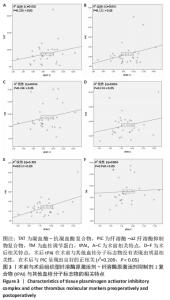
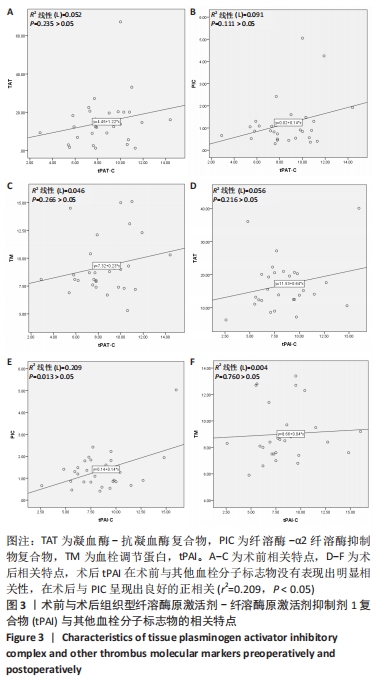
[1] SATTLER L, HING W, VERTULLO C. Changes to rehabilitation after total knee replacement. Aust J Gen Pract. 2020;49(9):587-591.
[2] MATHARU GS, CULLIFORD DJ, BLOM AW, et al. Projections for primary hip and knee replacement surgery up to the year 2060: an analysis based on data from The National Joint Registry for England, Wales, Northern Ireland and the Isle of Man. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2021. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2021.0206.
[3] 王广玲,袁慧,刘峰,等.术后不同抗凝药物对膝关节置换术后血栓发生及隐性失血的影响研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2021(23): 81-84.
[4] AGARWAL AR, WANG KY, XU AL, et al. Postoperative Complications in Patients With Hereditary Hemochromatosis Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Matched Cohort Analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(1):e99-e107.
[5] BADGE HM, CHURCHES T, NAYLOR JM, et al. Non-compliance with clinical guidelines increases the risk of complications after primary total hip and knee joint replacement surgery. PLoS One. 2021;16(11): e0260146.
[6] CHOTANAPHUTI T, ONGNAMTHIP P, SILPIPAT S, et al. The prevalence of thrombophilia and venous thromboembolism in total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(7):1342-1347.
[7] KELLER K, HOBOHM L, BARCO S, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients hospitalized for knee joint replacement surgery. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):22440.
[8] 王立群,段闪闪,廖灯彬,等.人工关节置换术后间歇充气压力泵使用时间对下肢深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):585-590.
[9] ZENG Y, SI H, WU Y, et al. The incidence of symptomatic in-hospital VTEs in Asian patients undergoing joint arthroplasty was low:a prospective,multicenter,17660-patient-enrolled cohort study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1075-1082.
[10] DAI X, WANG X, HUANG Z, et al. Exact Association Between Preoperative Blood Viscosity and Postoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis Risk in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021;27:10760296211048896.
[11] XIONG X, CHENG B. Preoperative risk factors for deep vein thrombosis in knee osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2021:S0949-2658(21)00344-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jos. 2021.09.016.
[12] 吴俊.精准抗凝的时代需要精准监测[J].中华检验医学杂志,2019, 42(4):232-235.
[13] 郑洋洋,闫海润,李琪,等.恶性肿瘤患者血栓分子标志物的临床评价[J].中华检验医学杂志,2020,43(1):78-84.
[14] TOU J, KUWASHIMA U, ITOH M, et al. No difference in the incidence or location of deep venous thrombosis according to use of pharmacological prophylaxis following total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):819.
[15] LEE JK, LEE KB, KIM JI, et al. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis even using low-molecular-weight heparin after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;33(1):29.
[16] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2):65-71.
[17] ROSENCHER N, BONNET MP, SESSLER DI. Selected new antithrombotic agents and neuraxial anaesthesia for major orthopaedic surgery: management strategies. Anaesthesia. 2007;62(11):1154-1160.
[18] GEERTS WH, BERGQVIST D, PINEO GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evi-dence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl): 381S-453S.
[19] FALCK-YTTER Y, FRANCIS CW, JOHANSON NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence -Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl):e278S-325S.
[20] 曹盛吉,冯丹,吕明琪.恶性肿瘤患者血栓分子标志物变化及临床意义[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(4):756-759.
[21] 文梦,赵慧茹,赵育婧,等.血栓分子标志物对下肢深静脉血栓形成的诊断及抗凝疗效的评价[J].临床检验杂志,2019,37(9):671-674.
[22] LEE SY, NIIKURA T, IWAKURA T, et al. Thrombin-antithrombin III complex tests. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):170840616684501.
[23] 李传保,徐冷楠,步霄霄,等.可溶性血栓调节蛋白对评估肾脏病患者内皮损伤状态的价值[J].中华医学杂志,2021,101(23):1812-1815.
[24] 赵慧茹,王聪,苏玉,等.关节置换围术期患者血浆内皮细胞蛋白C受体和血栓调节蛋白水平变化分析[J].现代检验医学杂志,2018, 33(2):125-126,133.
[25] 范鑫超,鲍文娟,张凯,等.D-二聚体、红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白在髋、膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成中的诊断价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(33):5324-5328.
[26] 陈辉,王岩.人工关节置换与深静脉血栓的生物标志物[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(17):2775-2781.
[27] 黄声淳,张劲丰,蔡惠兴,等.应用抗凝-纤溶标志物联合检测对髋关节置换术后静脉血栓进行诊断及疗效评估研究[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2019,26(2):294-298.
[28] CHENG Y, LIU J, SU Y, et al. Clinical Impact of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Markers for Predicting Postoperative Venous Thromboembolism in Total Joint Arthroplasty Patients. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019;25:1076029619877458.
[29] 孙京涛,魏瑄,王少华,等.氨甲环酸不同给药方式对全膝关节置换术后血清标志物的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(5):951-953.
[30] 杨玉宝,李海涛,高忠礼,等.氨甲环酸的关节腔灌注对膝关节置换术的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(2):348.
[31] GUO X, TAO H, LI D, et al. The α2-Plasmin Inhibitor-Plasmin Complex is a Potential Biomarker of Venous Thromboembolism in Orthopedic Trauma Patients. Clin Lab. 2021;67(4). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200856.
|