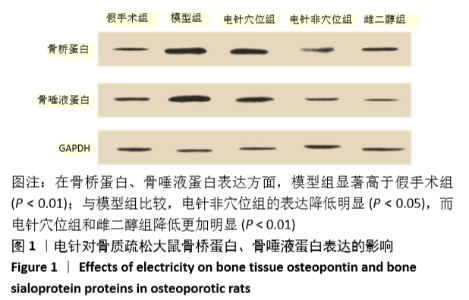
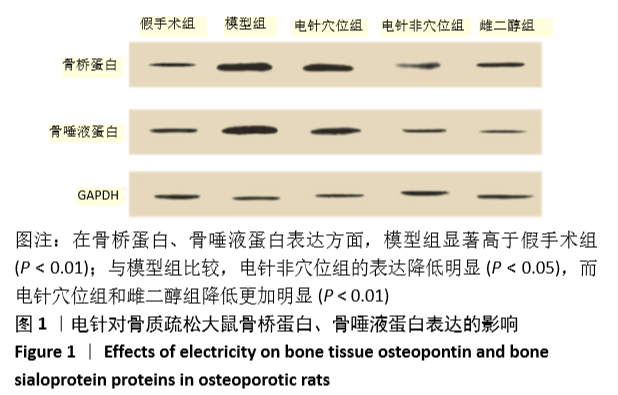
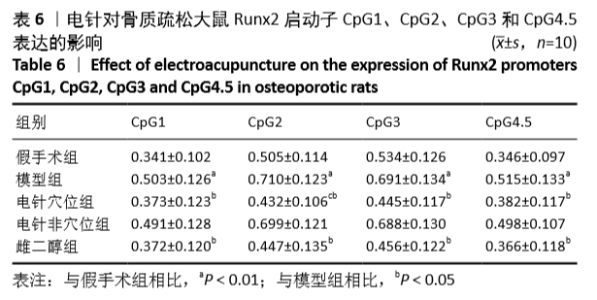
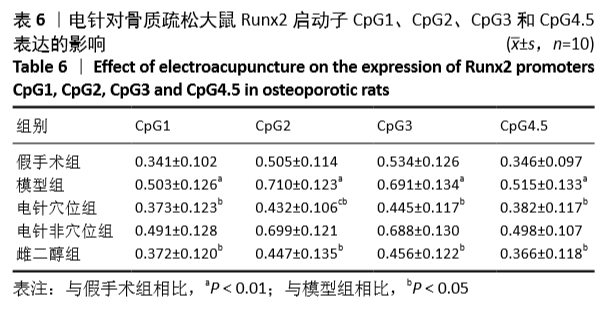
[1] 中华医学会,中华医学会杂志社,中华医学会全科医学分会,等.原发性骨质疏松症基层诊疗指南(实践版·2019)[J].中华全科医师杂志,2020,19(4):316-323.[2] 胡洁玫,刘晨.骨质疏松症流行病学概况及相关危险因素[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(42):55-57.
[3] BYUN JH, JANG S, LEE S,et al. The Efficacy of Bisphosphonates for Prevention of Osteoporotic Fracture:An Update Meta-analysis. J Bone Metab. 2017;24(1):37-49.
[4] 张立海.老年骨质疏松骨折的现状和挑战[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2020,19(7):481-484.
[5] 中华中医药学会.绝经后骨质疏松症(骨痿)中医药诊疗指南(2019年版)[J].中医正骨,2020,32(2):1-13.
[6] 张倩,王花欣,王媛,等.中药防治绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(7):1083-1088.
[7] EHRLICH M. DNA hypermethylation in disease: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Epigenetics. 2019;14(12):1141-1163.
[8] WAKITANI S, YOKOI D, HIDAKA Y, et al. The differentially DNA-methylated region responsible for expression of runt-related transcription factor 2. Vet Med Sci. 2017;79:230-237.
[9] CHEN JC, CHUA M, BELLON RB, et al. Epigenetic changes during mechanically induced osteogenic lineage commitment. Biomech Eng. 2015;137:020902.
[10] 李俐,余晓雯,吴广文,等.针刺肾俞、足三里抑制大鼠绝经后骨质疏松症的机制研究[J].云南中医学院学报,2018,41(4):29-34.
[11] 荀丹丹,臧晓明,孙琰,等.针灸治疗原发性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2017,33(8):197-199.
[12] 邵雨薇,舒晴,田峻.针灸防治骨质疏松症机制的研究进展[J].上海针灸杂志,2020,39(3):381-386.
[13] 王亚军,刘梅洁,鞠大宏,等,高原.针刺对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度、骨形态计量学的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2015,21(7):857-859+871.
[14] 巢传琦,蔡君,吕俊华.补骨方对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的防治作用研究[J].中药材,2015,38(4):807-809.
[15] 郭义.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社, 2008:417.
[16] 颜春鲁,王琳,安方玉,等.地黄饮子水煎剂对去势骨质疏松大鼠生物力学及OPG/RANKL/RANK含量的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(10):4642-4645.
[17] 鲍圣涌,王华,王彦春,等. “双固一通”针法对绝经后骨质疏松症模型大鼠骨组织保护蛋白mRNA表达水平的影响[J].针刺研究, 2006,31(3):23-26, 52.
[18] 王璐,许鸿新,张思伟,等.补肾健脾针刺法治疗老年男性原发性骨质疏松症的临床疗效评估研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(2): 224-227.
[19] 赵勤,范怀玲,纪峰,等.电针命门穴对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠股骨OPG/RANKL系统的影响[J].中国民族民间医药,2015,24(7):26-29.
[20] 张蓓蓓,商玮,蔡辉.骨质疏松症的表观遗传学调控[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(3):290-296.
[21] 朱筱. Runx2甲基化状态变化对血管平滑肌细胞成骨样分化影响的研究 [D].长沙:中南大学,2012.
[22] DAUDI J, CONLEY AB, YI SV, et al. On the presence and role of human gene-body DNA methylation. Oncotarget. 2012;3(4):462-474.
[23] 张晓蕾. DNA甲基化对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[D].杭州:浙江大学,2010.
[24] 刘志萍,曾怡乐,蓝艺鑫,等.表观遗传对成骨细胞的调控作用及与骨质疏松的关系[J].生物医学,2019,9(2):96-102.
[25] 申玉,杨璞,郝晋,等.DNA甲基化在调节干细胞成骨分化中的作用[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2016,34(5):526-530.
[26] XU J, LI Z, HOU Y, et al. Potential mechanisms underlying the Runx2 induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(12):2527-2535.
[27] NAKASHIMA K, DE CROMBRUGGHE B. Transcriptional mechanisms in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Trends Genet. 2003;19(8):458-466.
[28] 蔡鑫,唐芳,马武开,等.基于Wnt/nt/ 458-4信号通路的中医药调控骨代谢研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(5):1082-1087.
[29] XU L, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al.Melatonin suppresses estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis and promotes osteoblastogenesis by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Calcified Tissue Int. 2018;103(4):400-410.
[30] 王剑,李屹,王实,等.基于骨组织Runx2、Osterix启动子甲基化探究鹿茸中药复方对去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠的疗效机制[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2020,22(5):1744-1749.
[31] 王剑,刘剑辉,李屹,等.基于骨组织Dlx5启动子甲基化探究补肾中药复方对去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠的疗效机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):640-645.
[32] SHAN Y, WANG L, LI G, et al. Methylation of bone SOST impairs SP7, RUNX2, and ERalpha transactivation in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;97(4):369-374.
[33] YAN G, YUAN Y, HE M, et al. m(6)A Methylation of Precursor-miR-320/RUNX2 Controls Osteogenic Potential of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:421-436.
[34] ZHANG YX, SUN HL, LIANG H, et al. Dynamic and distinct histone modifications of osteogenic genes during osteogenic differentiation. J Biochem. 2015;158(6):445-457.
[35] LI Y, WANG L, ZHANG M, et al. Advanced glycation end products inhibit the osteogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived stem cells by modulating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway via DNA methylation. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(6):e12834.
[36] CAI N, LI C, WANG F. Silencing of LncRNA-ANCR Promotes the Osteogenesis of Osteoblast Cells in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis via Targeting EZH2 and RUNX2. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(8):751-759.
[37] LEI NB, LIANG X, WANG P, et al. Teriparatide alleviates osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs via miR-375/RUNX2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(24):11043-11050.
[38] 牛亚丹,林伊荷,张汉清,等.DNA甲基化与骨代谢调节及骨质疏松症研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(2):162-169.
|