Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 612-618.doi: 10.12307/2022.975
Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty
Xu Xiangjun1, Wang Chao2, Song Qunshan1, Li Bingyan3, Zhang Jichao4, Wang Guodong1, Dong Yuefu1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Lianyungang, Xuzhou Medical University, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China; 3Lianyungang Clinical College of Nanjing Medical University, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China; 4School of Materials Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
-
Received:2022-01-04Accepted:2022-02-11Online:2023-02-08Published:2022-06-23 -
Contact:Dong Yuefu, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital of Lianyungang, Xuzhou Medical University, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Xu Xiangjun, Master candidate, Affiliated Hospital of Lianyungang, Xuzhou Medical University, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31670956 (to DYF); Lianyungang City Health Science and Technology Project, No. 202101 (to DYF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
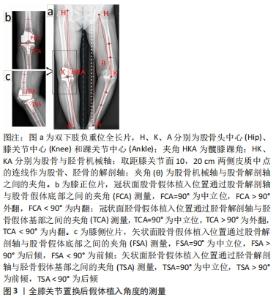
2.2.1 股骨髓内定位杆开口 股骨髓内定位杆开口位置的选择直接影响定位杆插入髓腔的位置,进而影响截骨的准确性。髓内杆直径约10 mm,插入深度常超过200 mm[11],10 mm的开口差异将导致3°左右截骨偏差。虞丁柱等[9]在100例膝关节三维建模中测量分析了4种不同开口点的相关性,发现以后交叉韧带止点内上方1 cm处作为开口点比股骨髁间切迹最深点、外科经髁轴(surgical trans epicondylar axis,sTEA)与Whiteside线交点及股骨远端解剖轴与关节面的交点更容易做到精确截骨和获得良好的下肢力线。XIAO等[12]通过50例建模分析发现以股骨髁间切迹最深处为髓内开口点的截骨误差最小。丁裕润等[13]在股骨CT上分别标记冠状面解剖轴与矢状面解剖轴,将两个层面解剖轴的交点在关节面的投影点作为开口点以提高手术成功率。虽然髓内定位的优势在全膝关节置换中被认可与应用[14],但是MADERBACHER等[15]研究发现髓内杆不能保证股骨假体在矢状面的对齐,同时也有学者通过特制的器械进行髓外定位,其截骨准确性可以媲美计算机导航[16]。 综上,以髁间切迹内侧、后交叉韧带止点上1 cm处为髓内开口点可以使股骨假体植入更精准。 2.2.2 股骨冠状面假体植入角度 按不同对齐理念可将冠状面假体植入分为经典机械力学对线全膝关节置换术(mechanical alignment TKA,MA-TKA)和运动力学对线全膝关节置换术(kinematic alignment TKA,KA-TKA)[6]。为使压力均匀地分布在假体内外侧,中立位对线被认为是机械力学对线全膝关节置换术“金标准”,即术后股骨头中心、踝关节中心、膝关节中心在一条直线上,也有学者将±3°范围内的下肢力线均称作是“安全区”。支持运动力学对线全膝关节置换术的学者在X射线片中测得健康人群的下肢力线并非都是中立位,其认为应该从三维层面恢复膝关节自然的运动状态,通过在重建的骨关节炎模型上模拟手术、制作个性化截骨器和定制假体,准确匹配假体的大小和植入位置,从而在最小的手术创伤下真正重建膝关节的生理运动[7,10]。见表1。 "

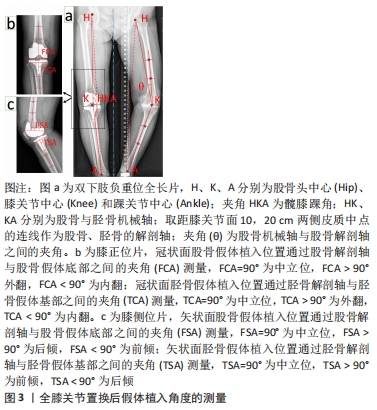
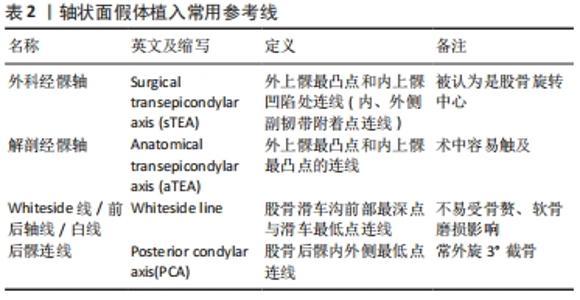
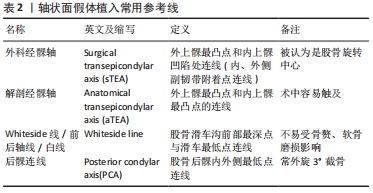
股骨冠状面的外翻截骨角度(valguscut angle,VCA)包括使用固定值和个体化测量两种方法。ANDREWS等[17-18]通过对1 135例膝骨关节炎患者(含347例难以辨认解剖标志的肥胖患者)术中固定的6°外翻截骨发现:无论术前患膝是否存在内外翻畸形,术后获得中性对齐的成功率均在82.5%以上,证实了固定外翻角度截骨的可行性。DAVIS等[19]在外翻膝中使用4°外翻截骨角度,在内翻膝和中立膝中使用5°外翻截骨角度,两组术后在冠状面均表现为中立位对齐。GLASSER等[20]发现与在尸体中通过膝关节压力传感器得到的数据差别较大,在下肢模型中3°,5°,7°外翻截骨角度术后的步态模拟评分无差别[21]。在使用股骨解剖轴与机械轴夹角作为个体化外翻截骨角度与3°-7°固定外翻截骨角度的临床对照研究中,学者们发现个体化外翻截骨角度可以提高术后下肢中立位对线的准确性,尤其是重度畸形的膝关节[22-25]。 与外翻截骨不同,内翻截骨在临床上存在较大的争议。DEAKIN等[26]分析步态周期中膝关节压力感受器的变化发现:每增加1°内翻,内侧间室负荷增加约5%,超过3°内翻导致聚乙烯异常磨损并显著增加内侧塌陷风险。LIU等[27]在假体的有限元分析中发现股骨假体的内翻角度越大,聚乙烯垫片最大接触应力和von Mises应力越大。但是SCHIFFNER等[28]经过3-5年随访发现术前存在内翻畸形的膝骨关节炎患者在全膝关节置换术后保留内翻对齐的临床评分高于术后恢复至中立位对线患者。 综上,尽管冠状面“最佳力线”仍存在争议,在未被可靠证实机械力学对线、运动力学对线哪个更准确之前,经典的机械力学对线仍是当前全膝关节置换的金标准。因此,为获得良好术后力线及临床功能,在全膝关节置换中应采用4°-6°外翻截骨角或根据术前测量进行个体化截骨,以保证股骨假体植入后的中性对齐。 2.2.3 股骨矢状面假体植入角度 矢状面股骨假体位置容易受股骨长度、股骨弓角度、股骨远端屈曲度、内外髁不同曲率、股骨远端截骨厚度、假体大小等因素的影响[29]。矢状面股骨假体术后放射学评价标准包括:股骨假体的前后倾(前倾即假体的屈曲,后倾即假体的伸展)、后髁偏心距(posterior condylar offset,PCO)和股骨前皮质切迹,临床功能运动评价标准主要是屈曲活动范围。 有学者认为股骨假体轻度前倾与术后下肢良好的生物力学相关[30]。TSUKEOKA等[31]发现股骨假体前倾2°导致屈曲间隙变化约为2 mm。在高屈曲型股骨假体的研究中,MURPHY等[32]发现增加前倾可立即增加膝关节最大屈曲角度,但是AMIN等[33]认为高屈曲假体与普通假体在膝关节活动度、负重屈曲和并发症方面均无明显差异。KIM等[34]将术后股骨假体矢状面位置分为3组:前倾大于3° 748例、后倾大于1° 565例、中性对齐1 735例,经过回顾研究发现超过3°前倾和大于1°后倾大幅增加翻修比例。 BELLEMANS等[35]在透视下发现后髁偏心距每减少2 mm,最大屈曲角减少12.2°,认为后髁偏心距与膝关节屈曲呈正相关,其原因是增加后髁偏心距可以在股骨假体与聚乙烯垫片撞击发生之前获得更大的屈曲。但ISHII等[36]对此持不同观点,并通过对170例患者术后1年的随访发现后髁偏心距与屈曲活动范围无显著相关性。 股骨前皮质切迹导致的髁上骨折(Notching)是矢状面假体植入不恰当的严重并发症。STAMIRIS等[37]发现股骨前皮质受损3 mm将使扭转强度降低31%,大于3.5°的前倾角使屈曲挛缩的风险增加3倍。值得注意的是,虽然股骨前皮质切迹发生率在30%-40%之间,髁上骨折发生率只在0.3%-2.5%[38]。 综上,矢状面股骨假体的植入应在前倾为0°-3°范围内,这样既可以有效避免股骨假体后倾导致的髁上骨折风险和过度前倾导致的伸膝障碍,也可以获得理想的屈曲范围。 2.2.4 股骨轴状面假体植入角度 动态的屈曲间隙平衡被认为是全膝关节置换股骨轴状面假体植入的关键。由于股骨远端并非是对称的球体,无论是内侧还是外侧,都无法以髁为中心拟合出一个符合整个股骨轮廓的圆形,并且屈膝时滚动和滑动同时存在于股骨与胫骨的相对运动中,这使得膝关节旋转中心更加复杂[39-40]。通过股骨远端的解剖标志,学者们定义了Whiteside线(前后轴线)、外科经髁轴、解剖经髁轴(anatomical trans epicondylar axis,aTEA)、后髁轴(posterior condylar axis,PCA)等参考线,借助精准的三维建模、有限元分析、计算机导航、个性化截骨工具和机器人等技术展开广泛研究。见图4,表2。 "

CHURCHILL等[41]突破了膝关节瞬时旋转中心的传统方法,将最佳屈曲轴固定在股骨上,证实外科经髁轴非常接近最佳屈曲轴。但是LUSTIG等[42]通过影像学标记外科经髁轴,发现外科经髁轴与股骨髁的后表面和远端的距离并不相等,认为外科经髁轴不是了解股骨远端屈曲运动的充分基础。OLCOTT等[43]对比Whiteside线、外科经髁轴和后髁轴产生的屈曲间隙,发现参照外科经髁轴植入假体产生的屈曲间隙最稳定,其次是Whiteside线和后髁轴。后髁轴除了受骨赘影响外,也受内外髁畸形影响,但因其操作方便,临床上常用后髁轴外旋3°-5°的方法进行假体植入[44]。与后髁轴易受骨赘、种族影响不同,AKAGI等[45]研究发现Whiteside线不在负重区,不受关节畸形、性别、年龄、种族的影响且与解剖经髁轴的关系相对固定,可以作为重度畸形患者的辅助标志。临床医师在术中可以使用多个参考轴以提高假体植入精确度,JANG等[46]用大量样本消除混杂变量后对比多条旋转轴发现,参考单一轴线并不准确可靠,将后髁轴、Whiteside线、外科经髁轴或解剖经髁轴组合使用时股骨假体旋转的准确性明显提高。 除了股骨解剖学标志定位技术外,胫骨优先截骨的屈曲间隙平衡技术也可以实现对称的屈曲间隙。LEE等[47]发现术中用间隙张紧装置植入假体与参照后髁轴外旋3°植入假体的患者术后2年在功能上无差异。 综上,股骨假体轴状面旋转对齐建立了平衡的屈曲间隙,这是获得正确与稳定的膝关节运动学的关键。为避免发生股骨假体旋转对位不良导致的屈曲间隙不平衡、髌股关节对位不良甚至髌骨脱位,应将股骨假体相对于后髁轴外旋3°植入。 2.3 胫骨假体的植入 "
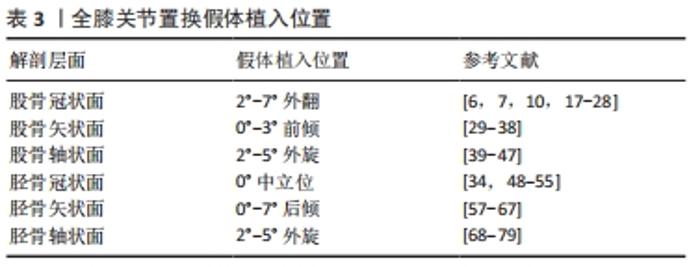
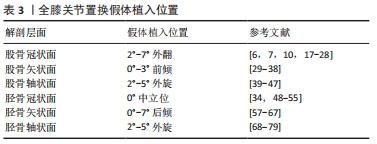
2.3.1 胫骨冠状面假体植入角度 全膝关节置换术后胫骨假体冠状面无论是内翻还是外翻都会影响假体的使用寿命[34,48-49]。DONG等[48]的有限元正交试验表明胫骨假体在90°中立位时聚乙烯垫片接触压力最小,内翻和外翻都将导致垫片接触压增大。KIM等[34]发现2 168例全膝关节置换胫骨假体中立位对齐组翻修率为0,而内翻组中880例全膝关节置换有3.4%需要翻修,其认为胫骨假体任何内翻均增加手术失败率。FANG等[49]通过随访6 070例全膝关节置换发现与中立位对齐相比,内翻和外翻时胫骨内侧塌陷的失败风险分别增加了6.9倍和3.7倍。 在下肢力线中,胫骨解剖轴与机械轴基本重合,因此通过胫骨髓内杆定位解剖轴和通过髓外定位标志辨别膝关节中心与踝关节中心是胫骨冠状面假体植入的关键。 有学者认为胫骨髓内定位工具相对简单、操作容易,而且适用于踝关节畸形、肿胀等异常情况,在精确性和可重复性方面比髓外定位有优势。但由于胫骨平台内外径与前后径不一致(近似椭圆形),且胫骨干中心与干骺端中心不也一致[50],理想的髓内开口点根据胫骨形态而变化。理想的冠状开口点在近端解剖轴和前交叉韧带止点附近,胫骨平台内侧缘39.8%-60.5%;理想的矢状开口点在近端解剖轴和胫骨平台前缘1/3处附近[51]。OH等[52]通过测量胫骨解剖特征计算出髓内定位杆开口位置,随着胫骨近端内侧角和胫骨近端弯曲角的增加,髓内开口向内侧移动;随着平台的内外宽度和胫骨长度的增加,髓内开口向外侧移动;随着胫骨后倾角和干骺端角的增加,髓内开口前移。 胫骨髓外定位因创伤小、术后脂肪栓塞和静脉血栓并发症少等原因在临床中应用广泛。髓外定位包括近端膝关节中心和远端踝关节中心两处定位,常通过胫骨结节、前交叉韧带止点、足背动脉(DPA)、第二跖骨(MT2)、趾长伸肌腱(EDLT)、拇长伸肌腱(EHLT)等解剖标志辅助定位[53-56]。SCHNEIDER等[53]认为拇长伸肌腱是最准确的解剖标志,在距骨中心内侧1 cm以内,踝关节内外旋对其影响小,即使足部严重畸形也可作为踝关节中心的标志。SUGIMURA等[54]认为足背动脉与踝关节中心距离最近,并且发现内踝中心更靠近距骨中心。值得注意的是,当使用第二跖骨作为髓外标志时应瞄准第二跖骨的近端,第二跖骨水平面5 mm差异可导致冠状面约1°的对齐变化[55]。 综上,为避免胫骨假体出现内外翻导致内外侧应力不平衡、胫骨塌陷、无菌性松动等问题,在冠状面胫骨假体植入时应借助髓内或髓外系统使假体与胫骨机械轴垂直,即90°植入。 2.3.2 胫骨矢状面假体植入角度 胫骨后倾角的生物学意义是使膝关节屈伸运动时股骨髁能正常地滑动及滚动,这有利于膝关节的屈曲运动。矢状面胫骨假体植入角度由胫骨近端后倾度与胫骨机械轴决定。 调整后倾截骨角简单易行的方法是调节定位杆与皮肤的距离[57-58],在截骨平面200 mm处,皮肤与定位杆之间的距离每增加3.5 mm,后倾增加1°。SHI等[59]发现胫骨后倾与术后屈曲活动范围正相关,后倾0°与7°之间的屈曲差异为5.0°,且后倾在0°-7°范围内的改变不影响膝关节稳定性。但是KANSARA等[60]认为后倾微小变化对屈曲范围无显著影响。此外KANG等[61-63]通过有限元分析发现过度后倾可导致膝关节韧带松弛松动,后倾越大副韧带张力越紧。 胫骨后倾与后髁偏心距存在复杂的交互作用,FUJIMOTO等[64]在分析整个膝关节活动过程中发现:在屈膝0°-90°时主要受后髁偏心距的影响,而在屈膝90°-135°时受胫骨后倾与内外侧韧带的屈曲平衡影响较大。HAN等[65]认为增加胫骨后倾会降低后髁偏心距的生物力学效应,要避免胫骨过度后倾。WANG等[66]通过建模分析发现股骨假体轻微的前倾对术后运动学影响不大,但相同程度的胫骨假体前倾对股骨前后平移和胫骨轴向旋转的影响均较大。 YOO等[67]发现矢状面常用的5个解剖参考线——胫骨前皮质线(ACL)、近端解剖轴(PAA)、中央解剖轴(CAA)、胫骨近端后皮质线(PCL)和腓骨轴(FSA)都有其独特的临床意义:胫骨前皮质线可用于髓外引导;中央解剖轴与髓内定位或翻修时的延伸杆有关;腓骨轴术中容易触诊;胫骨近端后皮质线可以辅助辨别胫骨假体柄的方向。通过90组参考线的数据对比分析认为最具代表性的是近端解剖轴。 综上,在任何情况下胫骨假体植入时都不应前倾,因为前倾导致屈曲间隙受损和膝关节的不稳定。同时为了避免超过8°后倾导致的韧带松弛和聚乙烯磨损,应该将胫骨假体相对于胫骨近端解剖轴后倾1°-7°植入。 2.3.3 胫骨轴状面假体植入角度 轴状面旋转截骨造成的偏差会导致异常的髌骨轨迹、髌股关节不稳等问题。解剖标志定位技术与ROM技术是轴状面胫骨假体植入的常用方法[68]。虽然解剖标志受个体解剖变异、关节畸形或软组织的影响,但仍具有重要的参考价值,主要包括:①Akagi线[69];②胫骨结节[70];③第二跖骨[69];④胫骨前皮质[71];⑤胫骨后髁轴[72]。 有学者认为,因为Akagi线与胫骨前后轴基本平行,可作为胫骨假体旋转对线的金标准[73]。在膝关节伸直时,股骨与胫骨横轴同时平行于股骨的旋转中心外科经髁轴,胫骨前后轴通过后交叉韧带止点且垂直于外科经髁轴,在胫骨平台的投影近似平行于后交叉韧带止点与髌腱内侧缘的连线即Akagi线。MA等[74]在重建膝关节三维模型后将外科经髁轴投影到胫骨平台,联合胫骨平台的几何中心、后交叉止点、髌腱、胫骨结节、第二跖骨定义多条参考线,研究发现Akagi线变异性最小。但是KAWAGUCHI等[75]认为Akagi线较难在截骨面上辨认,且在左膝参考Akagi线会造成胫骨假体的内旋。 在胫骨结节对准胫骨假体中心的基础上[70],有学者发现胫骨结节中内1/3比胫骨结节中心在旋转对线中更为精确可靠[76]。但是HOWELL等[77]在115例参照胫骨结节中内1/3的全膝关节置换术后影像学中发现,胫骨假体前后轴与胫骨结节中内1/3之间的距离≥2 mm,且有超过5°的旋转误差。在重度内翻畸形的患者中,赵旻暐等[78]发现参照胫骨结节中内1/3术后下肢力线不良率高达8.7%,胫骨假体容易相对股骨假体外旋。 研究者发现第2跖骨与胫骨前后轴之间存在21.5°-24.0°的外旋[69],定位简单但易受足畸形的影响。胫骨前皮质因受关节畸形影响小、变异率低,被认为是可靠的解剖标志[71,74]。参照胫骨后髁轴植入假体可以增加胫骨假体的覆盖率,但可能导致假体内旋[72]。 ROM技术又称自我形合技术[68],指在完成截骨及软组织松解平衡后,先精准植入股骨假体再放置胫骨假体试模和垫片,经过反复屈伸膝关节,标记胫骨假体试模相对于股骨假体自我调整的最合适位置。在理论上更符合胫股关节运动力学,常结合其他解剖标志共同完成胫骨假体的旋转定位。值得注意的是,当股骨假体植入位置不正确时,将胫骨假体与其“校正”以求得整体的中立位对齐会增加手术失败的风险[79]。 综上,胫骨假体旋转定位方法较多,但尚无一种通用于所有患者的可靠方法。Akagi线理论上平行于前后轴,但在合并严重内外翻畸形患者中的准确性还有待确认;ROM技术依赖于股骨假体的精准植入,并且可能发生髌股关节并发症;胫骨结节、第二跖骨、胫骨前皮质、胫骨后髁轴、跟腱等解剖标志的应用价值还需要进一步研究。因此,在胫骨假体植入时可以参照Akagi线的同时运用ROM技术,综合运用多种旋转定位方式,避免较大旋转误差。 目前常见的全膝关节置换假体植入位置,见表3。 "
| [1] 中华医学会骨科分会关节外科学组,吴阶平医学基金会骨科学专家委员会.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130. [2] ZHANG Z, HUANG C, JIANG Q, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(19):1213. [3] CANOVAS F, DAGNEAUX L. Quality of life after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(1S):S41-S46. [4] 袁伟.运动力学对线的人工膝关节有限元建模和生物力学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017. [5] MATHIS DT, LOHRER L, AMSLER F, et al. Reasons for failure in primary total knee arthroplasty - An analysis of prospectively collected registry data. J Orthop. 2020;23:60-66. [6] LUSTIG S, SAPPEY-MARINIER E, FARY C, et al. Personalized alignment in total knee arthroplasty: current concepts. SICOT J. 2021;7:19. [7] CASTELLI CC, FALVO DA, IAPICCA ML, et al. Rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(1):4. [8] 曲波,刘洋,马根成.术前负重位双下肢全长数字化X线测量在全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(8):843-845. [9] 虞丁柱,王翠,张驰,等.常用股骨髓内定位杆进针点选择的CT三维重建评价[J].青岛大学学报(医学版),2020,56(5):509-512. [10] 朱诗白,陈曦,钱文伟,等.浅谈全膝关节置换术中的冠状位下肢力线[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(9):665-669. [11] OU YL, LI PY, XIA H. Optimal Sagittal Insertion Depth and Direction of Femoral Intramedullary Rod in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Chinese Osteoarthritis Patients. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1238-1244. [12] XIAO J, WANG C, ZHU L, et al. Improved method for planning intramedullary guiding rod entry point in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(5):693-698. [13] 丁裕润,王伟力.CT三维重建在全膝关节置换中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(48):9020-9024. [14] BONO OJ, OLCOTT CW, CARANGELO R, et al. Femoral Intramedullary Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Indications, Results, Pitfalls, Alternatives, and Controversies. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(1):12-14. [15] MADERBACHER G, SCHAUMBURGER J, BAIER C, et al. Appropriate sagittal femoral component alignment cannot be ensured by intramedullary alignment rods. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8): 2453-2460. [16] MULLAJI AB, KHALIFA AA, SHETTY G, et al. Comparison with Navigation of a Novel Three-Step Technique for Improving Accuracy of the Distal Femoral Resection during Conventional TKA: A Case-Control Study. J Knee Surg. 2021 Jul 8. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1731458. [17] ANDREWS SN, BEELER DM, PARKE EA, et al. Fixed Distal Femoral Cut of 6° Valgus in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Radiographic Review of 788 Consecutive Cases. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4):755-759. [18] ANDREWS S, WELDON E, STICKLEY C, et al. Post total knee arthroplasty alignment of 347 consecutive obese patients receiving a fixed distal femoral cut of 6° valgus. J Orthop. 2019;18:113-116. [19] DAVIS JA, HOGAN C, DAYTON M. Postoperative Coronal Alignment After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Does Tailoring the Femoral Valgus Cut Angle Really Matter? J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(8):1444-1448. [20] GLASSER J, MARIORENZI M, BLOOD T, et al. Distal femoral valgus cut angles unreliable in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop. 2021;24:29-33. [21] WERNER FW, AYERS DC, MALETSKY LP, et al. The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):349-355. [22] ZHOU K, ZHOU Z, SHI X, et al. Effect of individual distal femoral valgus resection in total knee arthroplasty for patients with valgus knee: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;52:309-313. [23] NAM D, VAJAPEY S, HAYNES JA, et al. Does Use of a Variable Distal Femur Resection Angle Improve Radiographic Alignment in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):91-96. [24] PALANISAMI D, IYYAMPILLAI G, SHANMUGAM S, et al. Individualised distal femoral cut improves femoral component placement and limb alignment during total knee replacement in knees with moderate and severe varus deformity. Int Orthop. 2016;40(10):2049-2054. [25] SHI X, LI H, ZHOU Z, et al. Individual valgus correction angle improves accuracy of postoperative limb alignment restoration after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(1):277-283. [26] DEAKIN AH, SARUNGI M. A comparison of variable angle versus fixed angle distal femoral resection in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1133-1137. [27] LIU HX, SHANG P, YING XZ, et al. Shorter survival rate in varus-aligned knees after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8):2663-2671. [28] SCHIFFNER E, WILD M, REGENBRECHT B, et al. Neutral or Natural? Functional Impact of the Coronal Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(8):820-824. [29] ZHANG X, WANG Q, XU X, et al. Is the femoral component flexion affected by the sagittal femoral shaft bowing in conventional intramedullary guided TKA? J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):701. [30] KOH YG, LEE JA, LEE HY, et al. Effect of sagittal femoral component alignment on biomechanics after mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):400. [31] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, LEE TH. The effect of a sagittal cutting error of the distal femur on the flexion-extension gap difference in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(7):1099-1102. [32] MURPHY M, JOURNEAUX S, HIDES J, et al. Does flexion of the femoral implant in total knee arthroplasty increase knee flexion: a randomised controlled trial. Knee. 2014;21(1):257-263. [33] AMIN RM, VASAN V, ONI JK. Kneeling after Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(2):138-143. [34] KIM YH, PARK JW, KIM JS, et al. The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):379-385. [35] BELLEMANS J, BANKS S, VICTOR J, et al. Fluoroscopic analysis of the kinematics of deep flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Influence of posterior condylar offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(1):50-53. [36] ISHII Y, NOGUCHI H, TAKEDA M, et al. Posterior condylar offset does not correlate with knee flexion after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9): 2995-3001. [37] STAMIRIS D, GKEKAS NK, ASTERIADIS K, et al. Anterior femoral notching ≥ 3 mm is associated with increased risk for supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 Apr 26. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-02989-z. [38] PURANIK HG, MUKARTIHAL R, PATIL SS, et al. Does Femoral Notching During Total Knee Arthroplasty Influence Periprosthetic Fracture. A Prospective Study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(6):1244-1249. [39] NIKI Y, NAGAI K, SASSA T, et al. Comparison between cylindrical axis-reference and articular surface-reference femoral bone cut for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3741-3746. [40] KOH YG, NAM JH, CHUNG HS, et al. Gender difference exists in sagittal curvature of the distal femoral condyle morphology for osteoarthritic population. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(12):3740-3746. [41] CHURCHILL DL, INCAVO SJ, JOHNSON CC, et al. The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(356):111-118. [42] LUSTIG S, LAVOIE F, SELMI TA, et al. Relationship between the surgical epicondylar axis and the articular surface of the distal femur: an anatomic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(7):674-682. [43] OLCOTT CW, SCOTT RD. A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(1):22-26. [44] COHEN DA, GURSEL AC, LOW AK. How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based comparison of varus and valgus knees. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):92. [45] AKAGI M, YAMASHITA E, NAKAGAWA T, et al. Relationship between frontal knee alignment and reference axes in the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(388):147-156. [46] JANG ES, CONNORS-EHLERT R, LIARNO S, et al. Accuracy of Reference Axes for Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Computed Tomography-Based Study of 2,128 Femora. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(23):e125. [47] LEE JK, LEE S, CHUN SH, et al. Rotational alignment of femoral component with different methods in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):217. [48] DONG Y, ZHANG Z, DONG W, et al. An optimization method for implantation parameters of individualized TKA tibial prosthesis based on finite element analysis and orthogonal experimental design. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):165. [49] FANG DM, RITTER MA, DAVIS KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):39-43. [50] MEIER M, JANSSEN D, KOECK FX, et al. Variations in medial and lateral slope and medial proximal tibial angle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3):939-946. [51] LASKIN RS. Instrumentation pitfalls: you just can’t go on autopilot! J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3 Suppl 1):18-22. [52] OH SM, BIN SI, LEE BS, et al. The entry point of intramedullary tibia cutting guide should vary according to the individual tibia morphology in TKA. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(3):391-400. [53] SCHNEIDER M, HEISEL C, ALDINGER PR, et al. Use of palpable tendons for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(2):219-226. [54] SUGIMURA N, IKEUCHI M, IZUMI M, et al. The dorsal pedis artery as a new distal landmark for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(11):2618-2622. [55] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, LEE TH. Accuracy of the second metatarsal as a landmark for the extramedullary tibial cutting guide in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(12):2969-2974. [56] HINO M, NAKAGAWA S, ARAI Y, et al. Extensor hallucis longus tendon is a new distal landmark for coronal tibial component alignment in total knee arthroplasty: A study of magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020;28(1):2309499020912340. [57] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, YOSHINO K. Preoperative planned distance between the skin surface and the guide rod provides accurate posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019; 139(8):1133-1139. [58] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y. The distance from the extramedullary cutting guide rod to the skin surface as a reference guide for the tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2016;23(2):314-317. [59] SHI W, JIANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. The influence of posterior tibial slope on the mid-term clinical effect of medial-pivot knee prosthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):563. [60] KANSARA D, MARKEL DC. The effect of posterior tibial slope on range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6):809-813. [61] KANG KT, KWON SK, SON J, et al. The increase in posterior tibial slope provides a positive biomechanical effect in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(10):3188-3195. [62] KANG KT, KOH YG, SON J, et al. A computational simulation study to determine the biomechanical influence of posterior condylar offset and tibial slope in cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(1):69-78. [63] KANG KT, KOH YG, SON J, et al. Influence of Increased Posterior Tibial Slope in Total Knee Arthroplasty on Knee Joint Biomechanics: A Computational Simulation Study. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):572-579. [64] FUJIMOTO E, SASASHIGE Y, MASUDA Y, et al. Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope and medial/lateral ligament balance on knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(12):2704-2712. [65] HAN HS, KANG SB. Interactive effect of femoral posterior condylar offset and tibial posterior slope on knee flexion in posterior cruciate ligament-substituting total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(2):335-340. [66] WANG ZW, LIU YL, LIN KJ, et al. The effects of implantation of tibio-femoral components in hyperextension on kinematics of TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(10):2032-2038. [67] YOO JH, CHANG CB, SHIN KS, et al. Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(4):586-592. [68] GRASSI A, PIZZA N, LOPOMO NF, et al. No differences in knee kinematics between active and passive flexion-extension movement: an intra-operative kinematic analysis performed during total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):12. [69] AKAGI M, OH M, NONAKA T, et al. An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):213-219. [70] LU Y, REN X, LIU B, et al. Tibiofemoral rotation alignment in the normal knee joints among Chinese adults: a CT analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):323. [71] KIM JI, JANG J, LEE KW, et al. Anterior tibial curved cortex is a reliable landmark for tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):252. [72] OKAZAKI Y, PUJOL N. The use of an asymmetrical tibial tray in TKA optimises tibial rotation when fitted to the posterior tibial plateau border. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(12):3821-3826. [73] SAFFARINI M, NOVER L, TANDOGAN R, et al. The original Akagi line is the most reliable: a systematic review of landmarks for rotational alignment of the tibial component in TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(4):1018-1027. [74] MA Y, MIZU-UCHI H, USHIO T, et al. Bony landmarks with tibial cutting surface are useful to avoid rotational mismatch in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1570-1579. [75] KAWAGUCHI K, INUI H, TAKETOMI S, et al. Intraoperative Tibial Anteroposterior Axis Could Not Be Replicated After Tibial Osteotomy in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(10):2371-2375. [76] DREXLER M, BACKSTEIN D, STUDLER U, et al. The medial border of the tibial tuberosity as an auxiliary tool for tibial component rotational alignment during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(6):1736-1742. [77] HOWELL SM, CHEN J, HULL ML. Variability of the location of the tibial tubercle affects the rotational alignment of the tibial component in kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2288-2295. [78] 赵旻暐,田华,曾琳,等.中国人采用胫骨结节及胫前肌腱定位的髓外截骨法术后胫骨假体冠状位力线的测量与分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2):351-355. [79] RITTER MA, DAVIS KE, MEDING JB, et al. The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1588-1596. |
| [1] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [2] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [3] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [4] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [5] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinbiao, Li Xiaoming, Xing Wanlin, Ma Fei, Yu Qiaoya, Dai Rongqin. Early warning efficacy of thrombus molecular markers after total knee arthroplasty in patients complicated with venous thromboembolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 572-577. |
| [7] | Wang Shuai, Wang Liancheng, Zhang Shuhao, Li Fuli, Dong Jiaxing, Zhang Yajie. Correlation of the electromyography ratio of the paraspinal muscles on the convex and concave sides with Cobb angle, apical vertebra translation, and coronal balance distance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1402-1406. |
| [8] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [9] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [10] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [11] | Ma Qiaoqiao, Wu Zerui, Guo Zhuotao, Zhang Kai, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. Absence of a tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5831-5836. |
| [12] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Lu Yingzi. Intra-articular tranexamic acid at different volumes and doses affects blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5303-5310. |
| [13] | Quan Honglei, Zheng Jiejiao, Feng Youyan, Zhang Jie, Zhu Yinghui. Early hip abductor training to improve balance and walking ability after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5311-5316. |
| [14] | Song Wei, Zhang Yaxin, Jia Dazhou, Sun Yu. Adjective application of dexamethasone combined with furosemide for early pain and swelling after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5317-5322. |
| [15] | Li Kai, Liu Zhendong, Li Xiaolei, Wang Jingcheng. Risk factors for recurrent prosthesis dislocation after total hip arthroplasty through posterolateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 354-358. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||