Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 993-999.doi: 10.12307/2024.122
Previous Articles Next Articles
Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1
Wang Wen1, 2, Zheng Pengpeng1, Meng Haohao1, Liu Hao1, 2, Yuan Changyong1, 2
- 1School of Stomatology, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-01Accepted:2023-03-29Online:2024-03-08Published:2023-07-15 -
Contact:Yuan Changyong, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, School of Stomatology, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Wen, Master, Attending physician, School of Stomatology, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
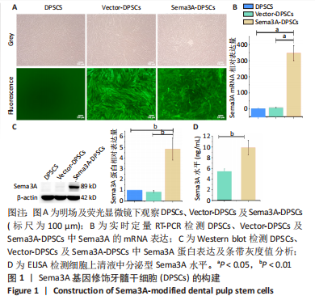
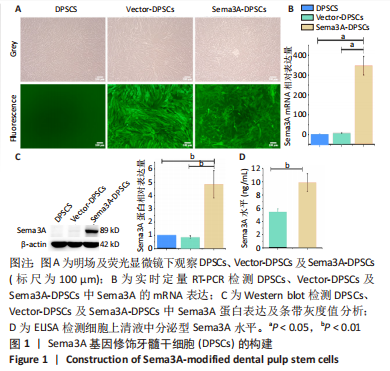
2.1 Sema3A基因修饰DPSCs的构建 使用慢病毒载体将Sema3A基因转导至DPSCs中构建Sema3A基因修饰DPSCs(Sema3A-DPSCs),并使用嘌呤霉素进一步筛选转导成功的细胞。在荧光显微镜下观察到慢病毒处理的Sema3A-DPSCs及Vector-DPSCs均表达绿色荧光,而未经慢病毒处理的DPSCs无绿色荧光,见图1A。相比于DPSCs及Vector-DPSCs,Sema3A-DPSCs中Sema3A的mRNA及蛋白水平均显著上调,见图1B,C。ELISA检测细胞上清液中分泌型Sema3A水平,结果显示,Sema3A-DPSCs组分泌型Sema3A水平明显高于其他2组,见图1D。以上结果证明,构建的Sema3A基因修饰DPSCs可成功高表达并分泌Sema3A因子。"
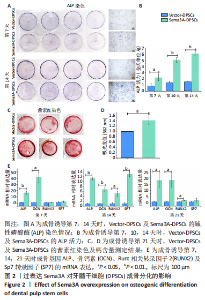
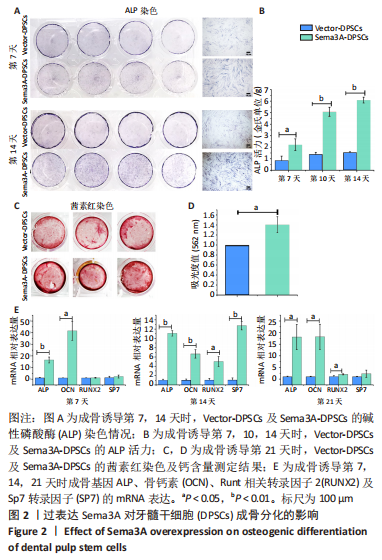
2.2 过表达Sema3A可促进DPSCs成骨分化 为研究过表达Sema3A对DPSCs自身成骨分化的影响,将Vector-DPSCs及Sema3A-DPSCs进行成骨诱导,并比较两者间的成骨分化水平。碱性磷酸酶染色结果显示,在成骨诱导第7,14天,Sema3A-DPSCs的碱性磷酸酶染色水平高于Vector-DPSCs,见图2A。碱性磷酸酶活性结果显示,在诱导第7,10,14天,Sema3A-DPSCs的碱性磷酸酶活性明显高于Vector-DPSCs,见图2B。对成骨诱导28 d的2种细胞进行茜素红染色,结果显示,Sema3A-DPSCs染色强度及钙含量高于Vector-DPSCs,见图2C,D。此外,在成骨诱导第7,14,21天提取2种细胞的mRNA,检测成骨分化相关基因mRNA表达,结果显示,在第7天时,Sema3A-DPSCs的碱性磷酸酶及骨钙素表达水平显著高于Vector-DPSCs;在第14天时,Sema3A-DPSCs的碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Runt相关转录因子2及SP7转录因子表达水平显著高于Vector-DPSCs;在第21天时,Sema3A-DPSCs的碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素及Runt相关转录因子2表达水平显著高于Vector-DPSCs,见图2E。以上结果表明,过表达Sema3A可促进DPSCs成骨分化。"
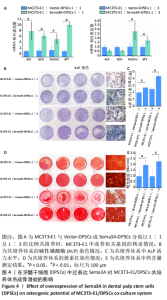
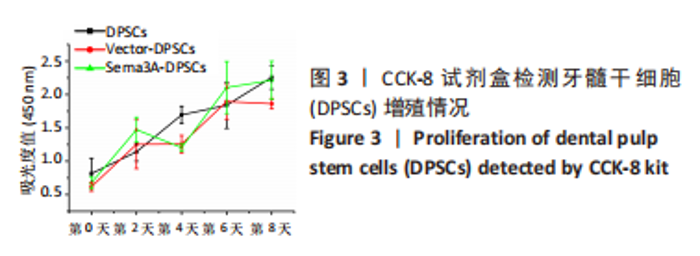
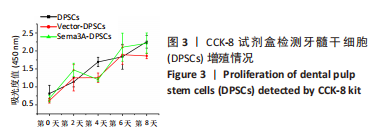
2.4 Sema3A-DPSCs可促进共培养体系中MC3T3-E1成骨分化 为研究Sema3A-DPSCs对MC3T3-E1成骨分化的影响,将MC3T3-E1分别与Vector-DPSCs及Sema3A-DPSCs以1∶1及1∶3的比例直接共培养,并进行成骨诱导。在诱导第21天,使用针对小鼠成骨基因的引物检测共培养体系中MC3T3-E1成骨基因转录情况。结果显示,当MC3T3-E1与Vector-DPSCs或Sema3A-DPSCs的比例为1∶1时,MC3T3-E1中碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Runt相关转录因子2及SP7转录因子的mRNA水平显著增高;当MC3T3-E1与Vector-DPSCs或Sema3A-DPSCs的比例为1∶3时,MC3T3-E1中Runt相关转录因子2及SP7转录因子的mRNA水平显著增高,见图4A。该结果表明,Sema3A-DPSCs可促进共培养体系中MC3T3-E1成骨分化。 2.5 Sema3A-DPSCs与MC3T3-E1共培养体系显示出更高的碱性磷酸酶活力及矿化结节形成情况 为评价在DPSCs中过表达Sema3A对DPSCs/MC3T3-E1共培养体系细胞成骨分化的影响,检测了成骨诱导后共培养体系中总的碱性磷酸酶活力及矿化结节形成情况。结果显示,当两种细胞以1∶1及1∶3比例共培养时,Sema3A-DPSCs/MC3T3-E1共培养体系的碱性磷酸酶染色更深,碱性磷酸酶活力水平更高,见图4B,C。而且,与Vector-DPSCs/MC3T3-E1共培养体系相比,Sema3A-DPSCs/MC3T3-E1共培养体系茜素红染色更深,矿化结节更多,见图4D,E。"

| [1] Di STEFANO M, POLIZZI A, SANTONOCITO S, et al. Impact of Oral Microbiome in Periodontal Health and Periodontitis: A Critical Review on Prevention and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):5142. [2] KINANE DF, STATHOPOULOU PG, PAPAPANOU PN. Periodontal diseases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17038. [3] BOTTINO MC, THOMAS V, SCHMIDT G, et al. Recent advances in the development of GTR/GBR membranes for periodontal regeneration--a materials perspective. Dent Mater. 2012;28(7):703-721. [4] CHEN FM, SUN HH, LU H, et al. Stem cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27):6320-6344. [5] VOLPONI AA, PANG Y, SHARPE PT. Stem cell-based biological tooth repair and regeneration. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20(12):715-722. [6] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [7] LEDESMA-MARTÍNEZ E, MENDOZA-NÚÑEZ VM, SANTIAGO-OSORIO E. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Dental Pulp: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4709572. [8] LAINO G, CARINCI F, GRAZIANO A, et al. In vitro bone production using stem cells derived from human dental pulp. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17(3):511-515. [9] LAINO G, D’AQUINO R, GRAZIANO A, et al. A new population of human adult dental pulp stem cells: a useful source of living autologous fibrous bone tissue (LAB). J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(8):1394-1402. [10] D’AQUINO R, DE ROSA A, LANZA V, et al. Human mandible bone defect repair by the grafting of dental pulp stem/progenitor cells and collagen sponge biocomplexes. Eur Cell Mater. 2009;18:75-83. [11] AIMETTI M, FERRAROTTI F, CRICENTI L, et al. Autologous dental pulp stem cells in periodontal regeneration: a case report. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34 Suppl 3:s27-33. [12] ALGE DL, ZHOU D, ADAMS LL, et al. Donor-matched comparison of dental pulp stem cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2010;4(1):73-81. [13] SONG D, XU P, LIU S, et al. Dental pulp stem cells expressing SIRT1 improve new bone formation during distraction osteogenesis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(2):832-843. [14] ZHONG T, GAO Y, QIAO H, et al. Elevated osteogenic potential of stem cells from inflammatory dental pulp tissues by Wnt4 overexpression for treating bone defect in rats. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(5):2962-2969. [15] ORIKASA S, KAWASHIMA N, TAZAWA K, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α induces osteo/odontoblast differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional cofactor BCL9. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):682. [16] WANG W, YUAN C, GENG T, et al. EphrinB2 overexpression enhances osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells partially through ephrinB2-mediated reverse signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):40. [17] RONG W, ROME C, YAO S. Increased Expression of miR-7a-5p and miR-592 during Expansion of Rat Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Their Implication in Osteogenic Differentiation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2022; 211(1):41-56. [18] SHAPIRO G, LIEBER R, GAZIT D, et al. Recent Advances and Future of Gene Therapy for Bone Regeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018; 16(4):504-511. [19] LU CH, CHANG YH, LIN SY, et al. Recent progresses in gene delivery-based bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(8):1695-1706. [20] HAYASHI M, NAKASHIMA T, TANIGUCHI M, et al. Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A. Nature. 2012;485(7396):69-74. [21] TIAN T, TANG K, WANG A, et al. The effects of Sema3A overexpression on the proliferation and differentiation of rat gingival mesenchymal stem cells in the LPS-induced inflammatory environment. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(10):3710-3718. [22] QIAO Q, XU X, SONG Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSC from type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J Mol Histol. 2018;49(4):369-376. [23] LIU X, TAN N, ZHOU Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A Shifts Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells towards Osteogenic Phenotype and Promotes Bone Regeneration In Vivo. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2545214. [24] FANG K, SONG W, WANG L, et al. Immobilization of chitosan film containing semaphorin 3A onto a microarc oxidized titanium implant surface via silane reaction to improve MG63 osteogenic differentiation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4649-4657. [25] ZHANG N, HUA Y, LI Y, et al. Sema3A accelerates bone formation during distraction osteogenesis in mice. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(4):382-392. [26] PHILLIPS JE, GERSBACH CA, GARCÍA AJ. Virus-based gene therapy strategies for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2007;28(2):211-229. [27] FEELEY BT, CONDUAH AH, SUGIYAMA O, et al. In vivo molecular imaging of adenoviral versus lentiviral gene therapy in two bone formation models. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(8):1709-1721. [28] HSU WK, SUGIYAMA O, PARK SH, et al. Lentiviral-mediated BMP-2 gene transfer enhances healing of segmental femoral defects in rats. Bone. 2007;40(4):931-938. [29] VIRK MS, SUGIYAMA O, PARK SH, et al. “Same day” ex-vivo regional gene therapy: a novel strategy to enhance bone repair. Mol Ther. 2011;19(5):960-968. [30] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, HE J, et al. Repairing critical-sized calvarial defects with BMSCs modified by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and a phosphate cement scaffold. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9707-9718. [31] LI CS, YANG P, TING K, et al. Fibromodulin reprogrammed cells: A novel cell source for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;83:194-206. [32] SUN Z, YAN K, LIU S, et al. Semaphorin 3A promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory environments by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(6):1245-1255. [33] WANG P, WANG W, GENG T, et al. EphrinB2 regulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells and alveolar bone defect regeneration in beagles. J Tissue Eng. 2019;10: 2041731419894361. |
| [1] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [2] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [3] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [4] | Zhu Zhiqi, Yuan Sijie, Zhang Zilin, Ji Shijie, Meng Mingsong, Yan Anming, Han Jing. Mechanism underlying the effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pill on osteolysis and osteogenesis induced by titanium particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 392-397. |
| [5] | Wei Yurou, Tian Jiaqing, He Xianshun, Zhan Zhiwei, Wei Tengfei, Lin Tianye, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Effect of lentiviral silencing of Piezo1 on osteogenic differentiation and TAZ expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [6] | Zhang Yuanshu, He Xu, Xue Yuan, Jin Yesheng, Wang Kai, Shi Qin, Rui Yongjun. Irisin alleviates palmitic acid-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [7] | Zhou Minghua, Hu Xiaoyu. LncRNA SNHG4 regulates miR-152-3p during osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 38-43. |
| [8] | Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [9] | Fan Yongjing, Wang Shu, Jin Wulong. Characteristics, advantages and application of osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [10] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [11] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [12] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [13] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [14] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [15] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||