Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5798-5803.doi: 10.12307/2021.345
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of crossing acupoints of the same name of hands and feet on pain after total knee arthroplasty
Ma Chenghao1, Huang Hai1, Lü Ruonan1, Qin Zuohai1, Wang Hao1, Nie Zhixing2, Han Dapeng2, Ouyang Guilin2
- 1Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 2Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China
-
Received:2021-01-06Revised:2021-01-08Accepted:2021-02-22Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-17 -
Contact:Ouyang Guilin, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China -
About author:Ma Chenghao, Master candidate, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
Supported by:Medical Key (Characteristic) Specialist Plan of Shanghai Changning District Health Committee, No. 20191003 (to OYGL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Chenghao, Huang Hai, Lü Ruonan, Qin Zuohai, Wang Hao, Nie Zhixing, Han Dapeng, Ouyang Guilin. Effect of crossing acupoints of the same name of hands and feet on pain after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5798-5803.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
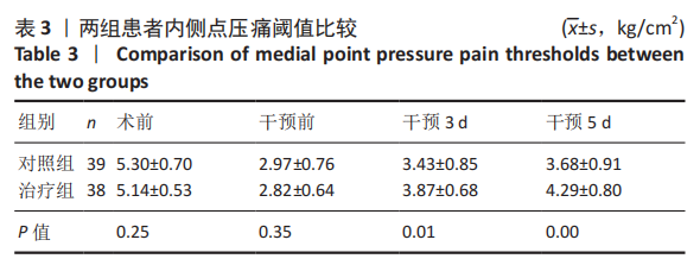
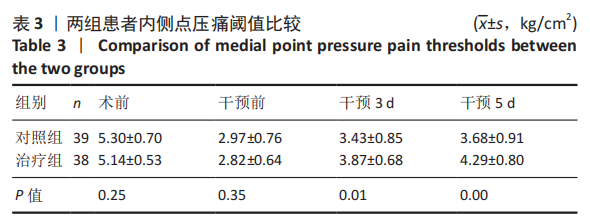
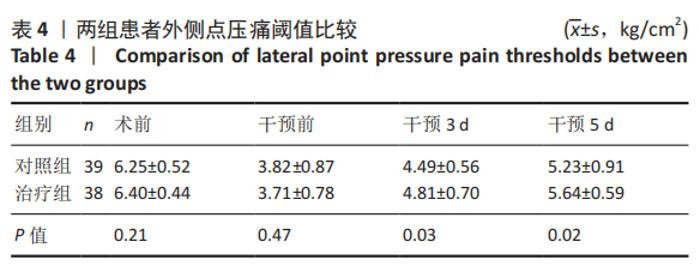
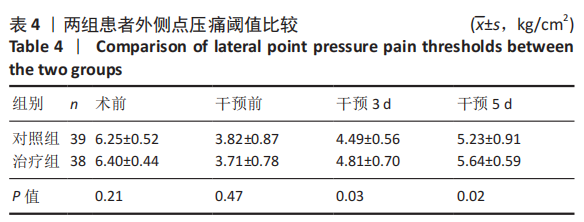
| [1] 赵光辉, 惠曙国, 贺强, 等. 全膝关节置换术后下肢绝对长度的变化模式[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2020,26(1):8-13. [2] 中华医学会麻醉学分会. 2017版中国麻醉学指南与专家共识[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2017. [3] SEIL R, PAPE D. Causes of failure and etiology of painful primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(9):1418-1432. [4] 康鹏德, 裴福兴. 加速康复外科国内外现状以及未来发展趋势[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(10):721-722. [5] 周宗科, 翁习生, 曲铁兵, 等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期管理策略专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1):1-9. [6] LUBIS A, RAWUNG R, TANTRI AR. Preemptive Analgesia in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparing the Effects of Single Dose Combining Celecoxib with Pregabalin and Repetition Dose Combining Celecoxib with Pregabalin: Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Pain Res Treat. 2018; 2018:3807217. [7] 吴厦, 房立业, 孙长鲛, 等. 全膝关节置换术中灌注“鸡尾酒”疗法的优势分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2020,26(10):877-879. [8] 宋海龙, 张雁. 酮咯酸氨丁三醇超前镇痛联合术后静脉自控镇痛用于全膝关节置换术的临床研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(20): 18-21. [9] 窦哲, 杨云, 黄健. 全膝关节置换围手术期的镇痛:措施与对策[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3716-3722. [10] PENG Z, ZHANG Y, GUO J, et al. Patient-Controlled Intravenous Analgesia for Advanced Cancer Patients with Pain: A Retrospective Series Study. Pain Res Manag. 2018;2018:7323581. [11] JUNG JY, CHO JH, CHUNG SH. Acupuncture for postoperative pain following total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review protocol. BMJ Open. 2015;5(11):e9573. [12] ZHONG S, HUANG H, XIE J, et al. Application of electroacupuncture for postoperative pain management after total knee arthroplasty: a study protocol for a single-blinded, randomised placebo-controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2019;9(4):e26084. [13] ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, LU M. Acupuncture combined with femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia after total knee arthroplasty and functional rehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2018;38(3):251-255. [14] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [15] 沈永勤. 浅论手足同名经上下相应交叉取穴法[J]. 陕西中医,2002, 23(8):730-731. [16] 黄海, 姚捷, 徐建斌, 等. 巨刺法联合中药熏蒸治疗风寒湿阻型膝骨关节炎的疗效观察[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(11):181-184. [17] HUANG H, SONG X, ZHAO L, et al. Opposing needling for analgesia and rehabilitation after unilateral total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, sham-controlled trial protocol. Trials. 2020;21(1):385. [18] BRIONES-CANTERO M, FERNANDEZ-DE-LAS-PENAS C, LLUCH-GIRBES E, et al. Effects of Adding Motor Imagery to Early Physical Therapy in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis who Had Received Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Pain Med. 2020;21(12):3548-3555. [19] JABER K, O’LEARY S, PEDLER A, et al. Evidence of generalised mechanical hyperalgesia in patients with advanced knee osteoarthritis undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(3):459-465. [20] LOYD BJ, STACKHOUSE SK, HOGAN C, et al. Peripheral Nociception Is Associated with Voluntary Activation Deficits and Quadriceps Weakness Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(17):1539-1545. [21] GOEL R, RONDON AJ, SYDNOR K, et al. Tourniquet Use Does Not Affect Functional Outcomes or Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(20):1821-1828. [22] AYTEKIN E, SUKUR E, OZ N, et al. The effect of a 12 week prehabilitation program on pain and function for patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: A prospective controlled study. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(2):345-349. [23] 董佩龙, 唐晓波, 王健, 等. 加速康复外科在全膝关节置换术中的随机对照研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(5):540-545. [24] ROSSO F, COTTINO U, DETTONI F, et al. Revision total knee arthroplasty (TKA): mid-term outcomes and bone loss/quality evaluation and treatment. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):280. [25] 蔡志清, 许杰, 邱梅玲, 等. “鸡尾酒”注射联合术后加速康复在膝关节置换术的应用[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(6): 675-679. [26] 徐莹, 刘士嘉, 田野. 术前下肢全长X线片测量在人工膝关节置换术中的价值[J]. 中国医科大学学报,2020,49(11):1035-1038. [27] ANNUNZIATA MA, MUZZATTI B, BIDOLI E, et al. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) accuracy in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer. 2020;28(8):3921-3926. [28] MASSAROTTI C, GENTILE G, FERRECCIO C, et al. Impact of infertility and infertility treatments on quality of life and levels of anxiety and depression in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019;35(6):485-489. [29] 程鹏, 朱琦, 姜婷, 等. TNF-α拮抗剂对传统治疗反应欠佳的强直性脊柱炎患者生活质量的影响[J]. 中华全科医学,2020,18(3):384-387. [30] 梁繁荣,王华. 针灸学[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社,2016. [31] 王庆勇, 屈媛媛, 冯楚文, 等. 针刺对神经病理性疼痛的镇痛机制[J]. 中国针灸,2020,40(8):907-912. [32] 田雪, 陶元祥. 术后持续性疼痛的研究进展[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2019(6):655-659. [33] 沈松坡, 翁习生, 冯宾. 全膝关节置换术后疼痛原因分析及疼痛预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(17):1082-1088. [34] BESWICK AD, WYLDE V, GOOBERMAN-HILL R, et al. What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open. 2012;2(1):e435. [35] 武晓冬, 王佩. 针刺镇痛机理研究概述[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 1999,5(12):59-62. [36] YIN C, BUCHHEIT TE, PARK JJ. Acupuncture for chronic pain: an update and critical overview. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2017;30(5):583-592. [37] 朱娟霞, 唐超, 肖丹秦. 丘脑中央下核内的阿片受体在介导大鼠电针镇痛中的作用[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2006,27(15):1376-1379. [38] BLIKMAN T, RIENSTRA W, VAN RAAIJ TM, et al. Duloxetine in OsteoArthritis (DOA) study: study protocol of a pragmatic open-label randomised controlled trial assessing the effect of preoperative pain treatment on postoperative outcome after total hip or knee arthroplasty. BMJ Open. 2016;6(3):e10343. [39] 龚萍, 娄必丹. 针刺上下肢同名经交叉对应穴治疗原发性膝关节骨病的临床观察[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2010,30(9):226-228. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [6] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [8] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [9] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [10] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [11] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [12] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [13] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [14] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [15] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||