Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 447-452.doi: 10.12307/2023.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology
Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping
- School of Stomatology • Stomatology Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-02Accepted:2022-01-13Online:2023-01-28Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:Wu Xiuping, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology • Stomatology Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zong Mingrui, Master candidate, School of Stomatology • Stomatology Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Innovation Project for Colleges and Universities of Shanxi Province, No. 2020L0212 (to LHY); Research Fund Project for Returned Overseas Students of Shanxi Province, No. HGKY2019-055 (to LB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
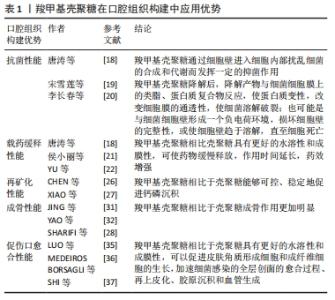
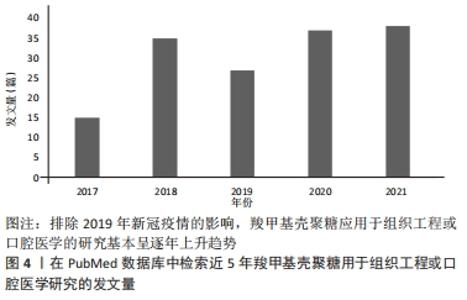
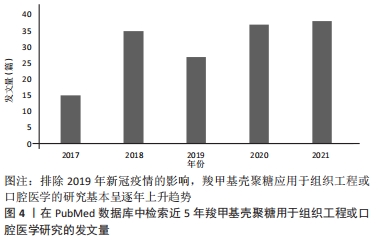
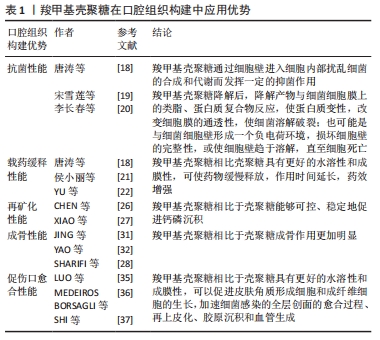
2.1.1 羧甲基壳聚糖的抗菌性能 羧甲基壳聚糖具有天然抗菌活性,抗菌谱广,对口腔变形链球菌等致龋菌有抑菌效果,还具有抑制口腔内重要厌氧菌生长的优点,其抑菌机制可能是羧甲基壳聚糖通过细胞壁进入细胞内部扰乱细菌合成和代谢而发挥一定的抑菌作用[18]。进一步的研究认为可能是羧甲基壳聚糖的有效基团NH3+,其呈碱性,在羧甲基壳聚糖降解后,降解产物与细菌细胞膜上的类脂、蛋白质复合物反应,使蛋白质变性,改变细胞膜的通透性,使细菌溶解破裂;也可能是与细菌细胞壁形成一个负电荷环境,损坏细胞壁的完整性,或使细胞壁趋于溶解,直至细胞死亡[19-20]。羧甲基壳聚糖的抗菌活性受NH2数量、脱乙酰度、溶液浓度、相对分子质量、pH值及溶液中NH3+浓度等影响[16]。因此,可以看出羧甲基壳聚糖的抑菌机制尚未明确,是未来研究的热点之一。 2.1.2 羧甲基壳聚糖的载药缓释性能 羧甲基壳聚糖相比壳聚糖具有更好的水溶性和成膜性。羧甲基壳聚糖溶胶是一种常用药物载体,可使药物缓慢释放,作用时间延长,药效增强。侯小丽等[21]观察奥硝唑羧甲基壳聚糖联合透明质酸辅助牙周基础治疗老年慢性牙周炎的效果较好,可明显改善患者牙周相关指标,降低龈下菌斑螺旋体数量及菌斑胰蛋白样酶水平。唐涛等[18]研究表明牙周袋内联合应用奥硝唑羧甲基壳聚糖溶胶比单纯牙周基础治疗效果更好。YU等[22]通过多巴胺辅助包被,用银、羧甲基壳聚糖和骨形成肽修饰,制备了一种双功能聚醚醚酮植入物,其中如何控制银离子的释放是减少银离子不良反应的关键。采用旋涂的方法在聚醚醚酮表面形成羧甲基壳聚糖薄膜,可以有效地控制银离子的缓慢释放,减少不良反应。在杀菌过程中它能与释放的银离子协同作用,从而赋予聚醚醚酮抗菌能力。以上研究可以看出羧甲基壳聚糖具有理想的载药缓释性能。 2.1.3 羧甲基壳聚糖的再矿化性能 目前,无定型磷酸钙被认为是牙体釉质或牙本质再矿化的最佳选择,然而由于其热力学的不稳定性,极易在体外水介质中迅速转变为稳定的羟基磷灰石结晶相,无法可控地释放无定型磷酸钙或矿物离子[23-24]。基于羧甲基壳聚糖是一种富含羧基的壳聚糖衍生物,可以隔离阳离子,能有效抑制钙、镁等金属离子与碳酸根、磷酸根等阴离子结合,生成沉淀物[25],平衡羧甲基壳聚糖、矿物质阳离子和酸根之间的相互作用,从而使含有无定形矿物纳米颗粒的溶液在pH=2时保持乳化状态,从而适当地抑制了这种沉积趋势[13]。因此,羧甲基壳聚糖可以延缓或抑制磷酸钙的自发沉淀速率,水溶性羧甲基壳聚糖能够通过其螯合能力在溶液中可控稳定地形成无定型磷酸钙纳米颗粒[26]。XIAO等[27]利用嵌合肽介导的羧甲基壳聚糖/无定形磷酸钙纳米复合物模拟釉质生物矿化中釉原蛋白,诱导无定型磷酸钙定向组装的矿化过程,寻求建立一种快速有效的人龋病牙釉质再矿化方法,该研究证明了羧甲基壳聚糖富含羧基,可用于提高钙磷沉积后的稳定性,是无定型磷酸钙纳米颗粒的良好稳定剂,对牙齿组织起到了再矿化作用。未来联合应用羧甲基壳聚糖和再矿化药物是口腔组织构建的研究热点。由于人类口腔环境的复杂性,应同时开展口腔温度、pH值和菌群生态等因素对羧甲基壳聚糖复合材料影响的研究。 2.1.4 羧甲基壳聚糖的成骨性能 羧甲基壳聚糖目前已广泛应用于组织工程领域。组织工程通常将细胞结合到三维多孔支架中制备复合材料。一方面,羧甲基壳聚糖制备的支架具有多孔结构,当新组织形成时,它们能够被降解,降解产物无毒或者引起的炎症反应最小[16];另一方面,相比于壳聚糖,羧甲基壳聚糖作为支架材料的成骨作用更加明显[22-23]。SHARIFI等[28]以聚己内酯-壳聚糖和聚己内酯-羧甲基壳聚糖共混物为材料,采用静电纺丝法制备了纳米纤维生物相容性支架,并在支架上培养人成骨细胞(MG63),与聚己内酯和聚己内酯-壳聚糖相比,聚己内酯-羧甲基壳聚糖纳米纤维具有明显的促增殖作用,聚己内酯-羧甲基壳聚糖组成骨细胞数量最多。 2.1.5 羧甲基壳聚糖的促伤口愈合性能 传统的创面敷料存在结构和功能缺陷,不能有效促进创面愈合[29]。未来敷料发展趋向于具有多重功能,可以加速血液凝固,抑制细菌感染,并触发全层创面进入再生过程[30]。羧甲基壳聚糖是一种壳聚糖衍生物,它既保持了壳聚糖的优良性能,又具有良好的水溶性、纤维、成膜和水凝胶能力,已广泛应用于口腔外科的伤口敷料中[31-32]。一方面,是得益于羧甲基壳聚糖可以促进皮肤角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞的生长,是一种良好的伤口敷料材料[26-27];另一方面,是由于羧甲基壳聚糖可以增加红细胞的聚集和血小板的黏附,缩短凝血时间[33-34]。最新研究显示,应用羧甲基壳聚糖制备的多功能创面敷料材料对革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌均有良好的抗菌能力;体内实验进一步证明,敷料能加速细菌感染的全层创面的愈合过程、再上皮化、胶原沉积和血管生成[35-37]。基于羧甲基壳聚糖优异的生物学特性,其用于口腔组织构建优势,见表1。"
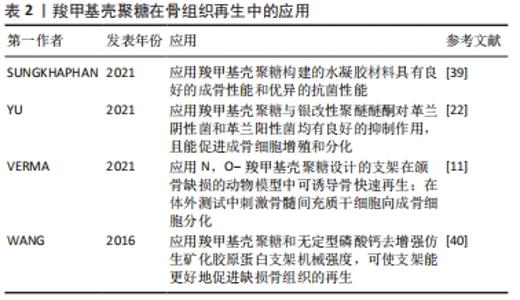
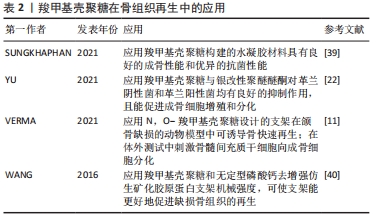
2.2.1 骨组织再生 颌骨疾病、颌面创伤和晚期牙周炎等都是导致颌面骨丧失的口腔疾病,为了修复骨缺损,恢复颜面丰满度是目前口腔骨组织工程的研究热点[38]。羧甲基壳聚糖作为一种生物活性支架或水凝胶材料在口腔骨组织构建修复中发挥着重要作用。SUNGKHAPHAN等[39]以羧甲基壳聚糖和克林霉素为载体,制备了具有抗菌和成骨双重活性的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(MCM-41)可生物降解复合水凝胶,测试了其抗菌和成骨效果,结果表明该水凝胶在体外对血链球菌的抗菌效果持续时间长达14 d以上,该复合水凝胶与人骨髓间充质干细胞具有细胞相容性,可诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞矿化,提示其在口腔颌骨感染治疗中具有潜在的临床应用价值。该研究证明了羧甲基壳聚糖构建的水凝胶材料不仅具有良好的成骨性能,而且具有优异的抗菌性能。进一步的一项研究表明,联合羧甲基壳聚糖与银改性聚醚醚酮对革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌均有良好的抑制作用,且能促进成骨细胞增殖和分化[22]。此外,VERMA等[11]设计和开发了腺苷/儿茶素5-N,O-羧甲基壳聚糖/Ⅰ型胶原成骨支架,在颌骨缺损动物模型中可诱导骨快速再生;在体外实验中可刺激骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素表达和钙沉积显著增加。另有研究创新地应用羧甲基壳聚糖和无定型磷酸钙去增强仿生矿化胶原蛋白支架机械强度,同时降低胶原支架的降解率,使仿生矿化胶原蛋白支架能更好地促进缺损骨组织的再生[40],这说明无论羧甲基壳聚糖作为支架材料还是改性支架材料都是一种理想的选择。表2总结了羧甲基壳聚糖在骨组织再生中的应用情况。"
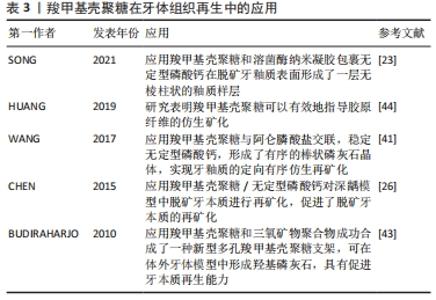
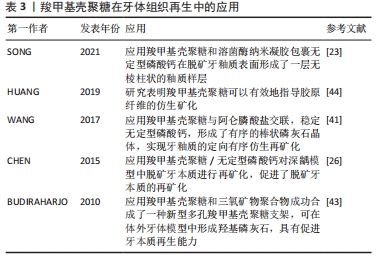
2.2.2 牙体组织再生 龋病是导致牙体组织缺损的主要原因,是由脱矿和再矿化过程不平衡引起的动态过程[41]。如不及时治疗(包括再矿化治疗和牙菌斑控制)恢复这种平衡,龋齿很可能会从釉质逐渐发展到牙本质,导致深龋,最终导致牙齿脱落[42]。当然如能在龋病早期抑制脱矿和致龋菌的黏附及生长,则能有效地预防和治疗早期龋病[20]。SONG等[23]制备了羧甲基壳聚糖和溶菌酶纳米凝胶,并包裹无定形磷酸钙实现可控释放,提高了无定形磷酸钙在水环境中的稳定性,并在脱矿牙釉质表面原位形成了一层无棱柱状的釉质样层。然而,如何在脱矿牙釉质表面实现定向有序的再矿化,使其力学性能恢复到接近最初牙釉质的水平,仍是牙体组织再生面临的挑战。WANG等[41]将羧甲基壳聚糖与阿仑膦酸盐交联,并稳定无定形磷酸钙,形成羧甲基壳聚糖/无定形磷酸钙纳米粒子;次氯酸钠作为蛋白酶在体内分解釉原蛋白,降解羧甲基壳聚糖-阿仑膦酸盐基质,生成羟基磷灰石@无定型磷酸钙纳米粒子;最后,在甘氨酸的介导下,阿仑膦酸盐修饰的羟基磷灰石@无定型磷酸钙纳米粒子可以有序排列,进一步形成有序的棒状磷灰石晶体,实现牙釉质的定向有序仿生再矿化。这些研究结果说明羧甲基壳聚糖在预防和治疗早期釉质龋方面具有广阔的应用前景。 在深龋阶段,促进牙本质再生是保存牙齿减少患者痛苦的理想治疗方案。此前已有学者采用冷冻干燥法制备交联羧甲基壳聚糖支架和三氧矿物聚合物包裹的羧甲基壳聚糖支架[43]。在4种不同矿化液(体液)和模拟体液中对支架的生物活性进行了体外测试,成功合成了具有高钙螯合能力的新型多孔羧甲基壳聚糖支架,可在体外牙体模型中形成羟基磷灰石,具有促进牙本质再生能力。然而,此方法用到的三氧矿物聚合物价格昂贵,临床可行性较低。目前,对牙科医生来说,深龋中牙本质的再生仍然是一项艰巨的任务。HUANG等[44]通过合成掺杂羧甲基壳聚糖和磷酸钙微填料的实验树脂,以实现人工牙本质的再矿化,提高树脂-牙本质黏结的耐久性,结果表明,羧甲基壳聚糖可以有效地指导胶原纤维的仿生矿化。另外,CHEN等[26]利用羧甲基壳聚糖/无定形磷酸钙纳米复合物对深龋牙齿模型中的脱矿牙本质进行再矿化。这些研究说明羧甲基壳聚糖复合物显示出良好的再矿化效果,有望成为一种构建牙本质再生的潜在材料。表3总结了羧甲基壳聚糖与不同生物材料结合在牙体组织再生中的应用情况。 "
2.2.3 牙周组织再生 牙周炎是口腔中最为常见的疾病,其能破坏牙齿支持组织,造成牙周组织大量丧失,引起牙周溢脓、牙齿松动[45]。牙周炎始于牙周袋的形成,随着骨缺损的发展而加重。在晚期的深牙周袋病例中,常可见到牙槽骨和牙周组织的不可复性丧失[46],这种情况下,临床上更多的考虑手术再生治疗。羧甲基壳聚糖基于对细胞良好的亲和性,无毒,无免疫原性以及可抑制口腔钙磷离子结合等优势,在牙周组织再生方面有广阔的应用前景[45,47]。王丹等[48]观察羧甲基壳聚糖温敏凝胶对病变牙根面NIH3T3细胞(与成纤维细胞生物学性质极为相似的小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞)附着和增殖的影响,发现使用羧甲基壳聚糖温敏凝胶处理牙根表面可以促进NIH3T3细胞在牙根面的附着与增殖。进一步研究发现,在羧甲基壳聚糖制成的可降解支架上培养人牙龈成纤维细胞,具有良好的促增殖和分化作用[49]。 此外,种植体的成功不仅需要最佳的骨结合,还需要种植体表面与牙周组织形成良好的生物学宽度,否则会导致种植体周围炎[50]。因此,促进种植体周围软组织与其结合同样十分重要。有学者研究发现将羧甲基壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石等生物活性因子修饰到钛种植体表面,为种植体植入早期的细胞黏附、铺展和增殖营造了良好环境[51]。这些结果表明壳聚糖在牙周纤维、牙龈纤维再生方面均有一定应用潜力。 羧甲基壳聚糖的再矿化性能研究和应用,见图5。 "
| [1] WANG W, MENG Q, LI Q, et al. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):487. [2] ZOU M, SUN J, XIANG Z. Induction of M2-Type Macrophage Differentiation for Bone Defect Repair via an Interpenetration Network Hydrogel with a GO-Based Controlled Release System. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(6):e2001502. [3] KOONS GL, DIBA M, MIKOS AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nature Reviews Materials. 2020;5(8):584-603. [4] REN B, CHEN X, DU S, et al. Injectable polysaccharide hydrogel embedded with hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate for drug delivery and bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):1257-1266. [5] BARANWAL A, KUMAR A, PRIYADHARSHINI A, et al. Chitosan: An undisputed bio-fabrication material for tissue engineering and bio-sensing applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 ;110:110-123. [6] NAGHIZADEH Z, KARKHANEH A, KHOJASTEH A. Self-crosslinking effect of chitosan and gelatin on alginate based hydrogels: Injectable in situ forming scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:256-264. [7] SUKPAITA T, CHIRACHANCHAI S, SUWATTANACHAI P, et al. In Vivo Bone Regeneration Induced by a Scaffold of Chitosan/Dicarboxylic Acid Seeded with Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4883. [8] FAKHRI E, ESLAMI H, MAROUFI P, et al. Chitosan biomaterials application in dentistry. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:956-974. [9] CHENG F, WU Y, LI H, et al. Biodegradable N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite gauze as a barrier for preventing postoperative adhesion. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;207:180-190. [10] LU HT, LU TW, CHEN CH, et al. Development of nanocomposite scaffolds based on biomineralization of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan/fucoidan conjugates for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B): 2335-2345. [11] VERMA NK, KAR AK, SINGH A, et al. Control Release of Adenosine Potentiate Osteogenic Differentiation within a Bone Integrative EGCG-g-NOCC/Collagen Composite Scaffold toward Guided Bone Regeneration in a Critical-Sized Calvarial Defect. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(7):3069-3083. [12] ARNAUD TM, DE BARROS NETO B, et al. Chitosan effect on dental enamel de-remineralization: an in vitro evaluation. J Dent. 2010;38(11):848-852. [13] LIU H, LIN M, LIU X, et al. Doping bioactive elements into a collagen scaffold based on synchronous self-assembly/mineralization for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):844-858. [14] HE J, BAO Y, LI J, et al. Nanocomplexes of carboxymethyl chitosan/amorphous calcium phosphate reduce oral bacteria adherence and biofilm formation on human enamel surface. J Dent. 2019;80:15-22. [15] JIANG Z, CHI J, HAN B, et al. Preparation and pharmacological evaluation of norcantharidin-conjugated carboxymethyl chitosan in mice bearing hepatocellular carcinoma. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;174:282-290. [16] SHARIATINIA Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B):1406-1419. [17] SULTANKULOV B, BERILLO D, SULTANKULOVA K, et al. Progress in the Development of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):470. [18] 唐涛,薛毅,信玉华.羧甲基壳聚糖复合奥硝唑后对口腔重要厌氧菌增效抑菌作用的评价[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2007,23(3):451-452. [19] 宋雪莲,孙莹莹,刘扬,等.羧甲基壳聚糖及其复合物对根管内粪肠球菌的作用评价[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(3):265-269. [20] 李长春,许晓燕,徐全臣,等.纳米羧甲基壳聚糖氟化钠涂膜预防龋齿的实验室研究[J].中国药房,2015,26(16): 2212-2215. [21] 侯小丽,谢光远.奥硝唑羧甲基壳聚糖联合透明质酸辅助牙周基础治疗老年慢性牙周炎效果观察[J].山东医药,2017,57(34):95-96. [22] YU Y, SUN Y, ZHOU X, et al. Ag and peptide co-decorate polyetheretherketone to enhance antibacterial property and osteogenic differentiation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;198:111492. [23] SONG J, LI T, GAO J, et al. Building an aprismatic enamel-like layer on a demineralized enamel surface by using carboxymethyl chitosan and lysozyme-encapsulated amorphous calcium phosphate nanogels. J Dent. 2021;107:103599. [24] NIU X, CHEN S, TIAN F, et al. Hydrolytic conversion of amorphous calcium phosphate into apatite accompanied by sustained calcium and orthophosphate ions release. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):1120-1124. [25] 刘学玉,潘克清,张丽,等.羧甲基壳聚糖锌多肽复合材料局部应用对巴马小型猪龈沟液中IL-1、TNF-α和PGE-2含量的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(2):172-176. [26] CHEN Z, CAO S, WANG H, et al. Biomimetic remineralization of demineralized dentine using scaffold of CMC/ACP nanocomplexes in an in vitro tooth model of deep caries. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116553. [27] XIAO Z, QUE K, WANG H, et al. Rapid biomimetic remineralization of the demineralized enamel surface using nano-particles of amorphous calcium phosphate guided by chimaeric peptides. Dent Mater. 2017;33(11):1217-1228. [28] SHARIFI F, ATYABI SM, NOROUZIAN D, et al. Polycaprolactone/carboxymethyl chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:243-248. [29] AGARWAL T, NARAYAN R, MAJI S, et al. Gelatin/Carboxymethyl chitosan based scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(Pt B):1499-1506. [30] HE Y, ZHAO W, DONG Z, et al. A biodegradable antibacterial alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan/Kangfuxin sponges for promoting blood coagulation and full-thickness wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167:182-192. [31] JING X, XIE B, LI X, et al. Peptide decorated demineralized dentin matrix with enhanced bioactivity, osteogenic differentiation via carboxymethyl chitosan. Dent Mater. 2021;37(1):19-29. [32] YAO M, ZOU Q, ZOU W, et al. Bifunctional scaffolds of hydroxyapatite/poly(dopamine)/carboxymethyl chitosan with osteogenesis and anti-osteosarcoma effect. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(9):3319-3333. [33] CHENG Y, LU S, HU Z, et al. Marine collagen peptide grafted carboxymethyl chitosan: Optimization preparation and coagulation evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:3953-3964. [34] WANG YL, ZHOU YN, LI XY, et al. Continuous production of antibacterial carboxymethyl chitosan-zinc supramolecular hydrogel fiber using a double-syringe injection device. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;156:252-261. [35] LUO P, NIE M, WEN H, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan sulfate/oxidized konjac glucomannan hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113:1024-1031. [36] MEDEIROS BORSAGLI FGL, DE SOUZA AJM, Paiva AE. Ecofriendly multifunctional thiolated carboxymethyl chitosan-based 3D scaffolds with luminescent properties for skin repair and theragnostic of tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt B):3051-3064. [37] SHI L, LIN F, ZHOU M, et al. Preparation of biocompatible wound dressings with dual release of antibiotic and platelet-rich plasma for enhancing infected wound healing. J Biomater Appl. 2021;36(2):219-236. [38] HENKEL J, WOODRUFF MA, EPARI DR, et al. Bone Regeneration Based on Tissue Engineering Conceptions - A 21st Century Perspective. Bone Res. 20135;1(3):216-248. [39] SUNGKHAPHAN P, THAVORNYUTIKARN B, KAEWKONG P, et al. Antibacterial and osteogenic activities of clindamycin-releasing mesoporous silica/carboxymethyl chitosan composite hydrogels. R Soc Open Sci. 2021;8(9): 210808. [40] WANG Y, VAN MANH N, WANG H, et al. Synergistic intrafibrillar/extrafibrillar mineralization of collagen scaffolds based on a biomimetic strategy to promote the regeneration of bone defects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:2053-2067. [41] WANG H, XIAO Z, YANG J, et al. Oriented and Ordered Biomimetic Remineralization of the Surface of Demineralized Dental Enamel Using HAP@ACP Nanoparticles Guided by Glycine. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40701. [42] YU F, LUO ML, XU RC, et al. A novel dentin bonding scheme based on extrafibrillar demineralization combined with covalent adhesion using a dry-bonding technique. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3557-3567. [43] BUDIRAHARJO R, NEOH KG, KANG ET, et al. Bioactivity of novel carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold incorporating MTA in a tooth model. Int Endod J. 2010;43(10):930-939. [44] HUANG Z, QI Y, ZHANG K, et al. Use of experimental-resin-based materials doped with carboxymethyl chitosan and calcium phosphate microfillers to induce biomimetic remineralization of caries-affected dentin. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;89:81-88. [45] 付军权,费瑞,张桂荣,等.羧甲基壳聚糖银对实验性大鼠牙周炎的治疗作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2009,35(4):669-672. [46] 姜明凯,曹文帅,徐全臣.羧甲基壳聚糖应用于牙周病学的研究进展[J].广东牙病防治,2014,22(5):275-278. [47] 郭珲,潘克清,邓婧,等.羧甲基壳聚糖锌多肽复合材料对人牙周膜成纤维细胞的毒性[J].上海口腔医学,2017,26(2):162-166. [48] 王丹,彭伟,李明珠,等.羧甲基壳聚糖温敏凝胶对NIH3T3细胞在病变牙根面附着和增殖的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2014,49(5):648-650. [49] CHICHIRICCO PM, RIVA R, THOMASSIN JM, et al. In situ photochemical crosslinking of hydrogel membrane for Guided Tissue Regeneration. Dent Mater. 2018;34(12):1769-1782. [50] ZHANG Y, GULATI K, LI Z, et al. Dental Implant Nano-Engineering: Advances, Limitations and Future Directions. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(10):2489. [51] YANG M, JIANG P, GE Y, et al. Dopamine self-polymerized along with hydroxyapatite onto the preactivated titanium percutaneous implants surface to promote human gingival fibroblast behavior and antimicrobial activity for biological sealing. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(8):1071-1082. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [6] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [7] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [8] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [9] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [10] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [11] | Yu Pengxin, Han Yuqiu, Guo Lina, Wang Xiuli. The construction of rat intestinal smooth muscle collagen band and evaluation of periodic stretching culture in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5630-5635. |
| [12] | Li Yulin, Yu Haipeng, Tang Huajing, Zhang Zitong, Lin Xingnan. The mechanism, safety and application of berberine in promoting bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5702-5708. |
| [13] | Shang Yonghui, Li Shuai, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Three-dimensional finite element study on the effect of posterior tooth forward movement on temporomandibular joint stress in orthodontic reduction patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5516-5520. |
| [14] | Huang Keqi, Li Jiagen, Chen Shangtong, Rong Xiangbin. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in osteoarthritis and traditional Chinese medicine intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5571-5576. |
| [15] | Yang Xiaoqian, Song Aimei, Song Hui. Co-culture technology of mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5055-5062. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||