-Femur Size Ratio During Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty Increases Risk for Intraoperative Fracture. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6(2):180-185. [22] KIM E, TALMO CT, ANDERSON MC, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Posterior Cruciate Ligament Avulsion during Cruciate Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(11):1138-1142. [23] 徐兴全,刘玉宝,孙梓荧,等.股骨髁间窝宽度指数在胫骨髁间嵴撕脱骨折与前交叉韧带损伤中的差异比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019,21(2):122-126. [24] CAY N, ACAR HI, DOGAN M, et al. Radiological Evaluation of Femoral Intercondylar Notch and Tibial Intercondylar Eminence Morphometries in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Pathologies Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Indian J Orthop. 2021;56(2):327-337. [25] BUDHIPARAMA NC, LUMBAN-GAOL I, IFRAN NN, et al. Mismatched knee implants in Indonesian and Dutch patients: a need for increasing the size. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(2):358-369. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [2] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [3] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [4] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [5] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinbiao, Li Xiaoming, Xing Wanlin, Ma Fei, Yu Qiaoya, Dai Rongqin. Early warning efficacy of thrombus molecular markers after total knee arthroplasty in patients complicated with venous thromboembolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 572-577. |
| [7] | Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618. |
| [8] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [9] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [10] | Alimujiang•Yusufu, Abuduwupuer•Haibier, Qin Qi, Liu Yuzhe, Zhang Qianlong, Ran Jian. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid in perioperative period of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5812-5817. |
| [11] | Li Xiaojuan, Zhang Yuanzhi, Yang Xiaoguang, Gao Yang, Wu Qiong. Quantitative evaluation of bone structure changes in femoroacetabular impingement syndrome by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4965-4970. |
| [12] | Li Haoran, Huang Jian. Application of finite element analysis in artificial knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5058-5063. |
| [13] | Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Correlation analysis of low back pain in middle-aged and elderly people in China and construction of a linear graph prediction mode [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4937-4942. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Ma Chenghao, Qin Zuohai, Zhou Haibo, Ding Haoyuan, Han Dapeng, Nie Zhixing, Pan Peijun, Gao Chenxin, Ouyang Guilin. Effect of tourniquet use on perioperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4943-4948. |
| [15] | Xiang Furong, Tang Shengxin, Ou Lizhen, Lin Xikai, Chen Jian. Effects of different taping methods on knee joint stress during drop jump landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4850-4855. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||