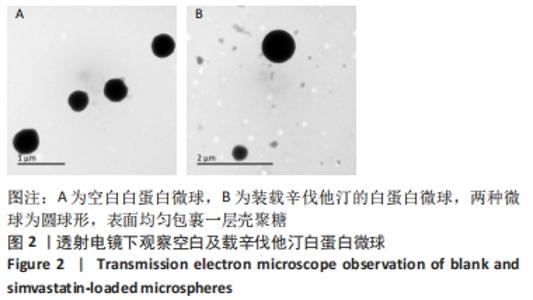
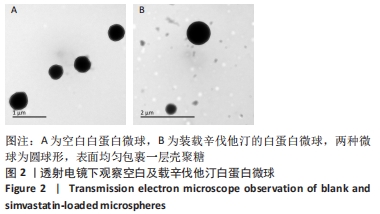
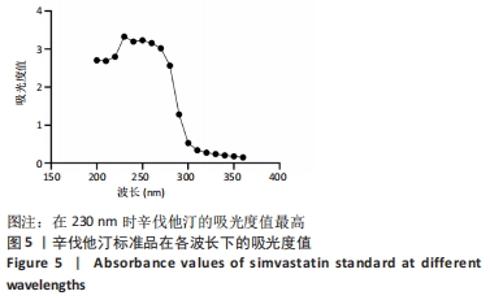
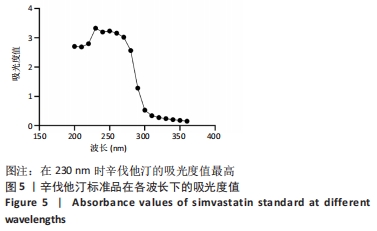
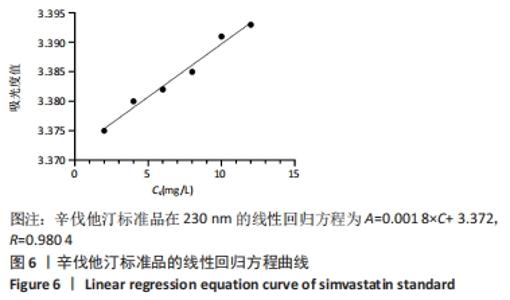
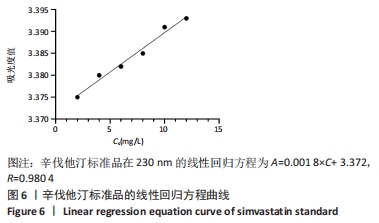
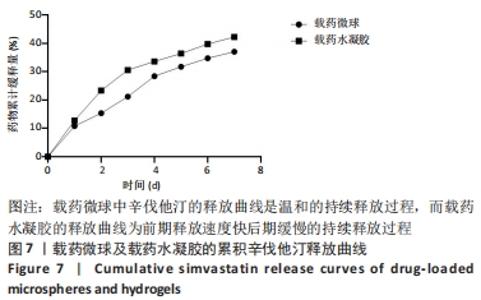
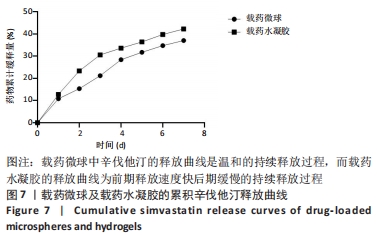
[1] CHANG PC, TAI WC, LUO HT, et al. Core-Shell poly-(D,I-Lactide-co-Glycolide)-chitosan Nanospheres with simvastatin-doxycycline for periodontal and osseous repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;158:627-635.
[2] ZHAO B, CHEN J, ZHAO L, et al. A simvastatin-releasing scaffold with periodontal ligament stem cell sheets for periodontal regeneration. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2020;18:2280800019900094.
[3] GROVER HS, KAPOOR S, SINGH A. Effect of topical simvastatin (1.2 mg) on gingival crevicular fluid interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic periodontitis - A clinicobiochemical study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2016;6(2):85-92.
[4] Bahammam MA, Attia MS. Effects of Systemic Simvastatin on the Concentrations of Visfatin, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, and Interleukin-6 in Gingival Crevicular Fluid in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Periodontitis. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:8481735.
[5] SHAO PL, WU SC, LIN ZY, et al. Alpha-5 Integrin Mediates Simvastatin-Induced Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):506.
[6] FENG C, XIAO L, YU JC, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in rat model of osteoporosis through BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(1):434-443.
[7] XU R, SHI G, XU L, et al. Simvastatin improves oral implant osseointegration via enhanced autophagy and osteogenesis of BMSCs and inhibited osteoclast activity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(5): 1209-1219.
[8] SUTHANTHIRAN T, ANNAMALAI S, CHELLAPANDI S, et al. Gingival Crevicular Fluid Levels of RANKL and OPG After Placement of Collagen Membrane With Simvastatin in the Treatment of Intrabony Defects in Chronic Periodontitis. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019;11(Suppl 2): S301-S304.
[9] SHAHEEN M, BASUDAN A, NIAZY A, et al. Impact of single or combined drug therapy on bone regeneration in healthy and osteoporotic rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;10:1089.
[10] XU R, SHI G, XU L, et al. Simvastatin improves oral implant osseointegration via enhanced autophagy and osteogenesis of BMSCs and inhibited osteoclast activity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(5): 1209-1219.
[11] ZHU K, ZHAO F, YANG Y, et al. Effects of simvastatin-loaded PLGA microspheres on treatment of rats with intervertebral disk degeneration and on 6-K-PGF1α and HIF-1α. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(1):579-584.
[12] LI Y, ZHANG Z, ZHANG Z. Porous Chitosan/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffolds Incorporating Simvastatin-Loaded PLGA Microspheres for Bone Repair. Cells Tissues Organs. 2018;205(1):20-31.
[13] JIN H, JI Y, CUI Y, et al. Simvastatin-Incorporated Drug Delivery Systems for Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater SCI Eng. 2021;7(6):2177-2191.
[14] LIU K, CHEN Y, ZHA XQ, et al. Research progress on polysaccharide/protein hydrogels: Preparation method, functional property and application as delivery systems for bioactive ingredients. Food Res Int. 2021;147(147):110542-110542.
[15] LI P, FENG Z, YU Z, et al. Preparation of chitosan-cu2+/NH3 physical hydrogel and its properties. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;133:67-75.
[16] AROKIANATHAN JF, RAMYA KA, JANEENA A, et al. Non-proteingenic amino acid based supramolecular hydrogel material for enhanced cell proliferation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;185:110581.
[17] LI QT, XU S, FENG Q, et al. 3D printed silk-gelatin hydrogel scaffold with different porous structure and cell seeding strategy for cartilage regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3396-3410.
[18] NANTAVISAI S, RODPRASERT W, PATHANACHAI K, et al. Corrigendum to “Simvastatin enhances proliferation and pluripotent gene expression by canine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (cBM-MSCs) in vitro” . Heliyon. 2019;5(11):e02805.
[19] PEI YC, JUI SS, YANG HT, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteoblast viability and differentiation via Ras/Smad/Erk/BMP-2 signaling pathway. Nutr Res. 2010;30(3):191-199.
[20] DEREN ME, EHTESHAMI JR, DINES JS, et al. Simvastatin Exposure and Rotator Cuff Repair in a Rat Model. Orthopedics. 2017;40(2):e288-e292.
[21] WANG X, JIA Z, ALMOSHARI Y, et al. Local Application of Pyrophpsphorylated Simvastatin Prevents Experimental Periodontitis. Pharm Res. 2018;35(8):164.
[22] 张金明,刘宝会,欧阳昭广,等.纳米银杂化的载辛伐他汀PLGA微球合成及性质研究[J].国家生物医学工程杂志,2020,43(3):199-206.
[23] CISNEROS K, CHOWDHURY N, COLEMAN E, et al. Long-Term Controlled Release of Simvastatin From Photoprinted Triple-Networked Hydrogels Composed of Modified Chitosan and PLA-PEG Micells. Macromol BIosci. 2021;21(8):e2100123.
[24] YAN S, REN J, JIAN Y, et al. Injectable Maltodextrin-Based Micelle/Hydrogel Composites for Simvastatin-Controlled Release. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(12):4554-4564.
[25] FARGHALY ALY U, ABOU-TALEB HA, ABDELLATIF AA, et al. Formulation and evaluation of simvastatin polymeric nanoparticles loaded in hydrogel for optimum wound healing purpose. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:1567-1580.
[26] FARUQ O, SAYED S, KIM B, et al. A biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic scaffold loaded with oxidized cellulose nanofiber-gelatin hydrogel with immobilized simvastatin drug for osteogenic differrentiation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1229-1238.
[27] CHEN N, REN R, WEI X, et al. Thermoresponsive Hydrogel-Based Local Delivery of Simvastatin for the Treatment of Periodontitis. Mol Pharm. 2021;18(5):1992-2003.
[28] LI X, LIU X, NI S, et al. Enhanced osteogenic healing process of rat tooth sockets using a novel simvastatin-loaded injectalbe microsphere-hydrogel system. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(7):1147-1154.
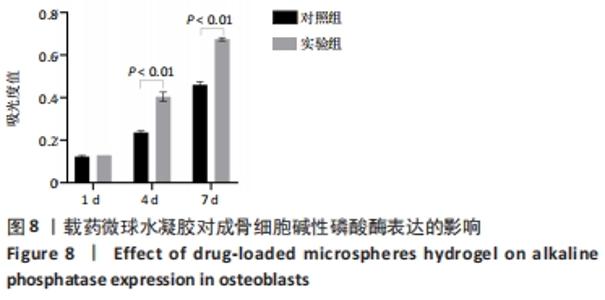
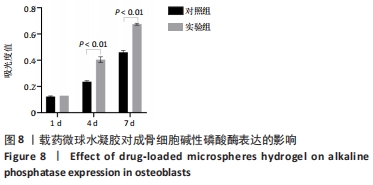
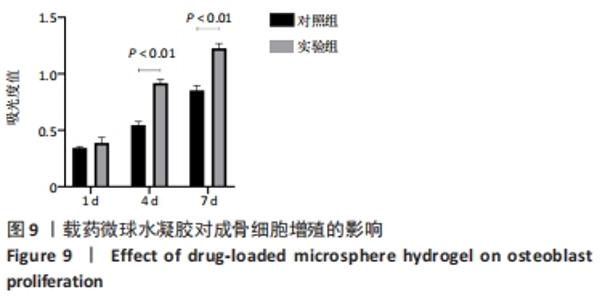
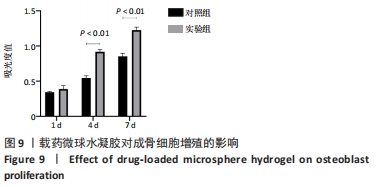
|