Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2554-2561.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3118
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing
Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi
- State Key Laboratory of Silkworm Genome Biology, College of Biotechnology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Received:2020-06-28Revised:2020-07-02Accepted:2020-08-04Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoning, PhD, Associate Professor, State Key Laboratory of Silkworm Genome Biology, College of Biotechnology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Chen Zhenyu, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Silkworm Genome Biology, College of Biotechnology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
Supported by:the Subsidy Funds for the Development of Silk Industry Sponsored by Chongqing Municipal Commission of Commerce, No. CQ2019JSCC03 (to ZXN); Venture & Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees, No. cx2019098 (to ZXN); National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates in Southwest University in 2020, No. 202010635088 (to YC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561.
share this article
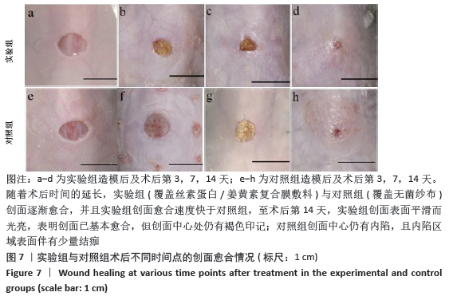
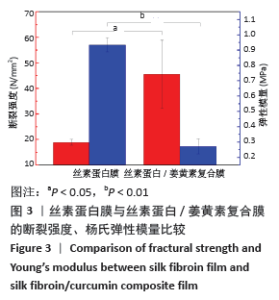
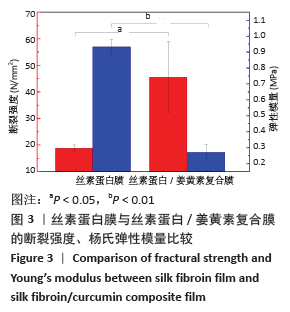
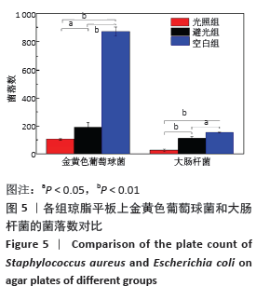
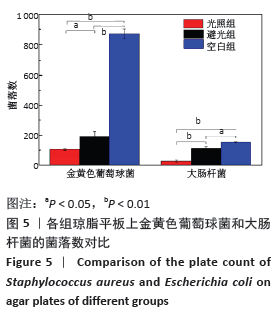
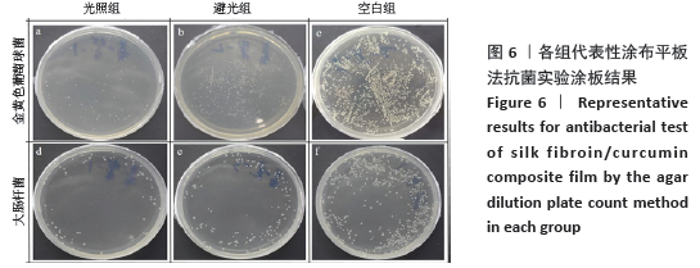
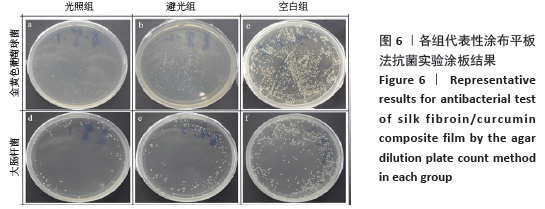
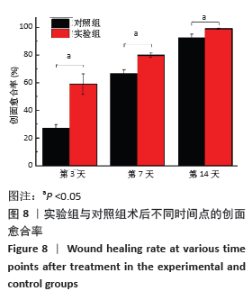
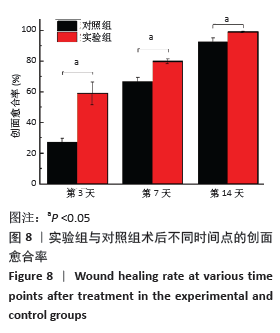
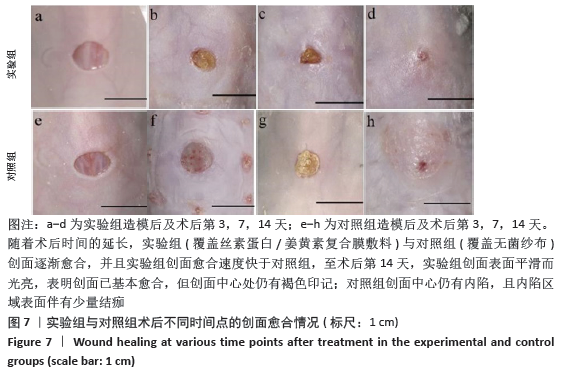
2.5 丝素蛋白/姜黄素复合膜敷料创面疗效观察 2.5.1 创面愈合率 各组小鼠不同时间点创面大体观见图7。术后第3天,实验组创面与丝素蛋白/姜黄素复合膜敷料紧密贴合,创面处无渗出液积累,且创面已经开始缩小;对照组创面处还有少许渗出液且有出血现象,创面愈合率低于实验组(P < 0.05)。术后第7天,实验组创面明显缩小,伤口结痂;对照组创面开始缩小,创面愈合率低于实验组(P < 0.05)。术后第14天,实验组创面表面平滑而光亮,表明创面已基本愈合,但创面中心处仍有褐色印记;对照组创面中心仍有内陷,且内陷区域表面伴有少量结痂,创面愈合率低于实验组(P < 0.05)。两组不同时间点创面愈合率见图8。 "
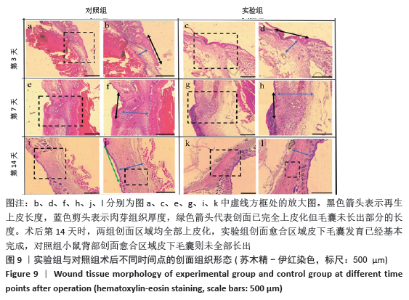
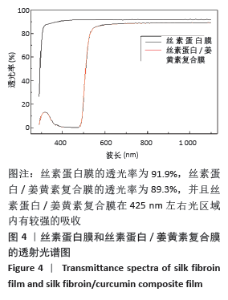
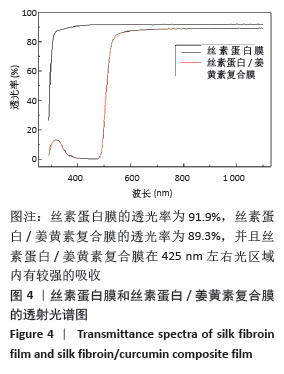
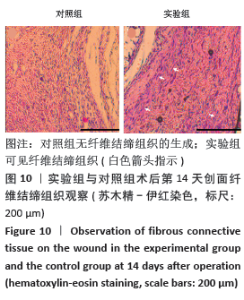
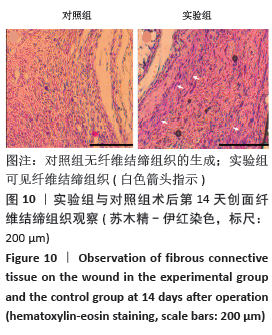
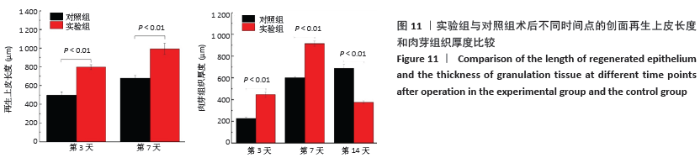
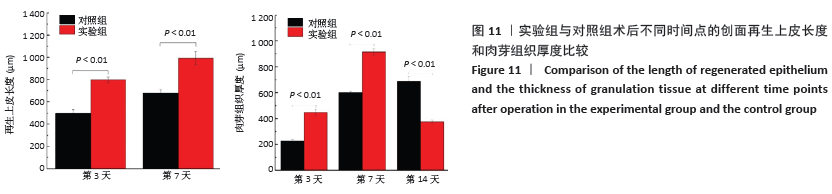
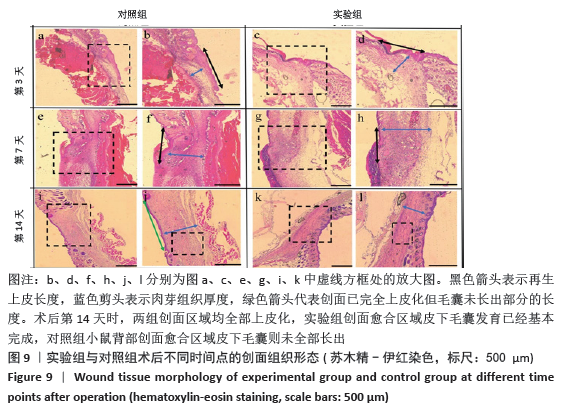
实验发现,最初使用丝素蛋白/姜黄素复合膜敷料处理小鼠背部皮肤缺损创面时,丝素蛋白/姜黄素复合膜敷料紧紧贴合在创面上,随着小鼠皮肤缺损创面的逐渐愈合,丝素蛋白/姜黄素复合膜敷料也逐渐从创面脱落。 2.5.2 组织切片结果分析 图9为两组术后不同时间点的创面组织形态学观察。术后第3天,两组创面区域均有上皮化现象,均有肉芽组织形成,实验组再生上皮长度、肉芽组织厚大于对照组。术后第7天,两组再生上皮长度、肉芽组织厚度均增加,实验组的再生上皮长度、肉芽组织厚度仍大于对照组。术后第14天,两组创面区域均全部上皮化,实验组创面愈合区域皮下毛囊发育已经基本完成,可见大量胶原纤维及成纤维细胞整齐排列,为成熟的纤维结缔组织;对照组小鼠皮肤缺损创面附近未发现有纤维结缔组织的形,对照组小鼠背部创面愈合区域皮下毛囊则未全部长出,见图10。两组术后不同时间点的再生上皮长度、肉芽组织厚见图11。"
| [1] MCGILL M, GRANT JM, KAPLAN DL, et al. Enzyme-mediated conjugation of peptides to silk fibroin for facile hydrogel functionalization. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020;48(7):1905-1915. [2] YANG N, QI P, REN J, et al. Polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin/borax hydrogel ionotronics: a highly stretchable, self-healable, and biocompatible sensing platform. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(26):23632-23638. [3] LI DW, HE J, HE FL, et al. Silk fibroin/chitosan thin film promotes osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(9): 088532821875776. [4] GUAN Y, SUN F, ZHANG X, et al. Silk fibroin hydrogel promote burn wound healing through regulating TLN1 expression and affecting cell adhesion and migration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31:48. [5] YANG C, CHEN S, SU H, et al. Biocompatible, small-sized and well-dispersed gold nanoparticles regulated by silk fibroin fiber from Bombyx mori cocoons. Front Mater Sci. 2019;13(2):126-132. [6] RAMESHBABU AP, BANKOTI K, DATTA S, et al. Bioinspired 3D porous human placental derived extracellular matrix/silk fibroin sponges for accelerated bone regeneration. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2020;113: 110990. [7] GOMAA F, FAWAL E, MARWA M, et al. Hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel for wound dressing: Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;111:649-659. [8] MIGUEL SP, SIMÕES D, MOREIRA AF, et al. Production and characterization of electrospun silk fibroin based asymmetric membranes for wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;121:524-535. [9] NOURMOHAMMADI J, HADIDI M, NAZARPAK MH, et al. Physicochemical and antibacterial characterization of nanofibrous wound dressing from silk fibroin-polyvinyl alcohol-elaeagnus angustifolia extract. Fiber Polym. 2020; 21(3):456-464. [10] ZHANG X, CHEN Z, BAO H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin/curcumin sustained-release film. Mater. 2019;12(20):3340. [11] WU CN, FUH SC, LIN SP, et al. Tempo-oxidized bacterial cellulose pellicle with silver nanoparticles for wound dressing. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(2):544-554. [12] SIMÕES D, MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, et al. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 127:130-141. [13] PATIL S, SINGH N. Antibacterial silk fibroin scaffolds with green synthesized silver nanoparticles for osteoblast proliferation and human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Colloid Surface B. 2019;176:150-155. [14] KARATEPE UY, OZDEMIR T. Improving mechanical and antibacterial properties of PMMA via polyblend electrospinning with silk fibroin and polyethyleneimine towards dental applications. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):510-515. [15] MAITI P, PALADUGU L, DUNBAR GL. Solid lipid curcumin particles provide greater anti-amyloid, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects than curcumin in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci. 2018;19(1):7-25. [16] TSUDA T. Curcumin as a functional food-derived factor: degradation products, metabolites, bioactivity, and future perspectives. Food Funct. 2018;9(2):705-714. [17] DE OLIVEIRA EF, TOSATI JV, TIKEKAR RV, et al. Antimicrobial activity of curcumin in combination with light against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria innocua : Applications for fresh produce sanitation. Postharvest Biol Technol. 2018;137:86-94. [18] ZINELIS S, BRANTLEY W. Orthodontic applications of biomaterials. Chapter 3 - Structure/property relationships in orthodontic ceramics. Woodhead Publishing, 2017:61-71. [19] PÉREZ L, CABRERA I, SANTIAGO AA, et al. Effect of the Al–CNT interlayer on the tensile elastic modulus of Al matrix composites with random dispersion of CNTs. J Braz Soc Mech Sci. 2018;40(11):550. [20] BORTHAGARAY G. Inorganic frameworks as smart nanomedicines.Chapter 8 - Silver-containing nanoparticles in the research of new antimicrobial agents against ESKAPE pathogens. William Andrew Publishing. 2018:317-386. [21] MARSLIN G, SELVAKESAVAN RK, FRANKLIN G, et al. Antimicrobial activity of cream incorporated with silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Withania somnifera. Int J Nanomed. 2014;10:5955-5963. [22] MARIANELLI C, PETRUCCI P, COMELLI MC, et al. Silver sucrose octasulfate (IASOS) as a valid active ingredient into a novel vaginal gel against human vaginal pathogens: in vitro antimicrobial activity assessment. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):97791-97798. [23] VIEIRA AC, VICENTE AF, PEREZ R, et al. Chloral hydrate anesthesia and lens opacification in mice. Curr Eye Res. 2009;34(5):355-359. [24] BERMUDEZ MA, VICENTE AF, ROMERO MC, et al. Time course of cold cataract development in anesthetized mice. Curr Eye Res. 2011; 36(3):278-284. [25] HUANG Y, SHI F, WANG L, et al. Preparation and evaluation of Bletilla striata polysaccharide/carboxymethyl chitosan/carbomer 940 hydrogel for wound healing. Int J Biol Macomol. 2019;132:729-737. [26] FAN Z, LIU B, WANG J, et al. A novel wound dressing based on Ag/Graphene polymer hydrogel: effectively kill bacteria and accelerate wound healing. Adv Fun Mater. 2014;24(25):3933-3943. [27] BORRERO-LOPEZ O, HOFFMAN M. Measurement of fracture strength in brittle thin films. Surf Coat Tech. 2014;254:1-10. [28] GADHAVE RV, MAHANWAR PA, GADEKAR PT. Effect of glutaraldehyde on thermal and mechanical properties of starch and polyvinyl alcohol blends. Des Monomers Polym. 2019;22(1):164-170. [29] ARIANITA A, CAHYANINGTYAS, AMALIA B, et al. Effect of glutaraldehyde to the mechanical properties of chitosan/nanocellulose. J Phys Conf Ser. 2019;1317:012045. [30] LEE SY, MOHAN DJ, KANG IA, et al. Nanocellulose reinforced PVA composite films: effects of acid treatment and filler loading. Fiber Polym. 2009;10(1):77-82. [31] TONG WY, BIN ABDULLAH AYK, BINTI ROZMAN NAS, et al. Antimicrobial wound dressing film utilizing cellulose nanocrystal as drug delivery system for curcumin. Cellulose. 2018;25:631-638. [32] PRIYADARSINI KI. The chemistry of curcumin: from extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules. 2014;19(12):20091-20112. [33] LIANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN Z, et al. Thiol-ene click reaction initiated rapid gelation of PEGDA/silk fibroin hydrogels. Polymers. 2019;11(12):2102. [34] SCHREML S, SZEIMIES RM, PRANTL L, et al. Wound healing in the 21st century. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:866-881. [35] SALIM MN, SILVIA M, ALIZA D, et al. Efficacy of jatropha curcas latex cream in the epithelialization phase of wound healing in mice skin. E3S Web Conf. 2020;151:01038. [36] XU R, LUO G, XIA H, et al. Novel bilayer wound dressing composed of silicone rubber with particular micropores enhanced wound re-epithelialization and contraction. Biomaterials. 2015;40:1-11. [37] SEIFERT AW, MADEN M. New insights into vertebrate skin regeneration. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;310:129-169. [38] CLARK RAF. Principles of Tissue Engineering. Chapter 76 - Wound Repair: Basic Biology to Tissue Engineering. Academic Press. 2014: 1595-1617. [39] JONES K. Fibrotic response to biomaterials and all associated sequence of fibrosis. Host Response Biomater. 2015:189-237. [40] BALAKRISHNAN B, MOHANTY M, UMASHANKAR PR, et al. Evaluation of an in situ forming hydrogel wound dressing based on oxidized alginate and gelatin. Biomaterials. 2005;26(32):6335-6342. [41] BUSH K, GERTZMAN AA. Skin tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Chapter 5 - Process development and manufacturing of human and animal acellular dermal matrices. Academic Press. 2016: 83-108. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [3] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun. A modified flap immediate implant is beneficial to soft tissue reconstruction in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [4] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [5] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [6] | Sun Qi, Zhou Yanan, Dong Xin, Li Ning, Yan Jiazhen, Shi Haojiang, Xu Sheng, Zhang Biao. Metal-ceramic interface characteristics of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [7] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [9] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [10] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [11] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [12] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [13] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [14] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [15] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||