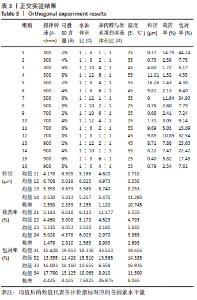
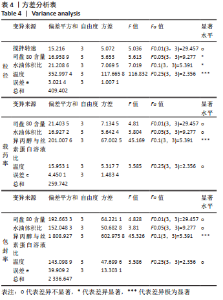
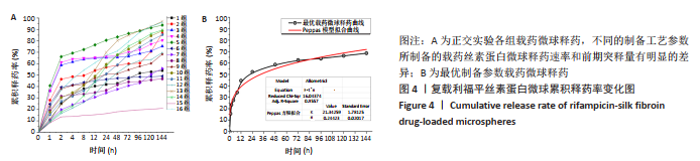
[1] 秦世炳,宋言峥,董伟杰.骨关节结核临床诊断与治疗进展及其规范化专题研讨会纪要[J].中国防痨杂志,2013,35(1):81-84.
[2] 赖小丽,邓永佳,姚叶萍.异烟肼联合利福平对菌阳性肺结核患者血清降钙素原及免疫功能的影响[J]. 中医临床研究,2020,12(18): 139-141.
[3] 刘琳,孔祥东,蔡玉荣,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/丝素蛋白复合支架材料的降解特性及生物相容性研究[J].化学学报,2008(16):1919-1923.
[4] OLIVEIRA BARUD HG, BARUD HDS, CAVICCHIOLI M, et al. Preparation and characterization of a bacterial cellulose/silk fibroin sponge scaffold for tissue regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;128:41-51.
[5] SHIN EY, PARK JH, SHIN ME, et al. Evaluation of Chondrogenic Differentiation Ability of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Using miR-30. Macromol Res. 2019; 27(4):369-376.
[6] CHEN SY, LIU S, ZHANG LL,et al. Construction of injectable silk fibroin/polydopamine hydrogel for treatment of spinal cord injury. Chem Eng J. 2020;399:125795.
[7] LI G, LI Y, CHEN GQ, et al. Silk-based biomaterials in biomedical textiles and fiber-based implants. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(8):1134-1151.
[8] 雷容.多孔丝素蛋白颗粒的制备及其作为阿霉素药物载体的研究[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2018.
[9] 任旭,刘涛,朱莹,等.丝素/海藻酸钠载药复合支架的药物缓释行为及其活性[J].浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,43(2): 209-215.
[10] 方敏,王璐,侯佳欣,等.丝素蛋白复合石墨烯类材料在生物医学领域中的研究进展[J].材料导报,2020,34(S1):511-515.
[11] 费正奇,胡蕴玉.抗骨结核缓释药物:载体材料的选择[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(21):3387-3391.
[12] 王钦,沈凯,王胜男,等.盐酸川芎嗪羧甲基壳聚糖丝素蛋白微球的制备和体外释放特性[J].中国药师,2020,3(8):1504-1509.
[13] 潘岳林,杨明英,邓连霞,等.自组装方法制备丝素微球及其结构与性能表征[J].蚕业科学,2015,41(4):729-733.
[14] SRIHANAM P, SRISUWAN Y, IMSOMBUT T, et al. Silk fibroin microspheres prepared by the water-in-oil emulsion solvent diffusion method for protein delivery. Korean J Chem Eng. 2011;28(1):293-297.
[15] PEPPAS NA. 1.Commentary on an exponential model for the analysis of drug delivery:Original research article: a simple equation for description of solute release: I II. Fickian and non-Fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs,1987. J Control Release. 2014;190:31-32.
[16] SINGH B, CHAUHAN GS, SHARMA DK, et al. The release dy-namics of model drugs from the psylium and N-hydroxym-ethylacrylamide based hydrogels. Int J Pharm. 2006;325(1-2):15-25.
[17] MASOUMI S, ESMAEILI A. New method of creating hybrid of buprenorphine loaded rifampin/polyethylene glycol/alginate nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;159:204-212.
[18] MISRA A, GANESH S, SHAHIWALA A, et al. Drug delivery to the central nervous system: a review. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2003;6(2):252-273.
[19] 邵文尧,何彩云,冯艳玲,等.乳化-溶剂挥发法制备聚乳酸载药微球[J].功能材料,2015,46(3):3121-3126.
[20] 刘亚珍,邱晓明,李松凯.正交设计优化万古霉素/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球的制备及体外药物释放[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(2):211-217.
[21] 陈英,刘中宁,李波,等.阿司匹林缓释微球的制备及体外缓释效果评估[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2019,51(5):907-912.
[22] MI FL, SHYU SS, LIN YM, et al. Chitin/PLGA blend microspheres as a biodegradable drug delivery system: a new delivery system for protein. Biomaterials. 2003;24(27):5023-5036.
[23] MENDES C, ANDRREJEWSKI RG, PINTO JMO, et al. Impact of Drug-Polymer Interaction in Amorphous Solid Dispersion Aiming for the Supersaturation of Poorly Soluble Drug in Biorelevant Medium. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2020;21(5):189-199.
[24] 杜姗,周伟涛,张一敏,等.表面介孔柞蚕丝素蛋白微球的制备及药物释放性能[J].材料科学与工程学报,2019,37(5):736-740.
[25] MATOS RL, LU T, LEEKE GA, et al. Single-step coprecipitation and coating to prepare curcumin formulations by supercritical fluid technology. J Supercrit Fluids. 2020;159:104758.
[26] ZHAO M, HUANG X, ZHANG H, et al. Probiotic encapsulation in water-in-water emulsion via heteroprotein complex coacervation of type-A gelatin/sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020;105:105790.
[27] 黄丽霞.壳聚糖微/纳米功能材料的构建及其生物医学应用研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2019.
[28] 丁婷婷.负载BMP-2的MPEG-PCL微球的制备及成骨活性评价[D].济南:山东大学,2018.
[29] MUNICOY S, ÁLVAREZ ECHAZÚ MI, ANTEZANA PE, et al. Stimuli-Responsive Materials for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4724.
[30] 李莹莹,王昉,刘其春,等.丝素蛋白及其复合材料的研究进展[J].材料工程,2018,46(8):14-26.
[31] 李祥明,王增凯,董明东,等.光交联丝素蛋白水凝胶的制备及生物医学应用[J].中国材料进展,2020,39(6):421-429.
[32] 王亚茹,张青,雷芳,等.丝素蛋白-氧化石墨烯多孔微球支架的制备及性能测试[J].蚕业科学,2019,45(2):231-236. |