Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (22): 3467-3473.doi: 10.12307/2022.272
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and properties of graphene oxide/silk fibroin/rifampicin drug-loading microspheres
Jiang Chaorui, Xu Yan, Xiong Ying, Zhang Xujing
- College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-11-23Revised:2021-01-26Accepted:2021-05-31Online:2022-08-08Published:2022-01-12 -
Contact:Xu Yan, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Jiang Chaorui, Master, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2017D01C021 (to XY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Chaorui, Xu Yan, Xiong Ying, Zhang Xujing. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide/silk fibroin/rifampicin drug-loading microspheres[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3467-3473.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
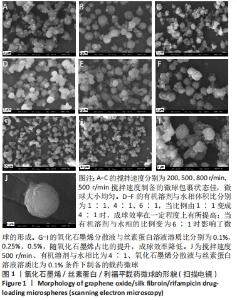
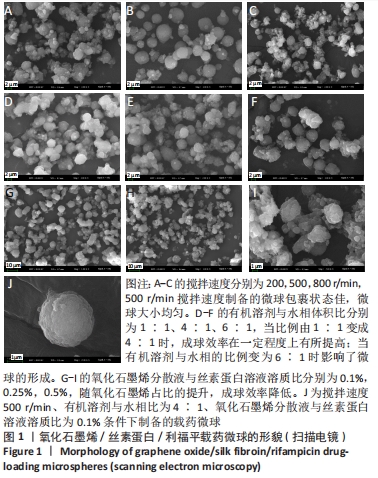
2.1 GO/SF/RFP载药微球扫描电镜分析 在制备工艺参数搅拌速度、有机溶剂与水相体积比、氧化石墨烯溶液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比的交互作用中,应用单一因素法对微球的粒径及形貌表征进行考察,设置丝素蛋白浓度3.5%、水油比为1∶6、司盘80与石蜡比为1∶10、利福平与药物载体溶液比50 mg∶1 mL作为定量时,以搅拌速度(200,500,800 r/min)为自变量时,微球粒径随搅拌速度的提高呈现逐渐减小趋势,当搅拌速度过慢时乳化不充分,油水包裹状态不佳,微球大小不均;搅拌速度过快增加了微球发生碰撞的机会,易使已分散的微球重新凝聚和粘连,出现微球集聚团簇的现象,见图1A-C。 以有机溶剂与水相体积比(1∶1、4∶1、6∶1)为自变量时,当比例由1∶1变成4∶1时,有机溶剂的加入可促使丝素蛋白结晶的速率加快,从而提高了交联反应速度,因此成球效率在一定程度上有所提高;但当有机溶剂与水相的比例变为6∶1时,有机溶剂加入量过大导致丝素蛋白结晶速率过快,交联反应也过快,从而影响微球的形成,见图1D-F。 以氧化石墨烯溶液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比(0.1%,0.25%,0.5%)为自变量时,随氧化石墨烯占比的提升,微球粒径并未发生明显变化,但成球效率会随氧化石墨烯溶液浓度的提升而降低,GO/SF/RFP载药微球表面的片层结构增多,同时微球形貌呈不规则球状甚至粘连现象严重,说明过高浓度的氧化石墨烯溶液不利于微球的形成,见图1G-I。因此在单因素的考察中,选取搅拌速度500 r/min、有机溶剂与水相比为4∶1、氧化石墨烯分散液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比为0.1%为自变量作为优化参数进行综合考察,结果见图1J所示,优化后的微球显著改善了团聚粘连现象,保持了较好的粒径均匀性、个体完整性和分散性。"
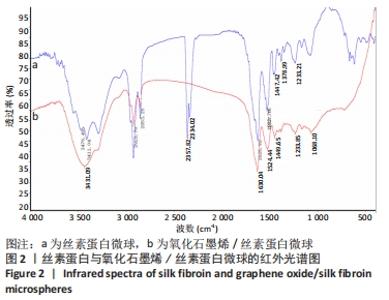
2.2 GO/SF/RFP载药微球红外光谱分析 图2的红外光谱图显示,以丝素蛋白为基材的空白微球,分别在1 630 cm-1和1 524 cm-1处出现属于丝素蛋白β-折叠结构构象的C=O伸缩振动和N-H变形振动酰胺Ⅰ带特征峰,以及在1 234 cm-1处出现无规线团结构的酰胺Ⅲ带特征峰。而以氧化石墨烯/丝素蛋白为基材制备的空白微球中也相应地加入了氧化石墨烯的特征峰,如氧化石墨烯中的2 357 cm-1及2 334 cm-1处出现了明显的氧化石墨烯特征峰,以及在3 411 cm-1处的羟基O-H振动吸收峰明显增强。同时,氧化石墨烯在1 620 cm-1处的C-OH变形振动峰与丝素蛋白中1 630 cm-1处的C=O伸缩振动峰相结合,使丝素蛋白基材的酰胺特征峰前移至1 625 cm-1,以及使在1 527 cm-1处的β-折叠结构构象的N-H变形振动特征峰后移,并且两处峰值明显增强,说明空白微球中氧化石墨烯与丝素蛋白已充分复合。"
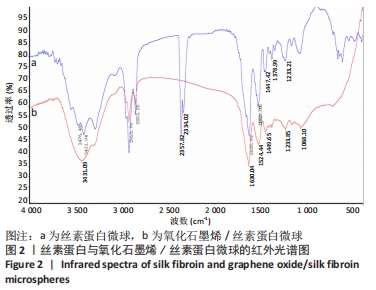
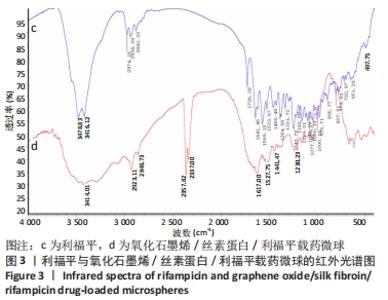
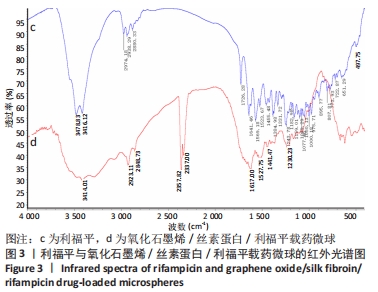
图3的红外光谱图显示,药物利福平分别在 3 478,3 461,2 974,2 938,2 880, 1 726,1 641,1 243 cm-1处出现明显吸收峰;在氧化石墨烯/丝素蛋白/利福平载药微球的红外光谱图中,利福平在3 478,3 461 cm-1处的峰值明显减弱,但2 923 cm-1处的峰值明显增强;同时,在2 357 cm-1和2 337 cm-1处出现氧化石墨烯的特征峰,以及丝素蛋白的酰胺Ⅰ带特征峰前移至1 617 cm-1和后退至1 527 cm-1处,酰胺Ⅲ带特征峰前移至1 230 cm-1处并且3处峰值均明显增强,其原因为利福平中苯环和C=O与氧化石墨烯碳平面发生π-π堆积并形成氢键,说明利福平与氧化石墨烯/丝素蛋白复合材料成功结合。"
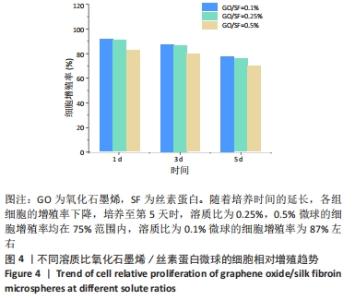
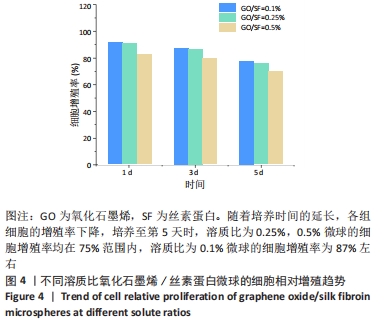
2.3 氧化石墨烯/丝素蛋白微球细胞的毒性分析 对微乳法制备的氧化石墨烯/丝素蛋白空白微球及制备应用到的食品级石蜡和司盘80等材料进行综合细胞毒性分析,重点验证氧化石墨烯含量对微球生物相容性的影响。 对比毒性反应分级标准及细胞相对增殖趋势可知,随氧化石墨烯含量的降低,微球毒性呈一定降低趋势,生物安全性能有所提高,见图4。当氧化石墨烯分散液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比在0.25%-0.5%范围内,培养第5天时的细胞增殖率均在75%范围内,说明微球材料对细胞增殖有抑制作用,药物载体材料对细胞有中、低度的毒性;当氧化石墨烯分散液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比为0.1%时,微球的细胞增殖率为87%左右,最终满足细胞生物安全性能要求,因此可作为生物材料应用于药物缓释载体材料研究。"
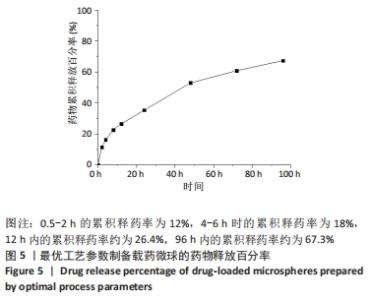
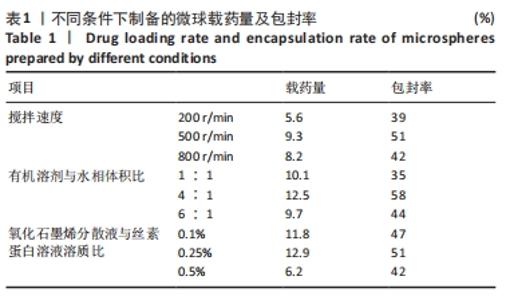
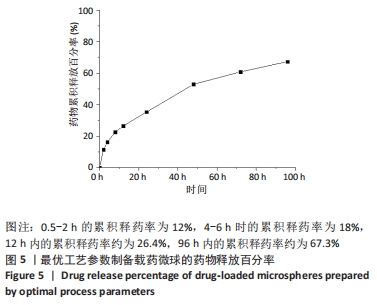
当搅拌速度较低时,仅有少量微球形成且粒径不均,载药率和包封率低;随着搅拌速度的上升,微球的载药量和包封率均有大幅增加,但在高速搅拌中微球发生粘连现象,微球成球效果差,导致包封率下降。 当加入与水相等体积的有机溶剂时,微球的载药量较高,但包封率较低,分析是由于少量有机溶剂未能完全清除油相,导致药物黏附在微球表面;当有机溶剂过量加入时,交联反应加快,微球粒径增大,使得载药量减少。因氧化石墨烯有较大的比表面积,可提高药物的负载,但过量的氧化石墨烯阻止丝素蛋白分子无规则结构向β-折叠结构转变,故载药量明显下降。 因此,综合单因素实验及细胞毒性实验结果,最终以搅拌速度为500 r/min、有机溶剂与水相体积比为4∶1、氧化石墨烯溶液与丝素蛋白溶液溶质比为0.1%制备GO/SF/RFP载药微球,其载药量为13.5%,包封率为61%。 2.5 GO/SF/RFP载药微球体外累积释药百分率 将各时间节点吸取的溶液用紫外分光光度计测出吸光值,代入利福平药物标准曲线中计算出药物浓度,再运用累积释药率公式计算各时间节点释药率,并用Origin 2018软件拟合,绘制累积释药曲线。根据2010年《中国药典》规定,缓释制剂从释药曲线图中至少选出3个取样时间点,由第1个取样点开始考察药物是否有突释,第1个取样点为0.5-2 h,控释量应控制在30%;第2个取样点4-6 h,释放量应控制在50%;第3取样点7-10 h,释放量应控制在75%。 从图5可知,药物释放前期(0.5-2 h)的累积释药率为12%,由于药物浓度差导致释药速率较快,但无突释现象产生;4-6 h时的累积释药率为18%,满足《中国药典》规定控制释放量,至前12 h内累积释药率约为26.4%;随着浓度差越来越小,释药速率放缓,在96 h内累积释药率约为67.3%,具有稳定释药趋势,从而提高药物疗效。参考利福平在动物体内的最低抑菌浓度约0.06-0.5 mg/L,最低杀菌浓度约5 mg/L[16],此次实验体外释药研究过程中最低释药浓度约17 mg/L,满足体内最低杀菌浓度。"

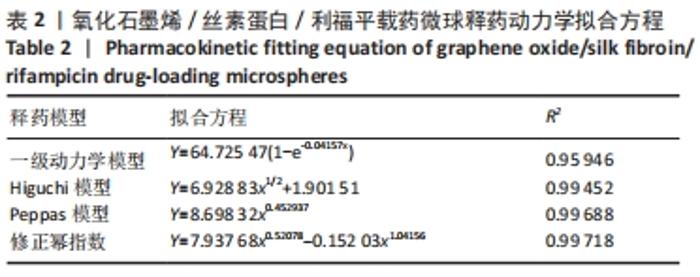
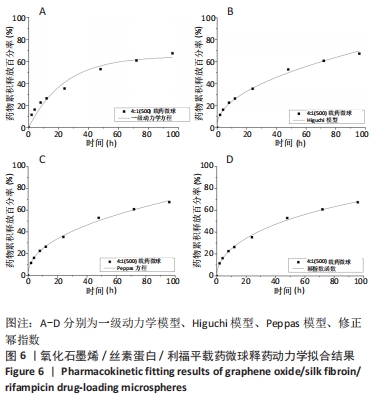
当相关系数R2更趋近于1时,说明实验数据拟合更符合该模型,因此通过相关系数R2对比分析,Peppas方程中R2=0.996 88,载药微球的药物释放机制更符合 Peppas模型,其中释药指数n用于表征药物的释放机制。其取值与几何特征相关,对于球体而言,当n取0.45和0.89时,药物释放规律分别作用扩散控制和溶蚀控制,当n介于二者之间时则表示为扩散和溶蚀的共同作用的结果,因此可根据Peppas方程中指数n=0.452 937粗略预测出微球中的药物释放由扩散和溶蚀机制共同作用。在此基础上,推广的幂指数模型在Peppas模型上又详细划分了扩散控制和溶蚀控制,拟合结果得R2=0.997 18,拟合效果优于Peppas模型,再次验证了载药微球的药物缓控释过程由扩散和溶蚀共同作用。更进一步,通过推广的幂指数方程Y=K1xm+K2x2m中扩散和溶蚀作用两者的比率R/F=K2xm/K1 (其中K1代表扩散常数、K2代表溶蚀常数、m是扩散指数),对药物缓释中的主要释药作用结合体外释药实验表明,随药物缓释时间的延长,R/F比值越大,溶蚀对药物释放的作用越大。同时,R/F比值表明此方法制备的载药微球药物释放以扩散机制作为主导作用。"

| [1] 李大伟,马远征.骨关节结核局部药物缓释材料研究进展[J].中国防痨杂志,2013,35(5):376-378. [2] 韩建军,宋金龙,谢印法,等.载药微球治疗恶性肝脏肿瘤的全程管理[J].中华介入放射学电子杂志,2020,2(7):7-16. [3] 沈俊海,张金敏,全微雷,等.新型磁性氧化石墨烯的制备及其载药性能[J].中国科学,2016,46(8):800-809. [4] 章美明.磁性氧化石墨烯基非共价修饰纳米复合材料的制备及其在药物递送方面的应用[D].镇江:江苏大学,2019. [5] 雷海琳.氧化石墨烯基非共价修饰纳米复合材料的制备及其在药物递送方面的应用[D].镇江:江苏大学,2017. [6] 沈贺,张立明,张智军.石墨烯在生物医学领域的应用[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2011,30(1):218-223. [7] 王晨,许军,刘燕华,等.功能化氧化石墨烯作为药物载体材料的研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2017,48(1):117-124. [8] KARKI N, TIWARI H, PAL M, et al. Functionalized graphene oxides for drug loading, release and delivery of poorly water soluble anticancer drug: A comparative study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;169: 265-272. [9] LIU Z, ROBINSON JT, SUN X, et al. PEGylated Nano-Graphene Oxide for Delivery of Water Insoluble Cancer Drugs. J Am Chem Soc. 2008; 130(33):10876-10877. [10] 杨琳,刘晓松,孙建立,等.氧化石墨纳米颗粒吸附的5-氟尿嘧啶、抗体和细胞因子的体外生物活性研究和细胞因子的体外生物活性研究[J].肿瘤防治研究,2014,41(4):340-344. [11] PEREZ-RIGUEIRO J, BIANCOTTO L, CORSINI P, et al. Supramolecular organization of regenerated silkworm silk fibroin bers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;44(2):195-202. [12] KUNDU B, RAJKHOWA R, KUNDU SC, et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470. [13] 刘纯,金梦瑶,张学农,等.双氯芬酸钠丝素蛋白-壳聚糖缓释微球的制备及体内外评价[J].中国药学杂志,2009,21(3):1642-1647. [14] SUBIA B, KUNDU SC. Drug loading and release on tumor cells using silk fibroin-albumin nanoparticles as carriers. Nanotechnology. 2013; 24(3):1-11. [15] 张云海.丝素蛋白药物缓释载体的制备及其性能研究[D].北京:北京理工大学,2015. [16] 马永海.异烟肼、利福平缓释微球的制备及体内外释药性能的研究[D].宁夏:宁夏医科大学,2019. [17] SUDIMACK J, LEE L. Targeted drug delivery via the folate receptor. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000;41:147-162. [18] LIU J, YAN L, WEI L, et al. Controlled-release neurotensin-loaded silk fibroin dressings improve wound healing in diabetic rat model. Bioact Mater. 2019;4:151-159. [19] CROMMELIN DJA, FLORENCE AT. Towards more effective advanced drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2013;454:496-511. [20] 陈建辉.具有靶向标记功能的抗肿瘤药物缓释载体的制备及其研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2018. [21] WANG Z, NIU H, LI Z, et al. Superselective arterial embolization with drug-loaded microspheres for the treatment of unresectable breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2019;8(6):740-747. [22] 刘亚珍,邱晓明,李松凯.正交设计优化万古霉素/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球的制备及体外药物释放[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(2):211-217. [23] 胡玉婷,李培源.氧化石墨烯作为药物载体的研究进展[J].山东化工,2019,48(24):50-56. [24] 曾鹏,朱雪芬,操江飞,等.氧化石墨烯的制备及其对大肠埃希菌的抑菌性能研究[J].山东化工,2019,46(2):30-31. [25] CHENG HKF, SAHOO NG, TAN YP, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanocomposites Filled with Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Grafted Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(5):2387-94. [26] 钱文昊,苏俭生.纳米氧化石墨烯控释载药体系研究现状[J].中国临床医学,2016,23(3):383-387. [27] 王亚茹,张青,雷芳,等.丝素蛋白-氧化石墨烯多孔微球支架的制备及性能测试[J].蚕业科学,2019,45(2):231-236. [28] LI S, XIAO L, DENG H, et al. Remote controlled drug release from multi-functional Fe3O4/GO/Chitosan microspheres fabricated by an electrospray method. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;151:354-362. [29] 熊龑,徐涛,龚良国.CCK-8法测定纤维蛋白胶对人脂肪干细胞的细胞毒性[J].中国当代医药,2019,26(18):38-40. [30] 冯华龙,何升华,黄飞强. CCK-8法定量检测亚甲蓝对人髓核细胞的毒性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2532-2536. [31] SINGH B, CHAUHAN GS, SHARMA DK, et al. The release dynamics of model drugs from the psylium and N-hydroxym-ethylacrylamide based hydrogels. Int J Pharm. 2006;325:15-25. |
| [1] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [2] | Liu Yue, Jiang Ziyi, Li Jingjing, Meng Kai, Zhao Huijing. Cell co-culture and in vivo biocompatibility of poly(L-lactic caprolactone)/silk fibroin small-diameter artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3505-3513. |
| [3] | Meng Lulu, Liu Hao, Liu Han, Zhang Jun, Li Ruixin, Gao Lilan. Mechanical properties of silk fibroin/type I collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffolds based on low-temperature 3D printing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3550-3555. |
| [4] | Guo Xiaopeng, Liu Yingsong, Shang Hui. Silk fibroin/nano hydroxyapatite composite combined with icariin can promote the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into nucleus pulposus like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3528-3534. |
| [5] | Yang Xinghua, Zhang Jing, Chen Daiyun, Xiong Shijiang. Selection of conditions for fabricated porous scaffolds in bone tissue engineering by silk fibroin protein [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2545-2550. |
| [6] | An Tiantian, Xu Yan, Chen Huiming, Zhang Xujing, Tan Hao. Preparation and performance of rifampicin-silk fibroin microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1515-1521. |
| [7] | Liu Xiaoyuan, Li Lei, Zhang Kai, Li Jun, Han Xiangzhen He Huiyu. Osteogenesis using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets combined with three-dimensional printed Cervus elaphus antler powder/silk fibroin/polyvinyl alcohol scaffold in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5420-5426. |
| [8] | Gan Fang. Effects of targeted graphene oxide loaded with atractylenolide-I on apoptosis and cell cycle of ovarian cancer cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4492-4496. |
| [9] | Wang Weiyu, Liu Jun, Yang Yong, Lu Tao, Liu Yin, Zhu Kunzhi, Shu Liping, Ye Chuan. Preparation and in vitro biocompatibility of egg white/polyvinyl alcohol/graphene oxide composite fiber scaffolds based on electrospinning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4497-4503. |
| [10] | Liu Jun, Yang Long, Wang Weiyu, Zhou Yuhu, Wu Ying, Lu Tao, Shu Liping, Ma Minxian, Ye Chuan. Preparation and properties of poly3-hydroxybutyrate 4-hydroxybutyrate/polyethylene glycol/graphene oxide tissue-engineered scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [11] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| [12] | Xu Changkui, Pu Xiaobing, Lu Yao, Chen Jiarong, Pan Lei. Safety and antibacterial properties of gentamicin-loaded silk fibroin in meniscus repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1545-1549. |
| [13] | Liu Xiaoyin, , Zhong Lin, Zheng Bo, Wei Pan, Dai Chen, Hu Liangcong, Wang Tiantian, Liang Xiaolong, Zhang Sai, Wang Xiaoli. Diffusion tensor imaging predicting locomotor function recovery with 3D printing scaffold after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4547-4554. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Song Shilei, Zhang Chi, Zhuo Yinghong, Yang Nan, Zhan Huasong, Xu Canhong. Good cell compatibility and permeability of silk fibroin/chitosan composite scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2544-2550. |
| [15] | She Rongfeng, Zhang Yi, Chen Long, Wang Yuanzheng, Zhang Bin, Huang Qixiang. Biocompatibility of tissue engineered cartilage constructed in vivo by silk fibroin-chitosan scaffold carrying bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 27-32. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||