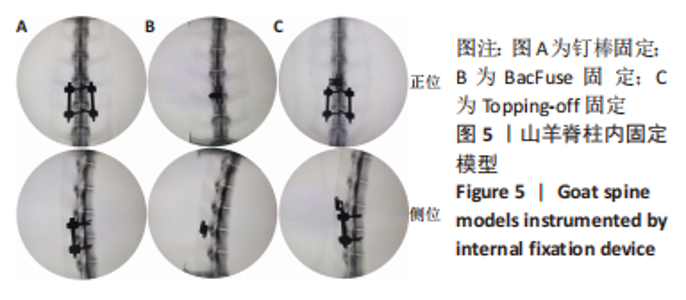
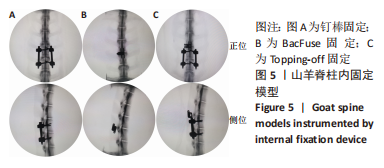
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1325-1329.doi: 10.12307/2023.912
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease
Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai
- Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
-
Received:2022-12-23Accepted:2023-02-08Online:2024-03-28Published:2023-07-25 -
Contact:Tang Hai, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China -
About author:Chen Mengmeng, MD, Physician, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1325-1329.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

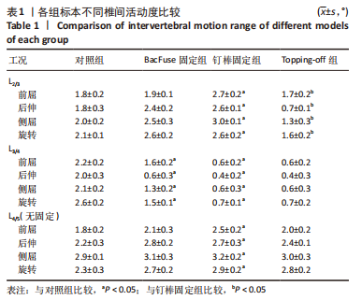
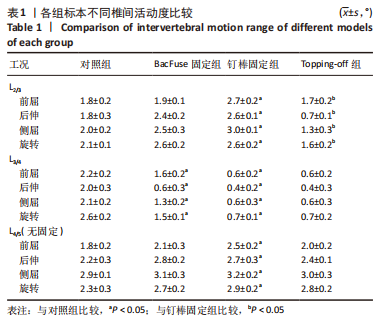
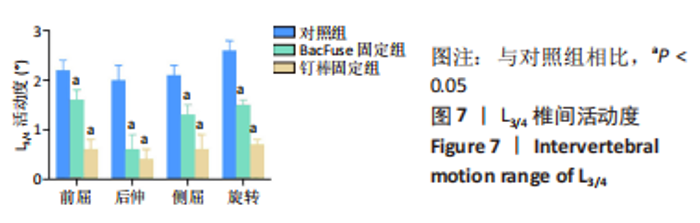
与对照组相比,钉棒固定组的近节邻近节段L2/3在前屈、后伸、侧屈与旋转方向上的活动度均明显增加,分别增加50%,44.44%,50%,58.96% (P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,BacFuse固定组邻近节段在后伸、侧屈及旋转方向上分别增加33.33%,25%,23.81%(P < 0.05);前屈活动未见明显变化。与钉棒固定组相比,Topping-off组L2/3椎间活动度在前屈、后伸、侧屈、旋转时分别减少37.04%,73.08%,56.67%,38.46% (P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,Topping-off组在后伸、侧屈、旋转时分别减少61.11%,35%,23.81% (P < 0.05),前屈无明显影响。见图6。"

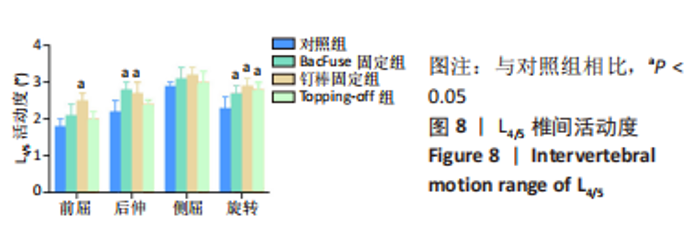
与对照组相比,BacFuse固定组远节邻近节段L4/5在后伸、旋转方向上分别增加27.3%,17.39%(P < 0.05);前屈、侧屈活动未见明显变化。与对照组相比,钉棒固定组的远节邻近节段在前屈、后伸、旋转方向上的活动度均明显增加,分别增加38.89%,22.73%,26.09%(P < 0.05);侧屈活动未见明显变化。与钉棒固定组相比,Topping-off组L4/5节段椎间活动度在前屈方向上减少20%(P < 0.05),后伸、侧屈及旋转未见明显区别。与对照组相比,Topping-off组L4/5节段椎间活动度在旋转方向上增加了21.74%(P < 0.05),前屈、后伸、侧屈及旋转未见明显差异。见图8。"
| [1] 唐海,张体栋,陈浩,等. 棘突融合钢板治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2016,36(6):344-352. [2] FALOWSKI SM, MANGAL V, POPE J, et al. Multicenter Retrospective Review of Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Minimally Invasive Lumbar Interspinous Fusion Device. J Pain Res. 2021;14:1525-1531. [3] WANG R, JI X, LIU L, et al. Changes of MRI in inter-spinal distraction fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: A retrospective analysis covering 3 years. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;81:455-461. [4] WEI H, TANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Preliminary efficacy of inter-spinal distraction fusion which is a new technique for lumbar disc herniation. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):899-907. [5] 陈萌萌,唐海.棘突间装置在腰椎退行性变疾病的相关生物力学研究进展[J]. 国际外科学杂志,2021,48(8):572-576. [6] LIU Z, ZHANG S, LI J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different interspinous process devices in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):585. [7] 王宝东,侯继春,何人可,等. 国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器体外生物力学测试及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1897-1904. [8] BONALDI G. Minimally invasive dynamic stabilization of the degenerated lumbar spine. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2010;20(2):229-241. [9] MANFRE L, DE VIVO AE, AL QATAMI H, et al. Successful use of percutaneous interspinous spacers and adjunctive spinoplasty in a 9 year cohort of patients. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12(7):673-677. [10] VERHOOF OJ, BRON JL, WAPSTRA FH, et al. High failure rate of the interspinous distraction device (X-Stop) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17(2):188-192. [11] WANG K, ZHU Z, WANG B, et al. Bone resorption during the first year after implantation of a single-segment dynamic interspinous stabilization device and its risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:117. [12] RAIKAR SV, PATIL AA, PANDEY DK, et al. Inter Spinal Fixation and Stabilization Device for Lumbar Radiculopathy and Back Pain. Cureus. 2021;13(11): e19956. [13] POSTACCHINI F, POSTACCHINI R, MENCHETTI PP, et al. Lumbar Interspinous Process Fixation and Fusion with Stand-Alone Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumented Fusion Implant in Patients with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Undergoing Decompression for Spinal Stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(1): 27-37. [14] CUELLAR JM, FIELD JS, BAE HW. Distraction Laminoplasty With Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumented Fusion (ILIF) for Lumbar Stenosis With or Without Grade 1 Spondylolisthesis: Technique and 2-Year Outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 8:S97-S105. [15] SCLAFANI JA, LIANG K, OHNMEISS DD, et al. Clinical outcomes of a polyaxial interspinous fusion system. Int J Spine Surg. 2014;8:35. [16] CHEN M, JIA P, FENG F, et al. A novel minimally invasive technique of inter-spinal distraction fusion surgery for single-level lumbar spinal stenosis in octogenarians: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022; 17(1):100. [17] KAYE AD, EDINOFF AN, TEMPLE SN, et al. A Comprehensive Review of Novel Interventional Techniques for Chronic Pain: Spinal Stenosis and Degenerative Disc Disease-MILD Percutaneous Image Guided Lumbar Decompression, Vertiflex Interspinous Spacer, MinuteMan G3 Interspinous-Interlaminar Fusion. Adv Ther. 2021;38(9):4628-4645. [18] CHEN M, TANG H, SHAN J, et al. A new interspinous process distraction device BacFuse in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with 5 years follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(26):e20925. [19] WILKE HJ, DRUMM J, HAUSSLER K, et al. Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(8):1049-1056. [20] LINDSEY DP, SWANSON KE, FUCHS P, et al. The effects of an interspinous implant on the kinematics of the instrumented and adjacent levels in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(19):2192-2197. [21] GUO Z, LIU G, WANG L, et al. Biomechanical effect of Coflex and X-STOP spacers on the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(7):5155-5163. [22] BRUSSEE P, HAUTH J, DONK RD, et al. Self-rated evaluation of outcome of the implantation of interspinous process distraction (X-Stop) for neurogenic claudication. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):200-203. [23] KARAHALIOS DG, KAIBARA T, PORTER RW, et al. Biomechanics of a lumbar interspinous anchor with anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12(4):372-380. [24] TECHY F, MAGESWARAN P, COLBRUNN RW, et al. Properties of an interspinous fixation device (ISD) in lumbar fusion constructs: a biomechanical study. Spine J. 2013;13(5):572-579. [25] GONZALEZ-BLOHM SA, DOULGERIS JJ, AGHAYEV K, et al. Biomechanical analysis of an interspinous fusion device as a stand-alone and as supplemental fixation to posterior expandable interbody cages in the lumbar spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(2):209-219. [26] LEE CH, KIM YE, LEE HJ, et al. Biomechanical effects of hybrid stabilization on the risk of proximal adjacent-segment degeneration following lumbar spinal fusion using an interspinous device or a pedicle screw-based dynamic fixator. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27(6):643-649. [27] SHEN H, FOGEL GR, ZHU J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of lumbar fusion with proximal interspinous process device implantation. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(8):e3498. [28] KONG C, LU S, HAI Y, et al. Biomechanical effect of interspinous dynamic stabilization adjacent to single-level fusion on range of motion of the transition segment and the adjacent segment. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(4):355-359. [29] 马亮,许永涛,佘远举.腰椎融合联合上一节段棘突间动态固定的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3647-3653. [30] DEER TR, SAYED D, MALINOWSKI MN, et al. A Review of Emerging Evidence for Utilization of a Percutaneous Interspinous Process Decompression Device to Treat Symptomatic Lumbar Adjacent-Segment Degeneration. Pain Med. 2019;20(Suppl 2):S9-S13. [31] CHEN MM, JIA P, TANG H. Cortical bone trajectory fixation in cemented vertebrae in lumbar degenerative disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(28):8609-8615. |
| [1] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [2] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [3] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [4] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [5] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [6] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [7] | Zhang Rui, Wang Kun, Shen Zicong, Mao Lu, Wu Xiaotao. Effects of endoscopic foraminoplasty and laminoplasty on biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc and isthmus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 833-839. |
| [8] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [9] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [10] | Huang Peizhen, Dong Hang, Cai Qunbin, Lin Ziling, Huang Feng. Finite element analysis of anterograde and retrograde intramedullary nail for different areas of femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 868-872. |
| [11] | Wang Mingming, Zhang Zhong, Sun Jianhua, Zhao Gang, Song Hua, Yan Huadong, Lyu Bin. Finite element analysis of three different minimally invasive fixation methods for distal tibial fractures with soft tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 879-885. |
| [12] | Hou Zexin, Xu Benke, Dai Yuan, He Chuan, Zhang Chaoju, Li Xiaolin. Finite element analysis of the mechanism of dorsiflexion injury of wrist joint in elderly people after falls [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 886-890. |
| [13] | Ning Tianliang, Wang Kun, Wang Lingbiao, Han Pengfei. Finite element analysis on correction effect of varus foot orthosis based on the three-point force principle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 891-899. |
| [14] | Zhang Lili, Zhang Xinglai, Zhang Jie, Zheng Jiejiao. Effect of visual feedback on landing biomechanics in chronic ankle instability patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 900-904. |
| [15] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||