Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1458-1464.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3765
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery
Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-03Revised:2020-04-13Accepted:2020-05-19Online:2021-03-28Published:2020-12-16 -
Contact:Wei Peng, Master’s supervisor, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Chen Jinping, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Health Commission, No. 19PJ202
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464.
share this article
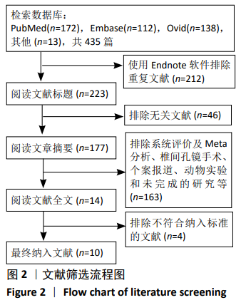
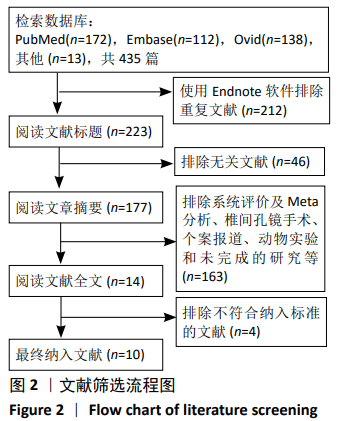
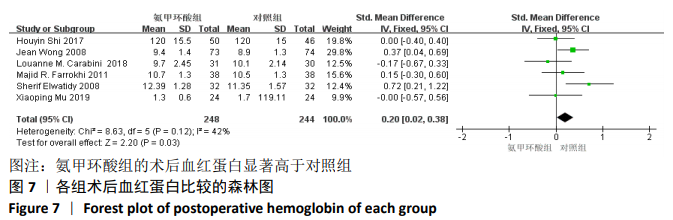
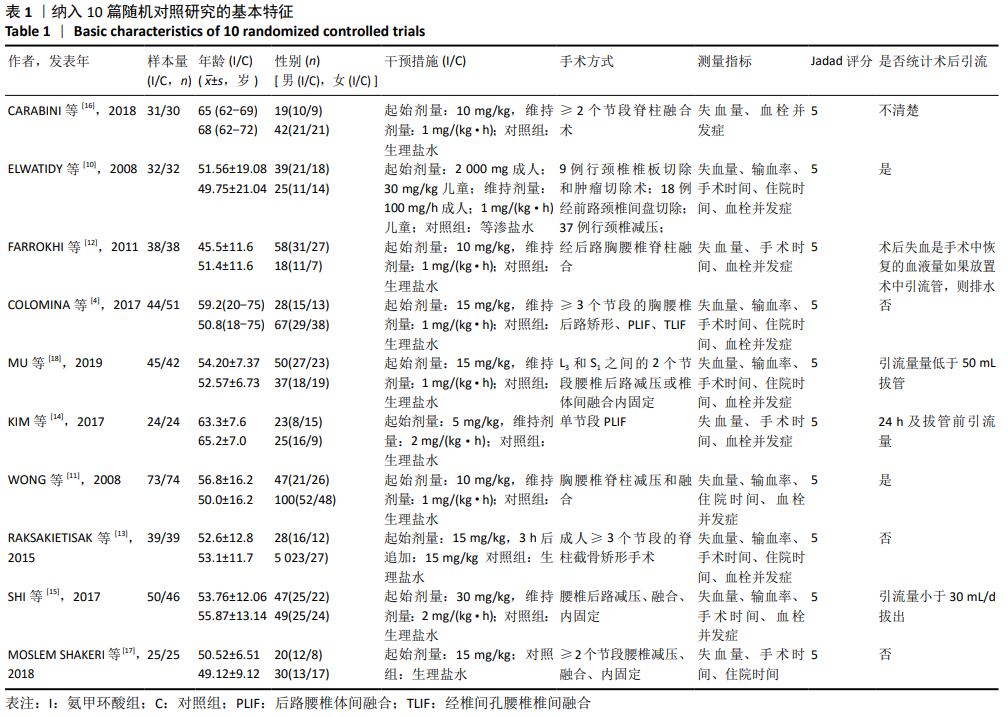
2.2 纳入文献质量评价结果 使用Cochrane评价手册中的风险偏倚评估工具对纳入研究的质量予以评价。在10项随机对照试验中[4,10-18],有8项研究说明使用随机数字表、计算机随机数字生成器和信封的方法[4,11-16,18],评为“低风险”;有1项研究通过奇数和偶数分配[10],评为“高风险”;有1项研究未提及具体随机序列的产生方法[17],评为“不清楚”;10项研究均未使用分配隐藏,评为“低风险”;10项研究均提及使用盲法,评为“低风险”;有5项研究存在少数脱落受试者[4,11,15-16,18],缺失数据的数目在各干预组相当并准确描述,完整结果数据评为“低风险”;有4项研究无法判断其他偏倚来源[10,13,15,17],评为“不清楚”。 在10篇研究中共计纳入病例802例,这些患者中对照组401例,氨甲环酸组401例。患者均接受开放性脊柱手术。10项研究均使用等量等速生理盐水作为安慰剂对照。所有纳入研究的氨甲环酸均给予静脉滴注,其中MU等[18]研究共分3组,静脉应用组、局部应用组、生理盐水对照组,故只纳入静脉应用组与生理盐水对照组进行此次研究。静脉滴注氨甲环酸的剂量和方式有:起始剂量有5,10,15,30,100,2 000 mg/kg成人、30 mg/kg儿童;维持剂量有1,2 mg/(kg·h),100 mg/h。给药时间包括术前给药、术中维持及术后给药等方式。由于氨甲环酸的给药剂量及给药方式存在较大差异,直接合并数据可能存在不合理性,因此文章复习相关文献后[19],首先对纳入文献进行进行异质性检验,若存在明显的异质性则分析讨论异质性来源,若多个研究结果之间有同质性则直接进行数据结果合并分析。统计术后引流出血量1-4 d。总失血量的计算为术中失血量加上术后引流量。纳入文献的基本特征见表1。"
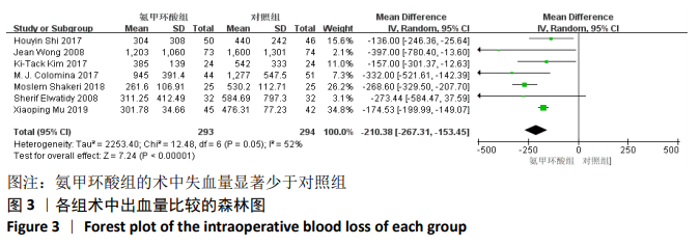
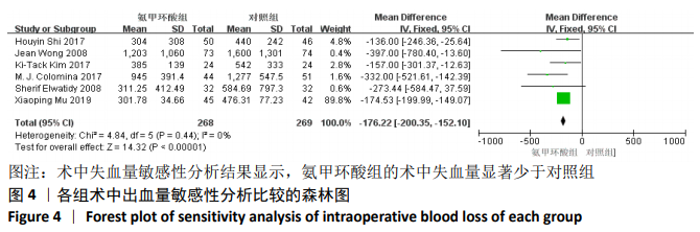
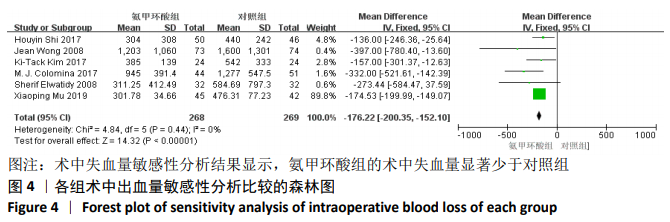
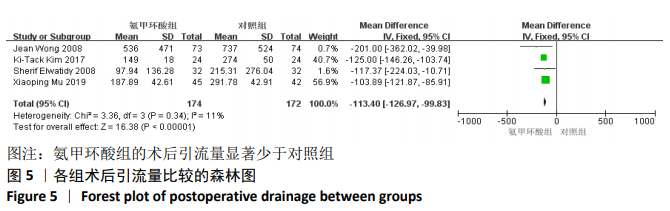
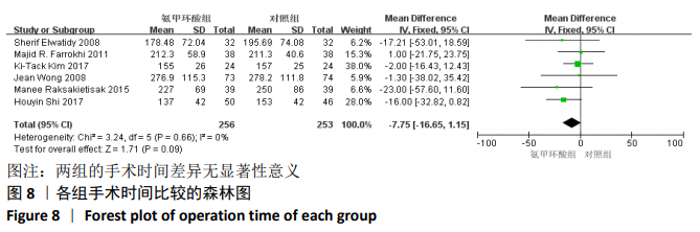
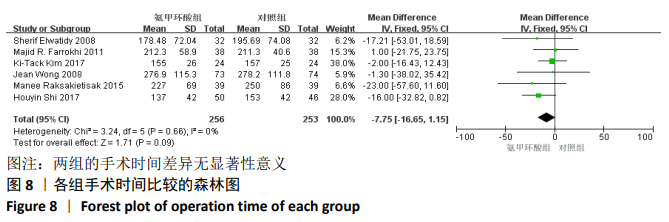
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 各组术中失血量变化 纳入7项随机对照研究[4, 10-11, 14-15, 17-18],各研究存在统计学异质性(P=0.05,I2=52%),故采用随机效应模型,术中失血量具有显著性意义(MD=-210.38,95%CI: -267.31至-153.45,P < 0.000 01),见图3,氨甲环酸能够显著减少开放性脊柱手术的术中失血量,但纳入研究存在异质性,通过敏感性分析[20],发现文献[4,10-11,14-15,18]术中均予以不同剂量的氨甲环酸静脉滴注维持,而1项研究术中未予以氨甲环酸静脉滴注维 持[17],复习相关文献[21],术中维持使用氨甲环酸可能是异质性来源,因此文章剔除1个研究并再次分析数据[17],结果显示:各研究之间不存在异质性(P=0.44,I2=0%),因此采用固定效应模型进行分析,氨甲环酸组术中失血量显著低于对照组(MD= -176.22,95%CI: -200.35至-152.10,P < 0.000 01),见图4。"
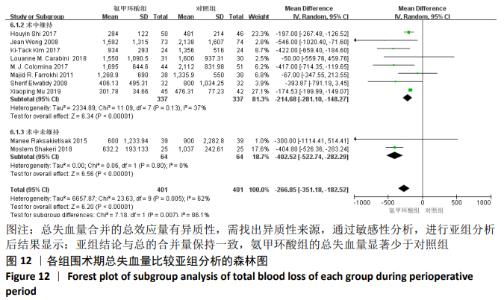
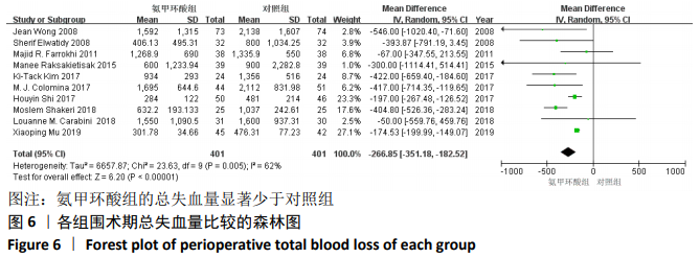
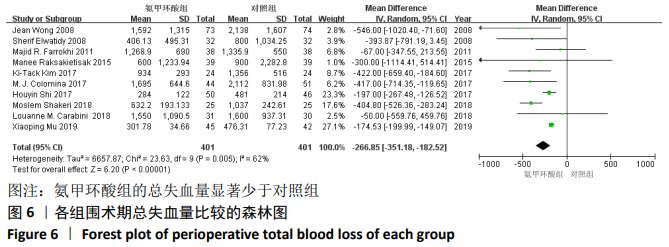
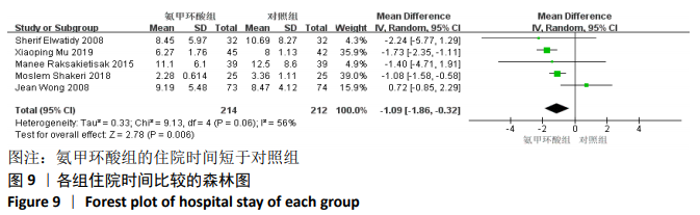
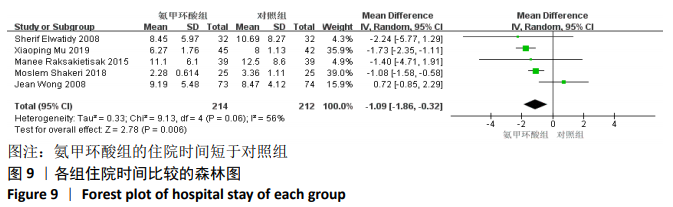
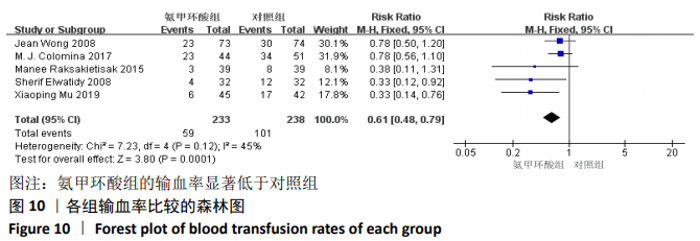
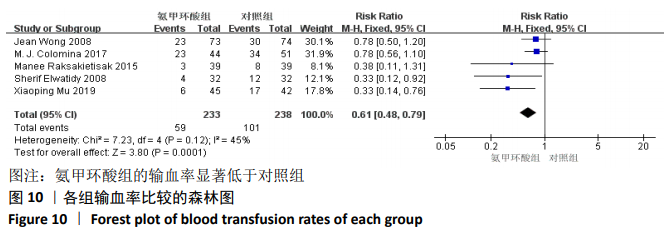
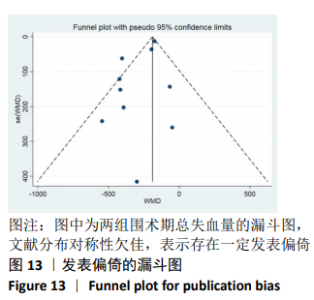
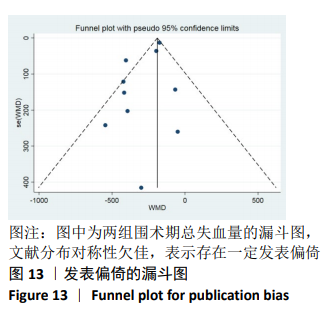
2.3.9 各组总失血量的亚组分析结果 围术期总失血量具有明显异质性(P=0.005,I2=62%),通过对比一般资料发现研究术中均予以不同剂量的氨甲环酸静脉滴注维持[4,10-12,14-16,18],通过敏感性发现研究术中未予以氨甲环酸静脉滴注维持[13,17],与术前单剂静脉应用氨甲环酸相比,术中维持的用药物剂量更大,一定程度的大剂量用药,具有更强的止血作用[21],因此与研究术中失血量的异质性来源一致,因而根据是否术中维持使用氨甲环酸进行亚组分析,术中维持的研究不具有异质性(P=0.13,I2=37%)[4,10-12,14-16,18],同时术中未维持的研究也不具有异质性(P=0.80,I2=0%)[13,17],结论与总的合并量保持一致,结合亚组分析的结果显示术中维持:(MD=-214.68,95%CI: -281.10至-148.27,P < 0.01),术中未维持:(MD=-402.52,95%CI:-522.74至-282.29,P < 0.01),总失血量具有显著性意义,氨甲环酸可以显著减少开放性脊柱手术围手术期总失血量,见图12。"

| [1] 裴福兴.加速康复外科是现代骨外科发展的趋势[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2017, 6(12):881-882. [2] 孙天胜,沈建雄,刘忠军,等.中国脊柱手术加速康复—围术期管理策略专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017, 10(4):271-279. [3] 周宗科,翁习生,孙天胜,等.中国骨科手术加速康复—围术期血液管理专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017, 10(1):1-7. [4] COLOMINA MJ, KOO M, BASORA M, et al. Intraoperative tranexamic acid use in major spine surgery in adults: a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled trialdagger. Br J Anaesth. 2017;118(3):380-390. [5] 中国康复技术转化及发展促进会,中国研究型医院学会关节外科学专业委员会,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会关节疾病防治分会,等.中国骨科手术加速康复围手术期氨甲环酸与抗凝血药应用的专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019, 12(2):81-88. [6] 翟荣华,佘勇军,屈文平.脊柱外科术中和术后应用氨甲环酸的临床效果[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(5):546-549. [7] LIU JM, PENG HM, SHEN JX, et al. A meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of using tranexamic acid in spine surgery. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;48(12): 937-942. [8] 谭响,匡荣彬,谢继勇,等.氨甲环酸对脊柱手术围术期作用的系统评价和Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(9): 785-791. [9] 郑菡,彭霁,任运钦,等.局部应用氨甲环酸对脊柱手术患者凝血及纤溶功能的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(5): 405-411. [10] ELWATIDY S, JAMJOOM Z, ELGAMAL E, et al. Efficacy and safety of prophylactic large dose of tranexamic acid in spine surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(24):2577-2580. [11] WONG J, EL BH, RAMPERSAUD YR, et al. Tranexamic Acid reduces perioperative blood loss in adult patients having spinal fusion surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008;107(5): 1479-1486. [12] FARROKHI MR, KAZEMI AP, EFTEKHARIAN HR, et al. Efficacy of prophylactic low dose of tranexamic acid in spinal fixation surgery: a randomized clinical trial. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011;23(4):290-296. [13] RAKSAKIETISAK M, SATHITKARNMANEE B, SRISAEN P, et al. Two doses of tranexamic acid reduce blood transfusion in complex spine surgery: a prospective randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(24): E1257-E1263. [14] KIM KT, KIM CK, KIM YC, et al. The effectiveness of low-dose and high-dose tranexamic acid in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled randomized study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(11):2851-2857. [15] SHI H, OU Y, JIANG D, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces perioperative blood loss of posterior lumbar surgery for stenosis or spondylolisthesis: a randomized trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(1):e5718. [16] CARABINI LM, MORELAND NC, VEALEY RJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of low-dose tranexamic acid versus placebo to reduce red blood cell transfusion during complex multilevel spine fusion surgery. World Neurosurg. 2018;110:e572-e579. [17] SHAKERI M, SALEHPOUR F, SHOKOUHI G, et al. Minimal dose of tranexamic acid is effective in reducing blood loss in complex spine surgeries: a randomized double-blind placebo controlled study. Asian Spine J. 2018;12(3):484-489. [18] MU X, WEI J, WANG C, et al. Intravenous administration of tranexamic acid significantly reduces visible and hidden blood loss compared with its topical administration for double-segment posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a single-center, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e821-e827. [19] CHERIYAN T, MAIER SN, BIANCO K, et al. Efficacy of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. Spine J. 2015;15(4):752-761. [20] 俞慧强,郑辉烈,李悦,等.Meta分析发表偏倚诊断方法研究[J].中国卫生统计, 2011,28(4):402-405. [21] 时亮,段亮,董向辉.大剂量氨甲环酸用于脊柱矫形及长节段固定手术的安全性和有效性分析[J].河北医学,2018, 24(10):1715-1719. [22] WINTER SF, SANTAGUIDA C, WONG J, et al. Systemic and topical use of tranexamic acid in spinal surgery: a systematic review. Global Spine J. 2016;6(3):284-295. [23] 朱前拯,于彩霞,陈星佐,等.氨甲环酸对人工关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折围手术期失血的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(7):623-626. [24] 石志刚,韩兵,付宇,等.氨甲环酸局部应用和静脉注射对全膝关节置换有效和安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018(11):1798-1804. [25] BIBLE JE, MIRZA M, KNAUB MA. Blood-loss Management in Spine Surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(2):35-44. [26] 杨明坤,李舟,何坤林,等.氨甲环酸在老年腰椎椎管狭窄症患者围手术期血液管理中的作用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2019, 17(4):235-239. [27] 罗兴鹏,解京明,王迎松,等.氨甲环酸在脊柱外科患者围手术期中的应用研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(11):87-90. [28] 王峰,王静成,南利平,等. 氨甲环酸应用于腰椎后路椎间融合术的安全性和有效性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(5): 422-430. [29] CRAVENS GT, BROWN MJ, BROWN DR, et al. Antifibrinolytic therapy use to mitigate blood loss during staged complex major spine surgery: Postoperative visual color changes after tranexamic acid administration. Anesthesiology. 2006;105(6):1274-1276. [30] 顾力军,张洪美,张斌,等.脊柱手术发生氨甲环酸相关型癫痫1例[J].中国骨伤, 2018,31(3):276-278. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [14] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [15] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||