Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 787-792.doi: 10.12307/2023.056
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration
Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin
- Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-16Accepted:2022-03-17Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-25 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoming, Master, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Min, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical and Health Technological Development Plan of Shandong Province, No. 2016WS0121 (to LTB [project participant]); the Science and Technology Program of Binzhou Medical University, No. BY2017KJ05 (to LTB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
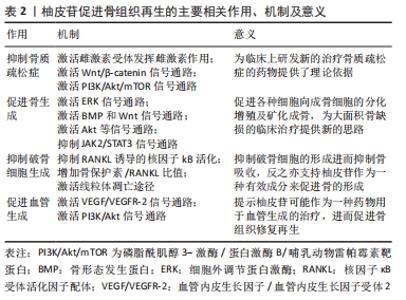
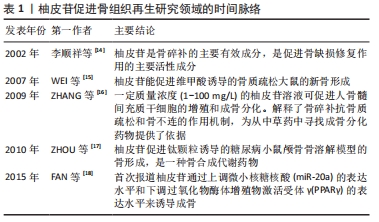
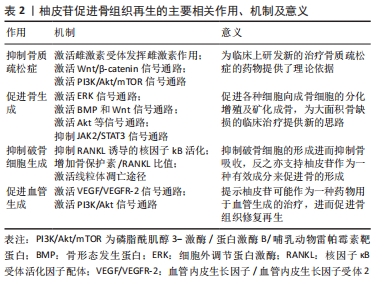
2.1 柚皮苷促进骨再生的主要相关作用 2.1.1 柚皮苷具有抑制骨质疏松症的作用 (1)柚皮苷抑制绝经后骨质疏松症:研究表明,绝经后的妇女易患骨质疏松症的主要原因就是其血液中雌激素分泌大幅度减少[19]。最近学者发现植物雌激素可能通过抑制骨吸收来降低骨缺失和改变骨形成来改善骨质疏松症[20]。柚皮苷已被证明是一种植物雌激素[21]。实验研究中通过切除卵巢建立绝经后妇女骨质疏松症的动物模型[22]。有报道表明雌激素作为配体通过激活雌激素受体调节碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、RUNX2、骨桥蛋白、破骨细胞分化因子核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator nuclearfactor κB ligand,RANKL)、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的表达,这些成骨和破骨相关基因的表达与雌激素受体密切相关[23]。已有研究表明10 nmol/L的柚皮苷对大鼠成骨样细胞(UMR-106)发挥雌激素样活性,通过雌激素受体模拟雌二醇刺激UMR-106细胞增殖、上调碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达活性,促进诱导成骨的作用,增强骨保护素/RANKL mRNA的表达活性,抑制破骨细胞的生成;柚皮苷发挥雌激素作用的机制可能是10 nmol/L的柚皮苷通过非配体依赖的方式优先独立激活UMR-106细胞内的雌激素受体,进而诱导细胞丝氨酸118位的雌激素受体α磷酸化,从而促进碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2、骨桥蛋白、RANKL等成骨及破骨相关的基因的转录表达,达到促进骨修复的作用[24]。WU等[25]研究发现,柚皮苷可增强人和小鼠成骨细胞雌激素受体α的转位和反式激活活性,促进碱性磷酸酶mRNA和蛋白的表达及酶活性,在碱性磷酸酶基因5’-启动子中发现了2个雌激素反应元件(ERE),因此柚皮苷在成骨细胞中通过激活雌激素受体α依赖途径诱导碱性磷酸酶基因的表达,促进成骨细胞增殖、分化及矿化成骨。此外,柚皮苷能够增加小鼠左股骨缺损部位骨小梁的体积和数量,促进骨愈合,提高骨的生物力学强度。综上所述,柚皮苷通过激活雌激素受体依赖途径或非配体依赖途径发挥雌激素样作用,为临床上治疗绝经后骨质疏松症提供了新的研究方向。 (2)柚皮苷抑制失用性骨质疏松症:失用性骨质疏松症是由于肢体运动受限或障碍,导致骨质吸收增加引起的,常用下肢固定或失神经制动作为诱导失用性骨质疏松症的动物模型[22]。在大鼠坐骨神经切断模型的研究中发现,柚皮苷可以减轻坐骨神经切断组大鼠骨膜蛋白和β-catenin基因表达的降低,抑制了硬化素表达的增加,并激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,进而增加成骨细胞相关基因的表达活性,促进骨修复和再生,从而抑制大鼠失用性骨质疏松症的进展[26]。在单侧坐骨神经切断所致骨丢失的研究中发现,加入柚皮苷后的去神经组骨密度增加、骨小梁微结构及力学性能明显改善,并且Sema 3A、β-catenin及Nrp1 mRNA的表达上调[27]。提示柚皮苷可能促进了支配胫骨的坐骨神经元Sema 3A表达活性,Sema 3A通过调节坐骨神经来间接调节骨代谢促进骨修复和再生[28];亦可能是柚皮苷通过促进成骨细胞分泌Sema 3A,Sema 3A与NRP1结合不仅激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路刺激成骨细胞分化促进骨生成,且抑制破骨细胞分化因子RANKL诱导的破骨细胞形成。综上可知,柚皮苷在抑制失用性骨质疏松症进展方面有一定的研究价值。 (3)柚皮苷抑制糖皮质激素性骨质疏松症:糖皮质激素性骨质疏松症是一种由疾病和药物引起的,与代谢异常相关的伴有骨缺失和骨组织结构损坏的全身性代谢性疾病[29-30]。GE等[31]通过建立糖皮质激素性骨质疏松症大鼠模型,发现柚皮苷激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(phosphatidylinositol3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin,PI3K/Akt/mTOR)信号通路,提高因地塞米松磷酸钠注射液所导致大鼠的PI3K、AKT及mTOR的mRNA和总蛋白表达的降低。并且柚皮苷通过增加成骨细胞自噬相关因子Beclin-1的表达、降低p62表达、升高阳性细胞率及增多自噬小体的数量,促进了成骨细胞的自噬,因为自噬是维持成骨细胞稳定状态的机制之一,所以柚皮苷能够在维持成骨细胞稳定下提高成骨细胞增殖分化能力,且呈剂量依赖性。总之柚皮苷通过激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强成骨细胞增殖分化及诱导成骨细胞自噬,增强骨密度,具有抑制糖皮质激素性骨质疏松症活动进展的作用。 2.1.2 柚皮苷具有促进骨生成的作用 在柚皮苷对人骨髓间充质干细胞的研究表明,柚皮苷对人骨髓间充质干细胞无细胞毒性且促进细胞的增殖,并可以激活细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)1/2的磷酸化,在0-100 mg/L质量浓度中呈剂量依赖性地促进成骨标记物的表达,包括碱性磷酸酶、RUNX-2、OSX、Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素等,并增加了钙结节数量和钙沉积水平;在抑制剂U0126存在的情况下,明显抑制了柚皮苷处理后激活的p-ERK蛋白的表达活性,进而抑制了相关成骨标记物的表达[32]。以上提示,柚皮苷通过激活ERK信号通路来调控成骨相关基因的表达水平及促进矿化结节形成进而促进人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及矿化成骨,具有促进骨生成的潜力。还有研究发现柚皮苷降低了p-JAK2和p-STAT3的蛋白水平,并呈剂量依赖性的方式促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶的表达活性,碱性磷酸酶活性可作为骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的功能指标[33]。柚皮苷通过逆转绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠骨密度、骨小梁厚度、骨小梁数、骨体积分数降低,骨小梁分离度、骨表面积骨体积比值升高,提高骨形成率,降低骨吸收率,最终减轻绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的骨丢失。柚皮苷通过部分恢复绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的碱性磷酸酶活力、降低骨钙素水平及升高环磷酰胺脱氢酶(TRAP)和环磷酰胺脱氧核糖核酸水平,改善了绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的骨代谢异常。另外,采用JAK2/STAT3信号抑制剂AG490处理后与柚皮苷处理的实验结果一致。以上提示柚皮苷通过抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化。 有学者研究柚皮苷对人源羊水干细胞作用中,发现1-100 mg/L的柚皮苷呈剂量依赖性地促进了细胞的增殖及碱性磷酸酶的活性,促进人源羊水干细胞成骨分化[34]。并且柚皮苷增加骨保护素的表达、降低RANKL的表达,骨保护素与RANKL比值进而增加,抑制破骨细胞的生成,减少骨吸收。还发现骨形成蛋白相关调节因子(骨形态发生蛋白4和RUNX2 mRNA)和Wnt相关调节因子(β-catenin和Cyclin D1)mRNA表达上调,并且在抑制剂noggin或dkk-1存在下,碱性磷酸酶活性显著降低。骨形态发生蛋白诱导RUNX2的表达,促进人源羊水干细胞成骨分化。细胞周期蛋白D1是Wnt途径的靶基因,Wnt信号通过β-catenin的激活促进人源羊水干细胞成骨分化及骨的形成。 林春淑等[35]发现柚皮苷明显改善了高糖环境下小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞的活力,柚皮苷提高了 MC3T3-E1 细胞在高糖环境下胰岛素样生长因子1、蛋白激酶1(Akt1)、成骨细胞转录因子Runx2的mRNA和蛋白的表达,上调碱性磷酸酶表达活性,从而促进了高糖下小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞的生长、增殖分化及矿化成骨的能力,进而促进了骨修复和再生。 2.1.3 柚皮苷具有抑制破骨细胞生成的作用 破骨细胞是参与骨吸收的主要功能细胞,也是目前主要抗吸收药物的主要靶点[36]。与破骨细胞生成相关的细胞因子包括:核因子kB(NF-kB)、核因子κB受体活化因子(receptor activator nuclearfactor κB,RANK)、RANKL等[37]。研究发现柚皮苷通过抑制RANKL诱导的人核因子kB抑制蛋白α(IkB-α)降解进而抑制核因子kB活化,进而抑制脂多糖诱导的一氧化氮(NO)的产生和炎性基因产物的表达,包括诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、肿瘤坏死因子α、环氧化酶2、白细胞介素6等与破骨细胞形成相关的正性调节因子的表达,从而抑制破骨细胞的分化和存活,起到抑制骨吸收的作用[38]。骨保护素是破骨细胞分化因子RANKL的诱导受体,骨保护素通过与RANKL结合可减少破骨细胞的生成,其骨保护素/RANKL比值是成骨和破骨细胞之间生理动态的重要因素之一。YANG等[39]发现柚皮苷通过诱导骨保护素表达的上调进而使骨保护素RANKL比值增加来抑制破骨细胞的生成。LI等[40]体外柚皮苷对破骨细胞的研究显示,柚皮苷可下调抗凋亡因子BCL-2 mRNA的表达,上调促凋亡因子BAX的表达,从而降低BCL-2/BAX的比值,因线粒体膜在柚皮苷的诱发下通透性增加,诱使促凋亡因子如细胞色素C等释放到细胞质中,进而导致细胞凋亡蛋白酶Caspase依赖的破骨细胞凋亡,故柚皮苷可通过激活线粒体凋亡途径诱导破骨细胞自发凋亡。 2.1.4 柚皮苷具有促进血管生成的作用 血管是骨代谢过程中的重要因素之一,血管生成在骨的发育、维持和修复中起着重要作用。其中血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)在血管生成中起了关键性的作用[41],血管化是骨形成的关键步骤。体外研究柚皮苷对大鼠骨质疏松性骨折血管生成的影响中发现,柚皮苷可以诱导出许多新生血管,增大血管面积、厚度,上调血管内皮生长因子、血管内皮生长因子受体2(VEGFR-2)的活性[42]。这表明柚皮苷可能通过调节血管内皮生长因子/血管内皮生长因子受体2信号通路直接刺激大鼠骨骼的血管生成、血管化和骨转换来促进骨修复和骨折愈合。骨修复的重要特征之一就是血管生成,骨再生成功的基础就是有充足的血液供应。有报道柚皮苷能够抑制内质网应激和线粒体去极化导致的血管内皮细胞凋亡,保护血管内皮细胞并促进细胞增殖,还可调节内皮细胞的功能,抑制内皮素,促进一氧化氮(NO)的合成,诱导血管生成,促进骨再生,表现出抗骨质疏松的作用[43]。近期,ZHAO等[44]研究发现,柚皮苷可以通过上调CXCL12、CXCR4的表达水平激活了PI3K/Akt信号通路,从而激发了内皮祖细胞的增殖并促进了新生血管的生成。血管内皮细胞和新生血管是骨形成过程中的重要因素。故以上提示柚皮苷可以通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路促进内皮祖细胞的增殖、分化成新生血管,进而促进骨组织再生。 综上所述,柚皮苷诱导成骨的潜力与柚皮苷在骨骼系统的多种相关作用有关,它参与了抗骨质疏松症、促进骨生成、抑制破骨细胞生成及促进血管等多条信号通路的调控,对促进骨组织再生具有重要的意义。见表2。 "
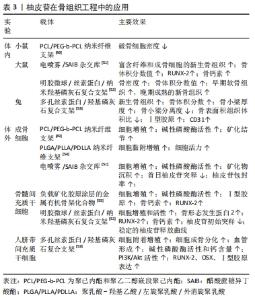
2.2 柚皮苷的安全性研究 已有许多研究表明,柚皮苷质量浓度在1-100 mg/L时,能呈剂量依赖性的刺激人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、人羊水来源干细胞及血管内皮细胞的增殖和碱性磷酸酶的表达活性增强,表明这个浓度范围内柚皮苷对人骨髓间充质干细胞、人羊水来源干细胞、血管内皮细胞是安全无毒性。当柚皮苷质量浓度达到200 mg/L时,柚皮苷对这些细胞增殖、分化等具有显著的抑制作用,表明该浓度下或更高浓度下的柚皮苷对细胞生长具有毒性作用[34,43,45]。研究发现10-100 μmol/L的柚皮苷均能够促进MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖与上调碱性磷酸酶活性,且呈浓度依赖性,在100 μmol/L时促进作用达到最佳,而在1 000 μmol/L的柚皮苷对细胞增殖表现出抑制作用[13]。PANG等[46]研究表明浓度在0.1 nmol/L-10 mmol/L的柚皮苷可促进大鼠成骨样UMR-106细胞的增殖和碱性磷酸酶活性,该浓度下柚皮苷对骨质疏松和骨缺损有潜在的治疗价值。柚皮苷在1,10,100 μmol/L浓度作用24 h对人成骨细胞没有细胞毒性,但是1 μmol/L对人成骨细胞无增殖作用,10 μmol/L和100 μmol/L的柚皮苷作用24 h后,人成骨细胞的增殖分别增加了29%和45%,且呈时间相关性,表明≤1 μmol/L的柚皮苷对人成骨细胞无促进增殖作用。总之,应用柚皮苷促进细胞成骨分化的过程中需要控制一定的安全浓度范围。 2.3 柚皮苷在骨组织工程中的应用进展 虽然柚皮苷在骨再生和骨修复方面具有强大的诱导成骨的潜力,是一个很有前景的天然骨诱导小分子药物,但因其水溶性较差,口服生物利用度较低,且单独在骨缺损处应用会使其突发性释放,阻碍了成骨作用或其他生物活性,故限制了其在临床的使用[47-48]。为解决这一问题,近几年学者通过将柚皮苷与骨组织工程载体支架材料结合引导骨组织再生进而修复大面积骨缺损,明显提高了柚皮苷的生物利用度。 为了促进骨形成以修复骨缺损,JI等[49]通过静电纺丝技术将柚皮苷加入聚已内酯和聚乙二醇嵌段聚己内酯电纺纳米纤维支架(PCL/PEG-b-PCL)中,结果显示纳米纤维支架对柚皮苷控释效果良好,体外释放3个月后仍保持释放,释放量达93%左右。负载柚皮苷的电纺纳米纤维支架对MC3T3-E1成骨细胞的附着和形态无明显影响,对细胞的增殖和分化的支持作用高于未加入柚皮苷的PCL/PEG-b-PCL纳米支架,这些结果表明柚皮苷具有潜在的骨诱导作用。 工程化骨移植复合支架的设计不仅需要在生物相容性、生物降解性和力学性能之间取得平衡,还需要控制生长因子或骨诱导小分子药物缓慢释放以达到长期促进骨修复的能力[50]。XUE等[51]采用电喷雾法制备了负载柚皮苷的PCL/PEG-b-PCL微球,然后将含柚皮苷的电喷雾微球植入醋酸蔗糖异丁酸酯(sucrose acetate iso-butyrate,SAIB)库中,结果显示,含柚皮苷的电喷雾微球加入SAIB库后的初始释放率降低至7.2%,相比于未加入SAIB库的柚皮苷电喷雾微球有效减少了柚皮苷的突释,并且能够保持长时间稳定缓慢释放,可维持柚皮苷的浓度并延长柚皮苷的作用时间。含柚皮苷电喷雾微球/SAIB杂交库由于柚皮苷的存在明显促进了大鼠成骨细胞的增殖成骨分化,并促进了大鼠颅骨缺损处新生骨组织的形成。以上结果归功于柚皮苷独特的成骨特性和SAIB杂交库对柚皮苷的长期缓释行为。 近期,YU等[52]通过冷冻干燥技术将柚皮苷负载到明胶微球中,然后将其包裹至纳米羟基磷灰石和丝素蛋白复合支架中,结果表明加入柚皮苷的复合支架不仅不会改变支架类似天然骨样的孔径孔隙率或力学性能,保持了柚皮苷的生物活性,而且具有良好的细胞相容性,能促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化;此复合支架明显减少了柚皮苷的初始突发释放并且延长了持续释放时间,可能是因为柚皮苷先从明胶微球里释放至纳米羟基磷灰石/丝素蛋白支架中,再从支架中顺序释放出来的结果;此复合支架在去卵巢后的大鼠腰椎缺损处表现出良好的骨传导和骨诱导作用,16周后缺损处被成熟新生骨组织修复几乎恢复正常,且支架材料已经完全生物降解,此生物复合支架降解率和骨缺损愈合率相平衡。综上表明此复合支架可通过控制柚皮苷的释放动力学促进骨修复,也表明了柚皮苷具有诱导骨组织再生的潜能。表3总结了柚皮苷在骨组织工程中的应用。 "

| [1] WALSH DP, RAFTERY RM, CHEN G, et al. Rapid healing of a critical‐sized bone defect using a collagen‐hydroxyapatite scaffold to facilitate low dose, combinatorial growth factor delivery. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2019;13(10):1843-1853. [2] GARCIA-GARETA E, COATHUP MJ, BLUNN GW, et al. Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2015;81(7):112-121. [3] GE R, XUN C, YANG J, et al. In vivo therapeutic effect of wollastonite and hydroxyapatite on bone defect. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(6):065-073. [4] MARGONAR R, DOS SPL, QUEIROZ TP, et al. Rehabilitation of Atrophic Maxilla Using the Combination of Autogenous and Allogeneic Bone Grafts Followed by Protocol-Type Prosthesis. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21(6):1894-1896. [5] DU XY, WEI DX, HUANG L, et al. 3D printing of mesoporous bioactive glass/silk fibroin composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;103(18):109731. [6] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;78(18):1246-1262. [7] ZHANG YH, MA JL, ZHANG WF. Berberine for bone regeneration: Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;27(7):114249. [8] WANG YG, WU H, CHEN P, et al. Fertility and early embryonic development toxicity assessment of naringin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;12(3):104938. [9] RIVOIRA MA, RODRIGUEZ V, TALAMONI G, et al. New Perspectives in the Pharmacological Potential of Naringin in Medicine. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(10):1987-2007. [10] KRISTIN E YU, KAREME DA, MONTANA TM, et al. Re-appraising the potential of naringin for natural, novel orthopedic biotherapies. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020;12(1):1-21. [11] LO KW, ASHE KM, KAN HM, et al. The role of small molecules in musculoskeletal regeneration. Regen Med. 2012;7(4):535-549. [12] YAN Y, ZHOU H, WU C, et al. Ultrasound-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of synephrine, naringin, and neohesperidin from Citrus aurantium L. fruitlets. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;51(8):780-791. [13] 徐高丽,柳毅,吴立立,等.柚皮苷协同骨形态发生蛋白-2促进小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖和分化的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2017,35(3):275-280. [14] 李顺祥,勉龙,张志光.骨碎补的研究进展[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2002,9(11):75-78. [15] WEI M, YANG Z, LI P, et al. Anti-osteoporosis activity of naringin in the retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis model. Am J Chin Med. 2007;35(4): 663-667. [16] ZHANG P, DAI KR, YAN SG, et al. Effects of naringin on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cell. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;607(1-3):1-5. [17] ZHOU XX, ZHANG P, ZHANG C, et al. Promotion of Bone Formation by Naringin in a Titanium Particle-Induced Diabetic Murine Calvarial Osteolysis Model. J Orthop Res. 2010;4(28):452-456. [18] FAN JF, LI J, QIAN F, et al. Naringin promotes differentiation of bone marrow stem cells into osteoblasts by upregulating the expression levels of microRNA -20a and downregulating the expression levels of PPAR γ. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3):4759-4765. [19] ENSRUD KE, CRANDALL CJ. Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(3): ITC17-ITC32. [20] WU GJ, CHEN JT, CHERNG YG, et al. Genistein Improves Bone Healing via Triggering Estrogen Receptor Alpha-Mediated Expressions of Osteogenesis-Associated Genes and Consequent Maturation of Osteoblasts. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(39):10639-10650. [21] GUO DY, WANG JZ, WANG XQ, et al. Double directional adjusting estrogenic effect of naringin from Rhizoma drynariae (Gusuibu). J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;138(2):451-457. [22] TOSHIHISA KOMORI. Animal models for osteoporosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;75(9):287-294. [23] NOIRRIT-ESCLASSAN E, VALERA M, Tremollieres F, et al. Critical Role of Estrogens on Bone Homeostasis in Both Male and Female: From Physiology to Medical Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):15-68. [24] PANG WY, WANG XL, SAU-KENG MOK, et al. Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells .Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(8): 1693-1703. [25] WU GJ, CHEN KY, YANG JD, et al. Naringin Improves Osteoblast Mineralization and Bone Healing and Strength through Regulating Estrogen Receptor Alpha-Dependent Alkaline Phosphatase Gene Expression. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(44):13020-13033. [26] LV JW, SUN XL, MA JX, et al. Involvement of periostin-sclerostin-Wnt_β-catenin signaling pathway in the prevention of neurectomy-induced bone loss by naringin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 4(468):587-593. [27] MA XL, LV JW, SUN XL, et al. Naringin ameliorates bone loss induced by sciatic neurectomy and increases Semaphorin 3A expression in denervated bone. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):245-262. [28]. FUKUDA T, TAKEDA S, XU R, et al. Sema3A regulates bone-mass accrual through sensory innervations. Nature. 2013;497(7450):490-493. [29] ZHANG ZD, REN H, SHEN GY, et al. Animal models for glucocorticoid-induced postmenopausal osteoporosis: An updated review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84(5):438-446. [30] SAAG KG, WAGMAN RB, GEUSENS P, et al. Denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, double-dummy, non-inferiority study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(6):445-454. [31] GE XT, ZHOU G. Protective effects of naringin on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6330-6341. [32] WANG HC, LI CB, LI GM, et al. Naringin enhances osteogenic differentiation through the activation of ERK signaling in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017;20(4):408-414. [33] WANG W, MAO J,CHEN Y, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenesis and ameliorates osteoporosis development by targeting JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;49(1):113-121. [34] LIU MM, LI Y, YANG ST. Effects of naringin on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(1):276-284. [35] 林春淑, 舒晓春, 肖菲娜, 等. 柚皮苷对高糖作用下MC3T3-E1细胞活力和Akt通路相关因子表达的影响[J]. 中华细胞与肝细胞杂志(电子版). 2020,10(6):321-327. [36] MATTSON AM, BEGUN DL, MOLSTAD DHH, et al. Deficiency in the phosphatase PHLPP1 suppresses osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and enhances bone formation in mice. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(31): 11772-11784. [37] HIDEKI K, ASEEL M, FUMITOSHI O, et al. Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):51-69. [38] ESTABELLE SMA, YANG XH, CHEN HH, et al. Naringin abrogates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via the inhibition of RANKL-induced NF-κB and ERK activation. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(17):2755-2762. [39] YANG C, LIU W, ZHANG XL, et al. Naringin increases osteoprotegerin expression in fibroblasts from periprosthetic membrane by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):600. [40] LI FB, SUN XL, MA JX, et al. Naringin prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis and promotes osteoclasts apoptosis through the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014;452(3):629-635. [41] RHONDA DP. Mechanical, hormonal and metabolic influences on blood vessels, blood flow and bone. J Endocrinol. 2017;235(3):R77-R100. [42] SONG N, ZHAO ZH, MA XL, et al. Naringin promotes fracture healing through stimulation of angiogenesis by regulating. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;261(1):11-17. [43] SHANGGUAN WJ, ZHANG YH, LI ZC, et al. Naringin inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress- and mitochondrial-mediated pathways and promotes intraosseous angiogenesis in ovariectomized rats. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1741-1749. [44] ZHAO ZH, MA XL, MA JX, et al. Naringin enhances endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) proliferation and tube formation capacity through the CXCL12/CXCR4/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;286(1):45-51. [45] ZHANG P, DAI KR, YAN SG, et al. Effects of naringin on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cell. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;607(1-3):1-5. [46] PANG WY, WANG XL, SAU-KENG MOK, et al. Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(8):1693-1703. [47] AJA A, DAISY MR, JONATHAN NIP, et al. Osteoinductive small molecules: growth factor alternatives for bone tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(19):3420-3428. [48] GULEID A, EDGAR W, KOMAL R, et al.Engineered Bone Tissue with Naturally-Derived Small Molecules. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(24):3585-3594. [49] JI Y, WANG L, WATTS DC, et al. Controlled-release naringin nanoscaffold for osteoporotic bone healing. Dent Mater. 2014;30(11):1263-1273. [50] JAME C, ADHITHI LK, CHRISTIAN B, et al. Characterization of a prevascularized biomimetic tissue engineered scaffold for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1655-1668. [51] XUE Y, HUTHAYFA NSA, ZHANG QY, et al. Electrosprayed naringin-loaded microsphere/SAIB hybrid depots enhance bone formation in a mouse calvarial defect model. Drug Deliv. 2019;26(1):137-146. [52] YU X, SHEN GY, SHANG Q, et al. A Naringin-loaded gelatin-microsphere/nano-hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin composite scaffold promoted healing of critical-size vertebral defects in ovariectomised rat. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193(Pt A):510-518. [53] ZHAO ZH, MA XL, ZHAO B, et al. Naringin-inlaid silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite scaffold enhances human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021; 54(7):130-143. [54] GUO ZJ, WU S, LI H, et al. In vitro evaluation of electrospun PLGA/PLLA/PDLLA blend fibers loaded with naringin for guided bone regeneration. Dent Mater J. 2018;37(2):317-324. [55] YU MF, YOU DQ, ZHANG JJ, et al. Controlled Release of Naringin in Metal-Organic Framework-Loaded Mineralized Collagen Coating to Simultaneously Enhance Osseointegration and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19698-19705. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [3] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [4] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [5] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [6] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [7] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [8] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [9] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [10] | Cheng Yunzhong, Liu Yuzeng, Hai Yong, Guan Li, Pan Aixing, Zhang Xinuo, Tao Luming, Li Yue. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and development trend of cortical bone trajectory screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 513-519. |
| [11] | Liu Hao, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Wang Liping, Yang Kunhai, Hu Yongrong, Qu Bo. Lumbar MRI vertebral bone quality score to evaluate the severity of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 606-611. |
| [12] | Cheng Mingguang, Zhang Chaoyu, Zhuang Kangle, Ruan Peng, Zuo Yi, Zhou Zhengchun, Kong Xiang, Ge Jianjun, Cheng Guangcun. In vitro construction of Stanford type A aortic dissection 3D dynamic simulation diagram and individual tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 335-338. |
| [13] | Liu Huan, Li Han, Ma Yunhao, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic capacity of partially demineralized dentin particles in the maxillary sinus lift [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [14] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| [15] | Lin Shi, Yuan Jiayao, Lin Xiancan, Yang Binbin, Wu Jianjun, Dongzhi Zhuoma, Tang Zijia, Yang Zhijie, Wan Lei, Huang Hongxing. Diagnostic value of peripheral blood interferon-gamma and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 165-170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||