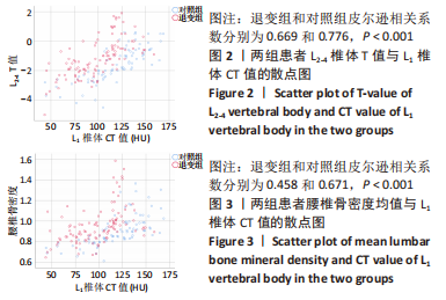
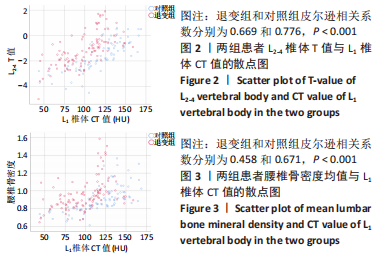
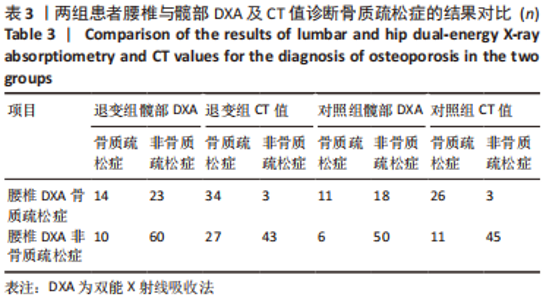
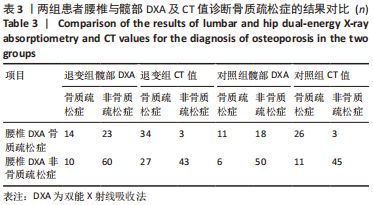
[1] SIVASUBRAMANIAM V, PATEL HC, OZDEMIR BA, et al. Trends in hospital admissions and surgical procedures for degenerative lumbar spine disease in England: a 15-year time-series study. Bmj Open. 2015;5(12):e009011.
[2] 程晓光, 董剩勇, 王亮, 等. 应用双能X线骨密度仪调查中国人群骨密度水平和骨质疏松症患病率[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志,2019,13(1):51-58.
[3] ZHANG R, ZHANG C, SHU X, et al. Effect of Osteoporosis on Adjacent Segmental Degeneration After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Under Whole Body Vibration. World Neurosurg. 2021;152:e700-e707.
[4] 赵继荣, 张天龙, 朱换平, 等. 腰椎间盘退变与骨质疏松的相关性[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2021,14(3):302-307.
[5] UEI H, TOKUHASHI Y, MASEDA M, et al. Exploratory analysis of predictors of revision surgery for proximal junctional kyphosis or additional postoperative vertebral fracture following adult spinal deformity surgery in elderly patients: a retrospective cohort study]. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1): 252.
[6] ZOU D, MUHEREMU A, SUN Z, et al. Computed tomography Hounsfield unit-based prediction of pedicle screw loosening after surgery for degenerative lumbar spine disease. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020:1-6. doi: 10.3171/2019.11.SPINE19868.
[7] MI J, LI K, ZHAO X, et al. Vertebral Body Hounsfield Units are Associated With Cage Subsidence After Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion With Unilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(8):E1130-E1136.
[8] 包洁, 邹达, 李危石. 椎体CT值评估腰椎退变患者骨密度的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(8):745-750.
[9] MURAKI S, YAMAMOTO S, ISHIBASHI H, et al. Impact of degenerative spinal diseases on bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in elderly women. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(9):724-728.
[10] ZOU D, LI W, DENG C, et al. The use of CT Hounsfield unit values to identify the undiagnosed spinal osteoporosis in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(8):1758-1766.
[11] WARD RJ, ROBERTS CC, BENCARDINO JT, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria(®) Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Density. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017; 14(5s): S189-S202.
[12] SCHREIBER JJ, ANDERSON PA, ROSAS HG, et al. Hounsfield units for assessing bone mineral density and strength: a tool for osteoporosis management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(11):1057-1063.
[13] ALACREU E, MORATAL D, ARANA E. Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis by routine CT in Southern Europe. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(3):983-990.
[14] ZAIDI Q, DANISA OA, CHENG W. Measurement Techniques and Utility of Hounsfield Unit Values for Assessment of Bone Quality Prior to Spinal Instrumentation: A Review of Current Literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(4):E239-E244.
[15] HENDRICKSON NR, PICKHARDT PJ, DEL RIO AM, et al. Bone Mineral Density T-Scores Derived from CT Attenuation Numbers (Hounsfield Units): Clinical Utility and Correlation with Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry. Iowa Orthop J. 2018;38:25-31.
[16] PICKHARDT PJ, POOLER BD, LAUDER T, et al. Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis using abdominal computed tomography scans obtained for other indications. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158(8):588-595.
[17] LEE SJ, BINKLEY N, LUBNER MG, et al. Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis using the sagittal reconstruction from routine abdominal CT for combined assessment of vertebral fractures and density. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(3):1131-1136.
[18] KIM JY, RYU DS, PAIK HK, et al. Paraspinal muscle, facet joint, and disc problems: risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar fusion. Spine J. 2016;16(7):867-875.
[19] WEISHAUPT D, ZANETTI M, BOOS N, et al. MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints. Skeletal Radiol. 1999;28(4):215-219.
[20] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318.
[21] CHOI MK, KIM SM, LIM JK. Diagnostic efficacy of Hounsfield units in spine CT for the assessment of real bone mineral density of degenerative spine: correlation study between T-scores determined by DEXA scan and Hounsfield units from CT. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158(7):1421-1427.
[22] HOCAOGLU E, INCI E, VURAL M. Could Computed Tomography Hounsfield Unit Values of Lumbar Vertebrae Detect Osteoporosis? Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(8):988-995.
[23] HAMDY RC, PETAK SM, LENCHIK L. Which central dual X-ray absorptiometry skeletal sites and regions of interest should be used to determine the diagnosis of osteoporosis? J Clin Densitom. 2002;5 Suppl:S11-S18.
[24] 边平达, 应奇峰, 钱素凤, 等. 270例高龄老人股骨近端和腰椎正位骨密度对比分析 [J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2013,6(3):255-256.
[25] SMITH AD. Screening of Bone Density at CT: An Overlooked Opportunity. Radiology. 2019;291(2):368-369.
[26] ZOU D, JIANG S, ZHOU S, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Combination of DXA and Hounsfield Units. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(7):E406-E410.
[27] 刘韵婷, 郭辉, 张一民. 骨骼肌含量、身体活动水平与骨密度的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2478-2482.
|