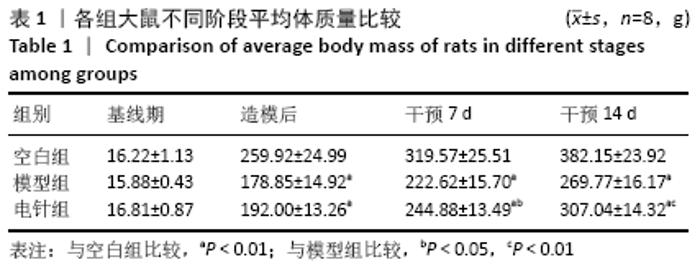
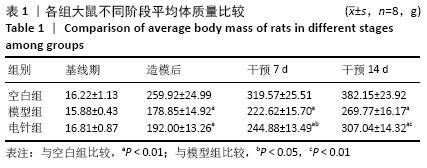
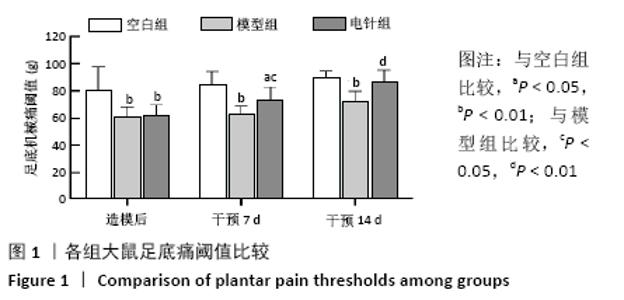
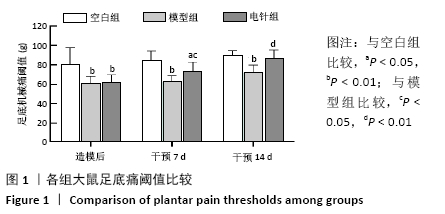
[1] 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组,中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠功能性疾病协作组.中国功能性消化不良专家共识意见(2015年,上海)[J].中华消化杂志,2016,36(4):217-229.
[2] TALLEY NJ, GOODSALL T, POTTER M. Functional dyspepsia. Australian Prescriber, 2017.
[3] Drossman DA. functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1262-1279.
[4] FANG YJ, LIOU JM, CHEN CC, et al. Distinct aetiopathogenesis in subgroups of functional dyspepsia according to the Rome III criteria. Gut. 2015;64(10):1517-1528.
[5] ENCK P, AZPIROZ F, BOECKXSTAENS G, et al. Functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17081.
[6] WANG YP, HERNDON CC, LU CL. Non-pharmacological Approach in the Management of Functional Dyspepsia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;26(1):6-15.
[7] SIMRÉN M, TÖRNBLOM H, PALSSON OS, et al. Visceral hypersensitivity is associated with GI symptom severity in functional GI disorders: consistent findings from five different patient cohorts. Gut. 2018;67: 255-262.
[8] STANGHELLINI V, CHAN FK, HASLER WL, et al. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1380-1392.
[9] Mawe GM, Hoffman JM. Serotonin signalling in the gut--functions, dysfunctions and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10(10):564-564.
[10] 陈海军.辨证针刺治疗功能性消化不良的临床观察及对肝胃不和型FD大鼠5-HT的影响[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2015.
[11] 潘小丽,周丽,王丹,等. 电针”足三里”对功能性消化不良大鼠胃排空及自噬信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2019,44(7):486-491.
[12] TACK J, CAENEPEEL P, FISCHLER B, et al. Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:526-535.
[13] ALCAINO C, KNUTSON KR, TREICHEL AJ, et al. A population of gut epithelial enterochromaffin cells is mechanosensitive and requires Piezo2 to convert force into serotonin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(32):E7632-E7641.
[14] DICKSON I. Gut mechanosensors: enterochromaffin cells feel the force via PIEZO2. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(9):519.
[15] WANG F, KNUTSON K, ALCAINO C, et al. Mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo2 is important for enterochromaffin cell response to mechanical forces. J Physiol. 2017;595(1):79-91.
[16] 石啸双.基于EPAC1-PIEZO2轴探讨EC在FD内脏高敏感中的作用及香砂六君子汤的干预研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2019.
[17] EIJKELKAMP N,LINLEY JE,TORRES JM, et al. A role for Piezo2 in EPAC1-dependent mechanical allodynia. Nature Commun. 2013;4:1682.
[18] SINGHMAR P, HUO XJ, EIJKELKAMP N, et al. Critical role for Epac1 in inflammatory pain controlled by GRK2-mediated phosphorylation of Epac1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(11):3036-3041.
[19] ZHAO J, ZHAO L, ZHANG S, et al. Modified Liu-Jun-Zi decoction alleviates visceral hypersensitivity in functional dyspepsia by regulating EC cell-5HT3r signaling in duodenum. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;250:112468.
[20] 王煜姣,凌江红,张钰琴,等.复合病因造模法制备功能性消化不良大鼠模型[J].世界华人消化杂志,2014(2):210-214.
[21] 吴震宇,张声生,李培彩,等.碘乙酰胺灌胃联合夹尾应激诱导大鼠FD模型的建立及评价[J].中国中西医结合消化杂志,2015,23(7): 18-22.
[22] 郭义,方剑乔.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2012.
[23] 张晓明,辛玉,康朝霞,等.电针通过SCF/c-kit通路对功能性消化不良模型大鼠Cajal间质细胞以及Cx43表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(11):426-429.
[24] 唐雷,徐派的,张红星.电针对功能性消化不良大鼠胃窦AMPK化及mTOR的影响[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(2):196-199.
[25] 王丹,张红星,荣培晶,等.电针对功能性消化不良肝郁脾虚大鼠十二指肠黏膜机械屏障及其调节蛋白的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2020,26(12):1843-1845,1882.
[26] 吴强. 电针敏化穴位对KOA模型大鼠的效应及对关节局部炎症因子的调节作用研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2019
[27] LACY BE, WEISER KT, KENNEDY AT, et al. Functional dyspepsia: the economic impact to patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 38(2): 170-177.
[22] TALLEY NJ, FORD AC. Functional Dyspepsia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(19): 1853-1863.
[28] BARLOW W, ORLANDO R. The pathogenesis of heartburn in nonerosive reflux disease: a unifying hypothesis. Gastroenterology. 2005;128: 771-778.
[29] RITCHIE J. Pain from distension of the pelvic colon by inflating a balloon in the irritable colon syndrome. Gut. 1973;14:125-132.
[30] ZHOU Q, PRICE DD, CAUDLE RM, et al. Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(2): 429-435.
[31] OUYANG X, LI S, ZHOU J, et al. Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Gastric Hypersensitivity via Adrenergic Pathway in a Rat Model of Functional Dyspepsia. Neuromodulation. 2020;23(8): 1137-1143.
[32] 刘武,马鋆,王富春,等.基于数据挖掘的功能性消化不良针灸取穴规律[J].亚太传统医药,2019,15(10):157-159.
[33] 徐派的,张红星,杨云,等.电针对功能性消化不良模型大鼠胃肠动力及VIP和CGRP水平的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2017,37(3): 360-364.
[34] 潘小丽,范建超,徐派的,等.电针对功能性消化不良肝郁脾虚模型大鼠胃电节律及胃窦Cajal间质细胞表达的影响[J].中医杂志, 2018,59(17):1503-1506.
[35] KULIG G, KLUPINRS KAG, JOCHYMSKI C, et al. Evaluation of the number of enterochromaffin cells in gastric mucosa in subjects with functional dyspepsia. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2009;26(155):370-372.
[36] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct Mechanically Activated Cation Channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60.
[37] 高瑞桐,许林琪,李峰.机械敏感性离子通道蛋白Piezo在机体机械转导中作用的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2019,45(3): 725-730.
[38] YANG J, ZHANG J, YANG H, et al. The potential role of Piezo2 in the mediation of visceral sensation. Neurosci Lett. 2016:158-163.
[39] PARNELL E, SMITH BO, YARWOOD SJ. The cAMP sensors,EPAC1 and EPAC2,display distinct subcellular distributions despite sharing a common nuclear pore localisation signal. Cell Signal. 2015;27(5): 996-999.
[40] PEREIRA L,REHMANN H,LAO DH, et al. Novel Epac fluorescent ligand reveals distinct Epac1 vs Epac2 distribution and function in Cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(13):3991-3996.
[41] 杨静,李坤,雷晓斐,等.Epac1对大鼠内脏高敏感的调控作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2016,56(24):9-12.
|