Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5475-5481.doi: 10.12307/2022.458
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and in vitro release of manganese-based metal-organic framework materials loaded with baicalin
Lin Lingqi1, Chen Jin1, Qian Kun2, Zhao Liang1, Shi Yijie1
- 1School of Pharmacy, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China; 2School of Public Basic Science, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-16Accepted:2021-08-04Online:2022-12-08Published:2022-04-15 -
Contact:Shi Yijie, MD, Associate professor, School of Pharmacy, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Lin Lingqi, Master candidate, School of Pharmacy, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education, No. JYTJCZR2020067 (to ZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Lingqi, Chen Jin, Qian Kun, Zhao Liang, Shi Yijie. Preparation and in vitro release of manganese-based metal-organic framework materials loaded with baicalin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5475-5481.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
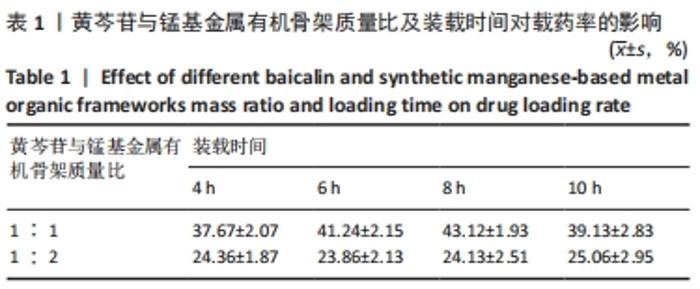
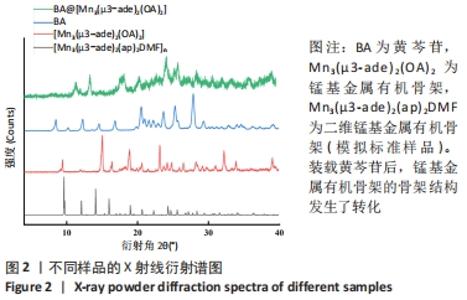
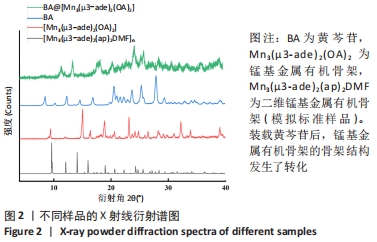
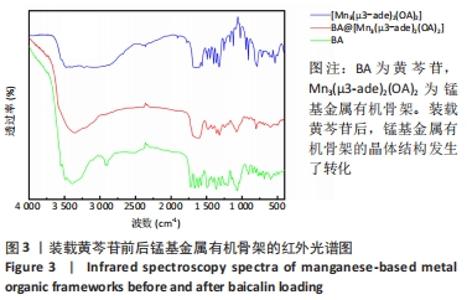
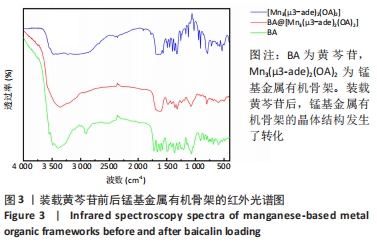
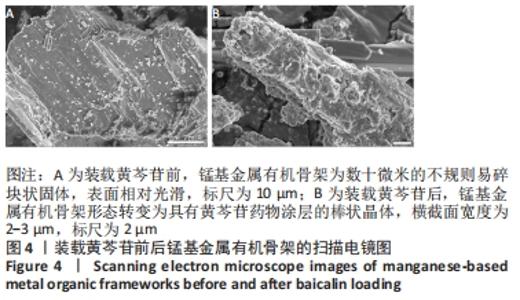
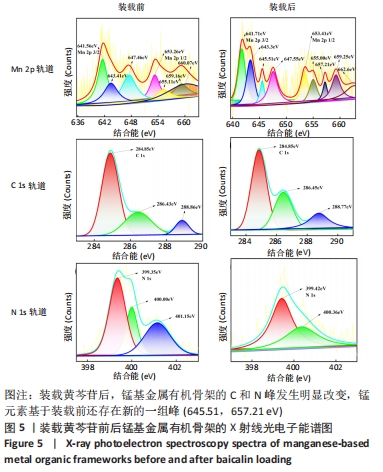
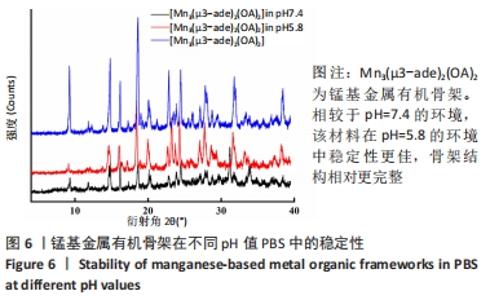
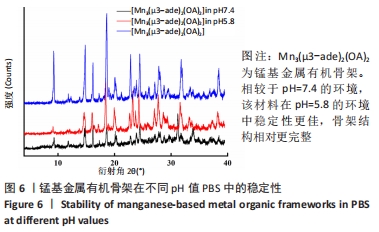
2.4 装载黄芩苷锰基金属有机骨架的表征 2.4.1 X射线衍射分析 从图2中可以看出,装载药物后,复合物在X射线衍射谱图中的衍射峰既不能与合成锰基金属有机骨架[Mn3(μ3-ade)2(OA)2]的衍射峰吻合,也不能与原始药物黄芩苷的衍射峰相吻合,基于上述结果分析可能是由于合成的锰基金属有机骨架[Mn3(μ3-ade)2(OA)2]在药物装载过程中参与了化学反应,从而导致骨架结构发生转化。 2.4.2 红外光谱分析 由图3可见,在锰基金属有机骨架的红外光谱图中,3 219 cm-1处的谱峰是骨架中-NH2的振动峰,在装载黄芩苷后该吸收峰消失,有可能是该氨基与黄芩苷中的羟基存在作用力;在游离黄芩苷的红外光谱谱图中,3 394 cm-1处对应的羟基振动峰在装载黄芩苷后也移动到3 356 cm-1处,进一步说明锰基金属有机骨架在装载黄芩苷时黄芩苷中的羟基与腺嘌呤存在相互作用,也证实了晶体结构转化的发生。 2.4.3 扫描电镜分析 由图4B可见,装载黄芩苷后,锰基金属有机骨架的形态转变为具有黄芩苷药物涂层的棒状晶体,横截面宽度为2.0-3.0 μm。装载前后的形态变化进一步支持了晶体材料发生转化的猜想。 2.4.4 X射线光电子能谱分析 药物装载后,锰基金属有机骨架的C和N峰发生变化,是由药物分子和骨架配体引起的。另一方面,基于药物装载前骨架Mn的峰位存在新的一组峰,这也证实了结构转化的发生,可以通过X射线衍射和红外光谱结果相互确认。 2.5 锰基金属有机骨架的载药率 如表1所示,当加入药物与载体质量相同时,载药率高,单纯增加载体投入量载药率会显著下降;在预实验中,增加药物投入量与药物质量至载体比为2∶1时,甚至出现药物装载失败的情况,说明最佳药物与载体质量比为1∶1,当药物与载体质量比为1∶1时,随着装载时间的延长,载药率在8 h达到峰值,药物装载达到饱和,这可能是药物吸附与解吸达到动态平衡;当装载时间延长到10 h时载药率呈现一定程度的下降,可能是吸附在晶体表面的药物因装载时间过长脱落所致,因此确定药物装载的最优条件为药物与载体质量比1∶1,装载时间8 h。"

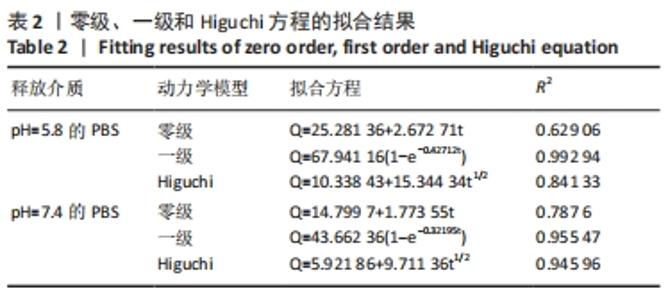
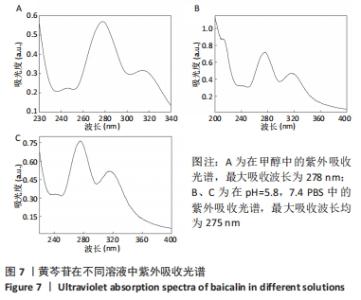
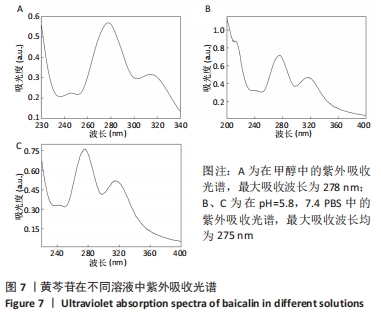
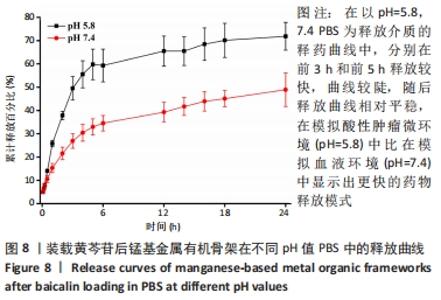
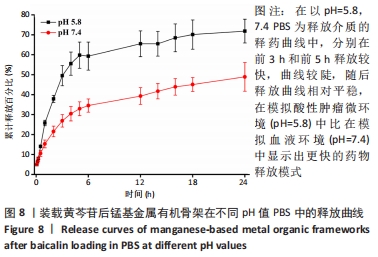
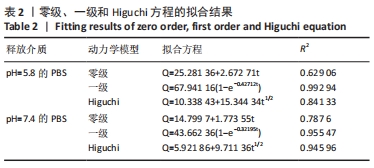
装载黄芩苷后锰基金属有机骨架在以pH=5.8,7.4 PBS为释放介质的释药曲线中,分别在前3 h和前5 h释放较快,曲线较陡,累计释放率可达(49.52±5.04)%和(32.93±3.45)%,这是吸附在金属有机骨架表面的黄芩苷快速扩散进入释放介质造成的,在随后的十几个小时中释放曲线相对平稳,是因为装载进金属有机骨架孔道内的黄芩苷被缓慢释放出来,呈现出良好的缓释效果。 装载黄芩苷后锰基金属有机骨架在模拟酸性肿瘤微环境(pH=5.8)中比在模拟血液环境(pH=7.4)中显示出更快的药物释放模式,表明锰基金属有机骨架[Mn3(μ3-ade)2(OA)2]作为药物载体能防止药物在循环过程中渗漏过快,并增强了药物在肿瘤部位的蓄积,从而提高了其抗肿瘤疗效。 释药方程拟合结果见表2。根据拟合结果,在pH=5.8和7.4的PBS释药环境中,拟合优度最高的均为一级释药方程,拟合效果显著,释药过程符合缓释制剂一级释药动力学过程。上述结果均表明,装载黄芩苷的锰基金属有机骨架[Mn3(μ3-ade)2(OA)2]在体外释放评价中具有良好的缓释效果。"
| [1] SAFAEI M, FOROUGHI MM, EBRAHIMPOOR N, et al. A review on metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. Trends Analyt Chem. 2019;118:401-425. [2] ZHOU HC, KITAGAWA S. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43(16):5415-5418. [3] LI H, LI L, LIN RB, et al. Porous metal-organic frameworks for gas storage and separation: Status and challenges. EnergyChem. 2019;1(1):100006. [4] LI H, WANG K, SUN Y, et al. Recent advances in gas storage and separation using metal–organic frameworks. Mater Today. 2018;21(2): 108-121. [5] LI D, XU HQ, JIAO L, et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Catalysis: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Opportunities. EnergyChem. 2019; 1(1):100005. [6] YANG D, GATES BC. Catalysis by Metal Organic Frameworks: Perspective and Suggestions for Future Research. ACS Catalysis. 2019;9(3):1779-1798. [7] ZHOU J, LI Y, WANG W, et al. Metal-organic frameworks-based sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;164: 112332. [8] LV M, ZHOU W, TAVAKOLI H, et al. Aptamer-functionalized metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021; 176:112947. [9] YANG J, YANG YW. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications. Small. 2020;16(10): 1906846. [10] PHAM H, RAMOS K, SUA A, et al. Tuning Crystal Structures of Iron-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery Applications. ACS Omega. 2020;5(7):3418-3427. [11] GAO X, CUI R, SONG L, et al. Hollow structural metal–organic frameworks exhibit high drug loading capacity, targeted delivery and magnetic resonance/optical multimodal imaging. Dalton Trans. 2019;48(46):17291-17297. [12] WEI LQ, LI Y, MAO LY, et al. A series of porous metal–organic frameworks with hendecahedron cage: Structural variation and drug slow release properties. J Solid State Chem. 2018;257:58-63. [13] BAHRANI S, HASHEMI SA, MOUSAVI SM, et al. Zinc-based metal–organic frameworks as nontoxic and biodegradable platforms for biomedical applications: review study. Drug Metab Rev. 2019;51(3): 356-377. [14] HORCAJADA P, CHALATI T, SERRE C, et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat Mater. 2010;9:172-178. [15] HORCAJADA P, SERRE C, MAURIN G, et al. Flexible porous metal-organic frameworks for a controlled drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2008; 130(21):6774-6780. [16] LENG X, DONG X, WANG W, et al. Biocompatible Fe-Based Micropore Metal-Organic Frameworks as Sustained-Release Anticancer Drug Carriers. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2490. [17] MIRI B, MOTAKEF-KAZEMI N, SHOJAOSADATI SA, et al. Application of a Nanoporous Metal Organic Framework Based on Iron Carboxylate as Drug Delivery System. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018;17(4):1164-1171. [18] WYSZOGRODZKA G, DOROŻYŃSKI P, GIL B, et al. Iron-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks as a Theranostic Carrier for Local Tuberculosis Therapy. Pharm Res. 2018;35(7):144. [19] WANG L, ZHU H, SHI Y, et al. Novel catalytic micromotor of porous zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 for precise drug delivery. Nanoscale. 2018;10(24):11384-11391. [20] LI J, LV F, LI J, et al. Cobalt-based metal–organic framework as a dual cooperative controllable release system for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Nano Res. 2020;13(8):2268-2279. [21] XIAO J, ZHU Y, HUDDLESTON S, et al. Copper Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles Stabilized with Folic Acid Improve Wound Healing in Diabetes. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1023-1032. [22] LIU W, ZHONG Y, WANG X, et al. A porous Cu(II)-based metal-organic framework carrier for pH-controlled anticancer drug delivery. Inorg Chem Commun. 2020;111:107675. [23] CHEN G, LUO J, CAI M, et al. Investigation of Metal-Organic Framework-5 (MOF-5) as an Antitumor Drug Oridonin Sustained Release Carrier. Molecules. 2019;24(18):3369. [24] JAVANBAKHT S, HEMMATI A, NAMAZI H, et al. Carboxymethylcellulose-coated 5-fluorouracil@MOF-5 nano-hybrid as a bio-nanocomposite carrier for the anticancer oral delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;155: 876-882. [25] JAVANBAKHT S, POORESMAEIL M, NAMAZI H. Green one-pot synthesis of carboxymethylcellulose/Zn-based metal-organic framework/graphene oxide bio-nanocomposite as a nanocarrier for drug delivery system. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;208:294-301. [26] XU Q, ZHAN G, ZHANG Z, et al. Manganese porphyrin-based metal-organic framework for synergistic sonodynamic therapy and ferroptosis in hypoxic tumors. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1937-1952. [27] AL HAYDAR M, ABID H R, SUNDERLAND B, et al. Multimetal organic frameworks as drug carriers: aceclofenac as a drug candidate. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;13:23-35. [28] CHEN X, YANG G, ZHANG B, et al. Effects of manganese-supplemented diets on growth performance, blood biochemistry, nitrogen metabolism and skeletal development of rex rabbits. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020; 61:126543. [29] CONSTANTOPOULOS G. Lipid Metabolism of Manganese-deficient Algae: I. Effect of Manganese Deficiency on the Greening and the Lipid Composition of Euglena Gracilis Z. Plant Physiol. 1970;45(1):76-80. [30] COASSIN M, URSINI F, BINDOLI A. Antioxidant effect of manganese. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992;299(2):330-333. [31] KE M, ZHANG Z, XU B, et al. Baicalein and baicalin promote antitumor immunity by suppressing PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105824. [32] JIANG H, YAO Q, AN Y, et al. Baicalin suppresses the progression of Type 2 diabetes-induced liver tumor through regulating METTL3/m6A/HKDC1 axis and downstream p-JAK2/STAT1/clevaged Capase3 pathway. Phytomed. 2022;94:153823. [33] KONG N, CHEN X, FENG J, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in bladder cancer cells by downregulating FTH1. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.036 [34] IKEMOTO S, SUGIMURA K, YOSHIDA N, et al. Antitumor effects of Scutellariae radix and its components baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin on bladder cancer cell lines. Urology. 2000;55(6): 951-955. [35] HUANG Q, ZHANG J, PENG J, et al. Effect of baicalin on proliferation and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9): 5645-5654. [36] HUANG Y, HU J, ZHENG J, et al. Down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and induction of apoptosis in CA46 Burkitt lymphoma cells by baicalin. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31(1):48. [37] XING J, CHEN X, ZHONG D. Absorption and enterohepatic circulation of baicalin in rats. Life Sci. 2005;78(2):140-146. [38] ZHAO H, HE H, WANG X, et al. Four unprecedented 2D trinuclear Mn(II)-complexes with adenine nucleobase controlled by solvent or co-ligand: Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic behaviour. J Mol Struct. 2018;1155:687-694. [39] PAGLIAI M, CAPORALI S, MUNIZ-MIRANDA M, et al. SERS, XPS, and DFT Study of Adenine Adsorption on Silver and Gold Surfaces. J Phys Chem Lett. 2012;3(2):242-245. [40] STOCK N, BISWAS S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem Rev. 2012;112(2):933-969. [41] KUMAR S, JAIN S, NEHRA M, et al. Green synthesis of metal–organic frameworks: A state-of-the-art review of potential environmental and medical applications. Coord Chem Rev. 2020;420:213407. [42] GAO X, GE F, ZHENG H. Improving the Stability and Visualizing the Structural Transformation of the Stimuli-Responsive Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Inorg Chem. 2020;59(7):5093-5098. [43] YIN Z, ZHOU YL, ZENG MH, et al. The concept of mixed organic ligands in metal–organic frameworks: design, tuning and functions. Dalton Trans. 2015;44(12):5258-5275. |
| [1] | Zhang Chang, Yu Zhengwen. Application of manganese in biomaterials: current situation and problems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5504-5511. |
| [2] | Mao Yilin, Zhu Zhou, Wang Jian. Nano materials of protein-carrying nanosystems for endosome/lysosome escape: research status and future [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5534-5542. |
| [3] | Gao Zhao, Zhao Yuhao, He Yixiang, Zhao Haiyan, Wang Wenji. DNA hydrogel based on drug delivery and bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4379-4385. |
| [4] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong. Novel nano-delivery system: engineered small extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4417-4422. |
| [5] | Zhu Meiying, Jiang Liming, Liu Shuangwei, Ma Mingqi, Yang Yutong. Application of drug delivery system in the field of periodontal tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4423-4428. |
| [6] | Xiakeerzhati•Xiaohalati, Wang Xiaobei, Wang Lin. Nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3566-3572. |
| [7] | Jiang Chaorui, Xu Yan, Xiong Ying, Zhang Xujing. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide/silk fibroin/rifampicin drug-loading microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3467-3473. |
| [8] | Wang Lu, Li Limei, Li Qing, Yang Hongcai, Lan Xiaoqian, Hu Yingrui. Application of polyurethane materials in the repair of osteoporotic bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3429-3434. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Yang Menglu, Zhang Na, Wang Fangyuan, Liu Jianguo. Application of chitosan in nano drug delivery system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4546-4552. |
| [11] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [12] | Cong Renyuan, Yuan Jing, Xia Jinchan, Sun Ying . Effects of baicalin on oxidative stress in BEAS-2B cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide combined with adenosine triphosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 286-291. |
| [13] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [14] | Fan Xuemin, Fang Shanbao, Chen Zhixing, Mo Shuixue. Status and application prospects of nano-clay Laponite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1622-1627. |
| [15] | Huang Hui, Dai Yao, Li Yongsheng, Chen Wei, Tang Fang, Huang Yuting, Zhou Zheng, Liu Hairong. Application and research of non-coding RNA in bone tissue engineering with cells and scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 596-605. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||