Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 5702-5708.doi: 10.12307/2024.592
Previous Articles Next Articles
The mechanism, safety and application of berberine in promoting bone regeneration
Li Yulin1, Yu Haipeng1, Tang Huajing1, Zhang Zitong2, Lin Xingnan1
- 1School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Changsha Medical University, Changsha 410000, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-15Accepted:2023-12-20Online:2024-12-18Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:Lin Xingnan, MD, Master’s supervisor, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Li Yulin, Master candidate, Physician, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:Crosswise Tasks of Zhejiang Chinese Medicine University, No. 2023-HT-444 (to LXN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yulin, Yu Haipeng, Tang Huajing, Zhang Zitong, Lin Xingnan. The mechanism, safety and application of berberine in promoting bone regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5702-5708.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

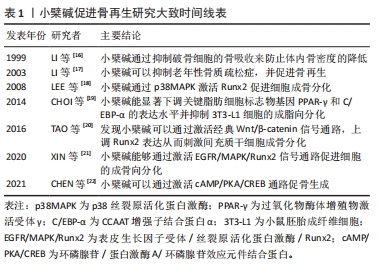
体内外研究表明,小檗碱可作用于多靶点信号通路,包括Wnt/β-catenin、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen activated protein kinase,p38MAPK)、单磷酸腺苷活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)、蛋白激酶A (protein kinase A,PKA)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt,PI3K/Akt)、核转录因子κB、核转录因子κB受体活化因子/核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素[receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB (RANK)/RANK ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG),RANK/RANKL/OPG]、活化T细胞核转录因子(nuclear factor of activated T cells,NFAT)、Hedgehog和氧化应激信号,使其具有利于预防肌肉骨骼疾病作用[27]。有学者先后报道了小檗碱的成骨作用后,小檗碱逐渐被骨组织工程领域的学者所关注[16, 20]。文章总结了小檗碱促进骨再生研究大致时间线,见表1。"
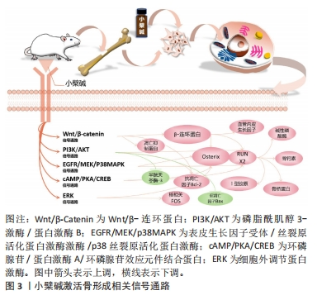
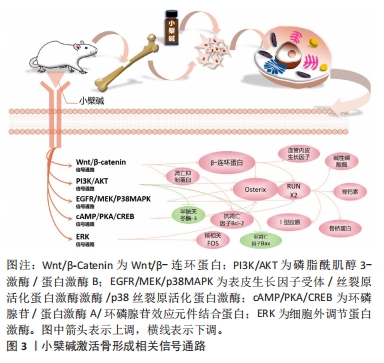
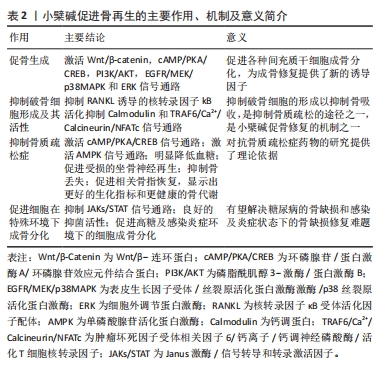
2.1 小檗碱促进骨再生的主要作用 2.1.1 小檗碱能激活骨形成相关信号通路和促进成骨细胞形成 (1)经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路:它主要由Wnt蛋白、卷曲蛋白家族的受体等相互作用,从而导致β-catenin积累,进而影响细胞行为。有研究介绍了小檗碱在间充质干细胞中Wnt/β-catenin通路的作用[20, 28-32],发现小檗碱对人骨髓间充质干细胞和人根尖乳头干细胞表现出类似于经典Wnt信号通路激活的成骨分化过程[20, 28],并且在经典Wnt通路拮抗剂DKK-1或β-catenin特异性小干扰RNA干预下,明显抑制了小檗碱诱导的人骨髓间充质干细胞内β-catenin、Runx2、骨钙素和骨桥蛋白mRNA等成骨相关基因谱的表达[20]。还有研究表明小檗碱可能通过调控经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,上调细胞中抗凋亡因子Bcl-2、下调促凋亡因子Bax和半胱天冬酶3的表达阻止细胞凋亡,提高了细胞移植过程中的存活率从而促进骨再生[29-33],并且小檗碱还可以通过激活经典Wnt信号,显著下调骨髓间充质干细胞和3T3-L1细胞内关键软骨形成和脂肪细胞形成标志物基因,如Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α等表达抑制细胞的成软骨成脂分化和促进成骨分化[19-20];但也有实验存在相反的结论,他们认为小檗碱能通过激活经典Wnt通路促进骨软骨(osteochondral)和软骨(cartilage)的再生[34-37]。这些都表明小檗碱可通过经典Wnt通路的激活促进间充质干细胞的成骨向分化,但Wnt/β-Catenin通路在骨和软骨分化中可能存在复杂的调控机制,其具体影响可能取决于细胞类型、环境和其他信号通路的相互作用等,这还需要研究者们进一步探索。 (2)环磷腺苷/蛋白激酶A/环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(cAMP/PKA/CREB)信号通路: cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路可以促进细胞成骨分化,提高成骨细胞的活力及数量并调节钙离子的代谢和骨细胞的凋亡等影响骨再生,CHEN等[22]学者发现小檗碱诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化后细胞内环磷腺苷、蛋白激酶A及磷酸化的环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白和Runx2激增,而环磷腺苷类似物二丁酰环磷腺苷能增强小檗碱诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力,并抑制成脂培养基诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞脂滴积累;蛋白激酶A抑制剂H89则引起成骨分化标记物表达下调,而脂肪细胞分化标记物上调。此外有学者合成了一种新的与小檗碱结构相似的衍生物Q8,发现其能稳定由蛋白激酶A介导的Runx2和Osterix的蛋白质丰度并延长其半衰期,从而促进细胞成骨分化[38-39]。 (3) PI3K/AKT 信号通路、表皮生长因子受体 / 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶 /p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶 (EGFR/MEK/p38MAPK) 信号通路、细胞外调节蛋白激酶 (ERK) 信号通路:实验表明,小檗碱通过激活PI3K/AKT通路来促进骨髓间充质干细胞向靶器官迁移和促进MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨谱系的表达,这种生物学行为既能为骨缺损区成骨修复提供细胞来源又能促进细胞成骨分化[40-41],另有实验发现在小檗碱诱导体系中表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶(MEK)、细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK1/2)和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38MAPK)的磷酸化水平显著升高,而加入EGFR抑制剂吉非替尼、MEK抑制剂U0126和p38MAPK抑制剂SB203580后,则显著抑制EGFR、MEK和p38MAPK的磷酸化水平,且明显下调小檗碱诱导的Runx2等成骨基因或蛋白的表达,提示小檗碱能够通过激活EGFR/MEK/p38MAPK信号通路调控成骨分化[18, 21]。此外小檗碱还能与人牙周膜干细胞膜上的EGFR结合,使细胞内ERK信号通路激活,引起人牙周膜干细胞的核相关基因FOS及碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和骨桥蛋白的上调[42]。 基于上述研究结果,可以证明小檗碱能有效促进间充质干细胞分化为成骨谱系,并明显上调碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素及Runx2等成骨相关基因和骨细胞外基质必需组分的表达。小檗碱激活骨形成相关信号通路,见图3。"
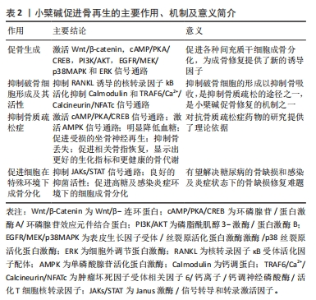
2.1.2 小檗碱具有抑制破骨细胞形成及其活性的作用 骨改建依赖于骨吸收和骨形成的动态平衡。破骨细胞自1873年被发现以来人们一直在研究其结构、功能以及生物分子机制,多年来的研究结果表明破骨细胞来源于单核造血骨髓谱系细胞,然而破骨细胞形成机制十分复杂尚未被完全诠释,但主要由两个因素调节:RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(macrophage colony-stimulating factor,M-CSF)[43]。 小檗碱可以在不影响骨髓巨噬细胞活性的情况下,抑制由RANKL诱导的核转录因子κB水平,下调破骨细胞标记基因,如组织蛋白酶K、NFAT、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和液泡型ATP酶等[44-45]。研究表明,小檗碱能通过上调microRNA-23a从而调节糖原合成酶激酶3途径和下调核转录因子κB、NFAT、原癌基因c-Fos和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶活性等减弱RANKL介导的破骨细胞形成和存活[46-54],还可以通过抑制NFAT来调节PI3K/Akt信号通路,从而抑制白细胞介素21介导的破骨细胞生成[45]。有趣的是,小檗碱的结构相似物巴马汀和黄连碱,也能通过降低RANKL等的生成,抑制破骨细胞增殖、分化和功能[49-52]。 钙调蛋白信号通路在破骨细胞发育、功能和细胞凋亡中也扮演着较为重要的角色,研究表明钙调蛋白拮抗剂可以保护骨骼,影响破骨细胞活性[55]。有研究称小檗碱可以抑制钙调蛋白信号通路,在人肝癌细胞中,小檗碱可以与钙调蛋白相互作用并阻断后续信号的传导,降低钙调蛋白激酶Ⅱ的磷酸化,阻止丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活和p27蛋白降解,从而使人肝癌细胞发生周期停滞[56]。YE等[57]学者的研究显示小檗碱通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6/钙离子/钙调神经磷酸酶/NFAT信号通路,降低脂多糖诱导的破骨细胞生成,这表明小檗碱抑制钙调蛋白信号通路可能是抑制破骨细胞生成和活性的另一途径。 2.1.3 小檗碱具有抑制骨质疏松症的作用 小檗属植物常出现在治疗骨质疏松症的中药方剂中,如虎潜丸和二仙汤等,小檗碱是其主要成分之一[58-59]。HU等[46]的研究表明小檗碱通过负向调节核转录因子κB和Akt通路抑制破骨细胞形成从而防止骨丢失。 (1)小檗碱具有抑制原发性骨质疏松症的作用:原发性骨质疏松症以骨质减少、骨微观结构退化为特征,致使骨脆性增加以及易于发生骨折的一种全身性的骨骼增龄性退行性改变。 老年性骨质疏松症:LI等[17]通过给快速衰老系模型6小鼠(SAMP6)中的雌、雄鼠灌胃小檗碱22周,发现小檗碱可以抑制雄鼠和雌鼠骨密度的下降,同时也降低了雌鼠的脱氧吡啶啉浓度,但对血清中Ⅰ型前胶原羧基端肽的浓度没有影响;CHEN等[22]学者以20月龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠为模型通过给予小檗碱、阳性对照药物雷奈酸锶和溶剂灌胃,结果表明小檗碱可能通过激活cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路促进骨形成、抑制骨髓脂肪积累和骨吸收。上述结论表明,小檗碱在治疗老年性骨质疏松症中具有一定的潜力。 绝经后骨质疏松症:研究发现小檗碱能抑制破骨细胞样多核细胞形成及活性,以缓解去卵巢雌性大鼠的骨吸收、提高骨密度和恢复骨骼结构,但是对于抑制雄性大鼠的骨丢失的机制还不明确[16, 60],总体而言小檗碱对预防和治疗卵巢切除模型大鼠的骨质疏松起积极作用,不过其预防及治疗作用机制仍待进一步探索。有研究为患有绝经后综合征的女性志愿者设计了为期14周的随机试验[61-62],结果表明服用含有200 mg Hop rho异α酸、100 mg小檗碱、500 IU 维生素D?和500 μg维生素K?营养补充剂的志愿者血清骨钙素明显下降而血清25-羟基维生素D表现为升高,而未服用的志愿者则表现出截然相反的结果,这表明营养补充剂治疗使志愿者产生了更有利的骨生物标志物,使其具有更健康的骨代谢。 此外白细胞介素17可以介导破骨细胞分化和抑制成骨细胞矿化结节形成,在绝经后骨质疏松症的发病机制中可能起关键作用,据报道在卵巢切除小鼠中由于雌激素缺乏,Th17细胞增多,促进了Th17细胞分化转录因子和循环白细胞介素17水平[63],并且白细胞介素17的水平的增加也会出现由慢性牙周炎引起的牙槽骨吸收等口腔表征[64-65],研究发现小檗碱可以上调肠道微生物群产生的丁酸盐来增强肠道屏障和下调血清内毒素以抑制白细胞介素17水平从而防止卵巢切除模型大鼠牙周骨组织丢失加剧[14]。这些研究表明,小檗碱对治疗绝经后骨质疏松是有益的,为治疗绝经后骨质疏松症提供了一个新思路。 (2)小檗碱具有抑制继发性骨质疏松症的作用:继发性骨质疏松症是由于疾病或药物等原因引起的骨量减少、骨微结构破坏、骨脆性增加和容易骨折的代谢性骨病[66]。导致继发性骨质疏松症的病因有很多,临床上以内分泌代谢疾病、结缔组织疾病、肾脏疾病、消化道疾病和药物所致者多见。 糖皮质激素性骨质疏松症:有研究称用溶剂、糖皮质激素、糖皮质激素联用小檗碱、糖皮质激素联用含维生素D的碳酸钙,分别作用于雄性SD大鼠12周,对大鼠骨组织进行包括生物力学质量、骨密度和骨小梁体积/总组织面积等在内的数十种指标的定量形态学分析,目前的结果表明小檗碱可以通过抑制骨吸收和改善骨形成来预防糖皮质激素引发的骨质疏松症[67-68]。 糖尿病性骨质疏松症:XIE等[69]用高脂饮食诱导联合腹腔注射链脲佐菌素建立糖尿病HFD/STZ大鼠模型,发现口服小檗碱能抑制糖尿病引起的骨质减少,可以预防部分糖尿病大鼠股骨微结构受损,并在一定程度上恢复糖尿病大鼠股骨骨形成和重吸收。另有研究发现小檗碱可以使得链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠血糖、糖化血红蛋白、血清胰岛素水平和异常尿钙降低,并显著改善糖尿病大鼠AMPK mRNA和骨转换标志物的表达,同时股骨骨骺微结构和骨密度也得到改善[6, 70]。值得注意的是,LONDZIN团队[71]认为小檗碱只是略微增加了骨形成并改善了松质骨微观结构的紊乱,但没有充分改善骨质量,研究结果不支持小檗碱用于预防糖尿病引起的骨损伤,这提示小檗碱预防和(或)治疗糖尿病性骨质疏松症的作用效果还有待继续探索。 失用性骨质疏松症:失用性骨质疏松症包括脊髓及其他神经损伤、神经肌肉疾病、骨折后固定和卧床休息而导致的骨质流失状态。目前认为失用性骨质疏松症发病的分子机制是Piezo1失活导致Wnt1表达降低,失用反应增加了骨细胞硬骨抑素的分泌,抑制了Wnt/β-catenin信号通路并导致成骨细胞活性受到影响,还导致骨细胞凋亡增加(部分通过Wnt/β-catenin信号)和RANKL表达增加,从而引起了骨质疏松[72]。小檗碱不仅可以通过抑制骨丢失对骨质疏松症起到预防和(或)治疗作用,还可以促进受损的坐骨神经再生[73]。上述研究证明,小檗碱可能是治疗抑制失用性骨质疏松的潜在药物,不过还需要更严谨的实验证明。 因此,小檗碱可能是控制骨质疏松症骨丢失的潜在药物[74],但小檗碱溶解度低和首关消除现象是导致小檗碱口服生物利用度低的主要原因,为解决此问题除了可以采用药物共晶等办法提高溶解度,还可采用皮肤微针、载药生物支架材料等局部用药方式改变给药途径,总之小檗碱作为一种新的抗骨质疏松症的药物,为骨组织工程领域带来了新的启迪。 2.1.4 小檗碱在特殊条件中促进骨再生修复的作用 骨组织损伤区的感染和炎症,以及糖尿病患者的骨缺损修复一直是临床治疗中的难题。高糖环境能显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞和MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨相关基因的表达,还使骨髓间充质干细胞内活性氧含量激增,影响其增殖[7-8],细菌引发的感染和炎症因子的升高也同样具有骨破坏作用[12-13]。研究表明小檗碱能够降低高糖环境和感染炎症环境对骨髓间充质干细胞和MC3T3-E1等细胞的不利影响,同时抑制骨吸收和促骨生成,是治疗糖尿病患者骨缺损和局部有炎症感染骨缺损的潜力药物。 (1)小檗碱在炎症及感染环境下的促成骨作用:细菌和促炎因子的存在会抑制成骨效能,影响成骨基因表达和矿化组织数量等[12-13]。复方小檗碱作为一种非处方药在中国已经使用多年,最早用于治疗感染性疾病。小檗碱对于牙龈卟啉单胞菌和金黄色葡萄球菌等均有良好的抑菌活性[12,75],ZHANG等[12]研究者表示小檗碱能够恢复牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞中成骨相关基因表达的下调。研究显示小檗碱能通过抑制Janus 激酶/信号转导和转录激活因子(JAKs/STATs)等信号通路减轻炎症反应[76-83],结扎性牙周炎会引发雄性Wistar大鼠牙龈组织致炎因子,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β升高和抗炎因子白细胞介素10下降,釉牙骨质界至牙槽嵴顶的距离也随之变长,骨吸收增加,小檗碱能明显降低致炎因子逆转这一病变过程[13],小檗碱还可以通过降低肠道通透性和血清内毒素水平从而抑制白细胞介素1、白细胞介素17的生成和降低甲状旁腺素等诱导形成的破骨细胞数量,防止骨组织丢失加剧[14, 16]。 这为研究者们将小檗碱用于治疗感染、炎症部位骨缺损提供了有力证据。基于小檗碱上述特性,有学者尝试将小檗碱引入骨替代材料中去修复感染状态下骨缺损取得了较好的效果[84-88]。 (2)小檗碱在高糖环境下的促成骨作用:众所周知心脏、大脑、神经、眼睛和肾脏的大血管和微血管是长期糖尿病的既定器官靶标,长此以往会引发一系列的损伤,相较于上述这些,糖尿病对肌肉骨骼系统的影响受到的关注要少得多。在糖尿病状态中骨形成率会下降[89],高糖会引起骨脆性增加,包括骨密度下降、晚期糖基化终产物水平升高和骨中微血管系统受损等,患有糖尿病的老年人骨折和骨折并发症的风险较高,且降糖药物也会提高骨折的发生概率[90],而当身体长期处于高血糖环境时会使得骨骼系统中脂肪细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞、骨细胞、内皮细胞及细胞外基质产生变化[91],总而言之血糖控制不佳与骨形成障碍、骨脆性增加密切相关。 自古以来黄连就被广泛地用于治疗消渴症,小檗碱就是黄连的主要有效成分之一,其也被证明了治疗糖尿病有效[92-94]。研究显示小檗碱可有效降低糖尿病大鼠血糖、炎症因子水平和破骨细胞数目,改善颌骨微观结构,减少牙槽骨吸收[10-11],减轻骨髓间充质干细胞和MC3T3-E1细胞的高葡萄糖抑制成骨作用[7-8]。SHAO等[9]学者发现小檗碱能通过上调活性氧介导的IRS-1信号传导促进糖尿病大鼠种植体周围成骨。目前的研究表明小檗碱能促进高糖环境下的成骨作用,但鲜有将小檗碱用于骨组织工程中治疗患有糖尿病的骨缺损动物模型,不过在此之前有学者开发出用于糖尿病骨缺损动物模型的其他骨替代材料,而且效果显著[95-96],因此可以尝试借鉴他们的经验,利用小檗碱的多重药理作用,来解决糖尿患者骨缺损的难题,总之小檗碱在糖尿患者骨缺损修复中有着很大的潜力。 因此,小檗碱可以通过调节多信号通路促进骨形成、抑制破骨细胞形成及其活性、抗骨质疏松和促进细胞在特殊环境下成骨分化等方面对骨骼系统发挥作用,是代替生长因子的潜力药物,对骨组织再生具有重大意义。小檗碱促进骨再生的主要作用、机制及意义见表2。"
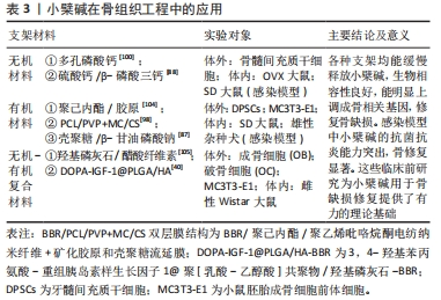
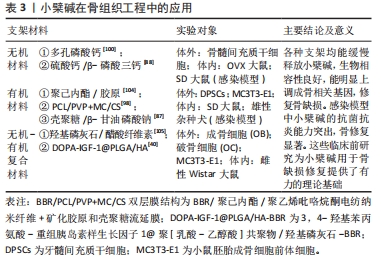
2.2 小檗碱的安全性 小檗碱发现至今已逾百年,多年以来复方小檗碱常作为临床用药以治疗感染性疾病,基本已明确其口服安全性,但在骨组织工程应用中以局部用药为主,所以其临床安全性研究还需进一步完善。 已经有研究表明0-30 μmol/L小檗碱呈现出剂量依赖性地上调人骨髓间充质干细胞和大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中包括碱性磷酸酶、血管内皮生长因子在内的数种指标,在1-10 μmol/L范围中碱性磷酸酶的表达活性明显增强,且3 μmol/L时RUNX2、Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素、Osterix、碱性磷酸酶和骨桥蛋白的基因表达最高,而超过10 μmol/L后,随着浓度的增加细胞的增殖还是表现出了抑制趋势,可能存在一定的细胞毒性[20, 29, 38-39, 97]。研究发现小檗碱浓度为0-10 μg/mL时人牙乳头间充质干细胞的细胞活性较好,且在1 μg/mL时成骨标志物活力较高[28],小檗碱浓度在0-5 μmol/L时明显刺激人牙髓间充质干细胞增殖以及浓度在0.01-0.1 mg/L时对人牙周膜干细胞无明显细胞毒性[21, 42]。 有学者把含有10 μmol/L小檗碱的骨替代材料植入大鼠骨缺损处4,8周后采集血液样本和心、肝、脾、肺和肾的脏器样本进行分析,发现红细胞、血红蛋白、血小板和白细胞的数量均在正常范围内,与未治疗对照的数量相当,脏器苏木精-伊红染色也没有明显的炎症或病理迹象[98]。 宋淼[87]研究表明,250 μg/mL小檗碱对犬不会发生溶血反应,将材料植入犬股部肌肉组织7 d后取注射部位肌肉组织和28 d后取犬心、肝、脾、肺和肾脏器样本进行组织学分析,也并未发现任何异常。大量的研究表明支架材料负载小檗碱对于成骨是有益的,支架能够缓慢释放小檗碱,将药物浓度控制在一定范围内从而降低毒副反应,提高成骨效能。 综上,现有的研究表明小檗碱局部用药时仍旧表现出良好的生物安全性,但浓度过高时会表现出细胞的抑制,这可能对于成骨是不利的,所以说骨组织工程中应用小檗碱促进细胞成骨分化需要控制在一个安全的范围,目前小檗碱在骨组织工程领域中的安全性研究还仅限于临床前阶段,其生物安全性还有待继续探索。 2.3 小檗碱在骨组织工程中的应用 小檗碱具有优秀的骨诱导潜力,并且还能够改善感染炎症环境和高糖环境对骨组织的不利影响,这使得其在骨修复领域中具有巨大的应用前景,许多学者通过将小檗碱与多种支架材料结合,来引导骨组织再生。在此前已有研究表明负载小檗碱的支架材料能缓慢释放药物,这一释药行为极大地保障了生物安全性,并表现出良好的抗菌性能,符合骨替代生物材料的抗菌要求[84-86]。 2.3.1 无机支架材料 由于无机生物材料与骨的矿物相有相似性且生物相容性好,具有优异的成骨性能,被视作是人工骨替代材料的最佳选择之一[99]。为修复骨缺损,小檗碱/多孔磷酸钙和小檗碱/硫酸钙/β-磷酸三钙先后被制作出来[88, 100],这些支架均表现出对骨髓间充质干细胞极好的生物相容性,能明显上调细胞内碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、骨形态发生蛋白2和RUNX2,促进钙结节生成,能有效地促进缺损区新骨形成。而且小檗碱/硫酸钙/β-磷酸三钙利用小檗碱的多重药理作用,对大鼠感染性骨缺损表现出优异的抑菌效果同时促进感染性骨缺损的骨愈合。 2.3.2 有机支架材料 生物材料的长期存在和功能,关键在于它们不会引起有害的免疫反应[101],一些高分子聚合物能表现出良好的生物相容性[102-103],可作为药物的控释载体和供细胞爬行的支架,以达到修复骨缺损的目的。MA等[104]学者将不同浓度小檗碱加入到聚己内酯/胶原电纺支架中形成BBR/PCL/COL,研究发现药物可以稳定释放达27 d,与人牙髓间充质干细胞生物相容性好,明显促进细胞向成骨谱系分化,并加快SD大鼠颅骨缺损处新生骨形成。ZHANG等[98]合成负载有小檗碱的BBR@PCL/PVP+MC/CS双层膜结构,由于小檗碱的存在,能较好地促进MC3T3-E1细胞增殖,以及促进SD大鼠股骨骨缺损的愈合。宋淼[87]将负载小檗碱的温敏壳聚糖水凝胶用于MC3T3-E1培养,结果显示此材料能促进MC3T3-E1增殖,在治疗犬感染性股骨骨缺损模型中也表现出优异的抗菌性能和促新骨形成作用。 2.3.3 无机-有机复合支架材料 无机材料和有机材料各有利弊,于是有学者尝试将两者结合起来,制作出新的人工骨替代物。有学者将纳米羟基磷灰石/小檗碱掺入纳米醋酸纤维中形成复合物纳米纤维[105],研究表明其可能在RUNX2、RANKL、p38MAPK和Wnt信号通路之间存在交叉作用,能显著上调碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Osterix水平并下调RANKL水平等,促进成骨细胞增殖、钙合成和抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收活性,从而对骨再生过程产生积极影响。CHEN等[40]学者通过带电液体喷射和相分离技术将不同浓度的小檗碱与羟基磷灰石和聚[乳酸-乙醇酸]制成微球,再将3,4-羟基苯丙氨酸-重组胰岛素样生长因子1吸附在微球上,这种材料被命名为“DOPA-IGF-1@PLGA/HA-BBR微球”,其能够缓慢释放小檗碱和胰岛素生长因子1,通过激活胰岛素样生长因子1受体/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR)信号通路诱导MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化,显著修复Wistar大鼠颅骨骨缺损。 综上所述,小檗碱可以通过与不同支架材料结合实现缓释作用并促进骨再生,并且基于小檗碱广泛药理作用在未来很有希望制作出一种新的人工骨替代材料用于治疗糖尿病患者的骨缺损或局部有感染炎症的骨缺损。小檗碱在骨组织工程中的应用见表3。"
| [1] XUE N, DING X, HUANG R, et al. Bone tissue engineering in the treatment of bone defects. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(7):879. [2] CAMPANA V, MILANO G, PAGANO E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(10):2445-2461. [3] SHU YH, LIN RM, CHIU YS, et al. Effects of IL-1β, IL-20, and BMP-2 on intervertebral disc inflammation under hypoxia. J Clin Med. 2020;9(1):140. [4] TIAN H, ZHAO J, BROCHMANN E, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and tumor growth: diverse effects and possibilities for therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;34:73-91. [5] HASHIMOTO K, KAITO T, FURUYA M, et al. In vivo dynamic analysis of BMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation. Sic Rep. 2020;10(1):4751. [6] 郑晓明,王康振,郑炜宏,等.小檗碱可以通过改善氧化应激和成骨活性减少2型糖尿病大鼠骨量的流失[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(10):1426-1430,1450. [7] 元建民,李璐,余阳,等.黄连素对高糖环境下成骨细胞MC3T3-E1的影响[J].中药与临床,2019,10(2):23-26. [8] 苟秋童,罗文豪,王频,等.黄连素在高糖环境下促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(19):2974-2980. [9] SHAO J, LIU S, ZHENG X, et al. Berberine promotes peri-implant osteogenesis in diabetic rats by ROS-mediated IRS-1 pathway. BioFactors. 2021;47(1):80-92. [10] 刘灵鲁,杨岚,李莎.小檗碱对糖尿病大鼠牙周炎影响的实验观察[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2019,29(4):187-194. [11] 戴璇,叶紫梦玮,刘亚鸽,等.马钱苷与黄连素联合用药对糖尿病小鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(2):239-247. [12] ZHANG R, YANG J, WU J, et al. Berberine promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells with therapeutic potential in periodontal regeneration. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;851:144-150. [13] GU L, KE Y, GAN J, et al. Berberine suppresses bone loss and inflammation in ligature-induced periodontitis through promotion of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-mediated inactivation of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;122:104992. [14] JIA X, JIA L, MO L, et al. Berberine ameliorates periodontal bone loss by regulating gut microbiota. J Dent Res. 2019;98(1):107-116. [15] 忻鼎熙.关于盐酸黄连素(小蘗硷)——答读者[J].中国兽医杂志,1959(10):316. [16] LI H, MIYAHARA T, TEZUKA Y, et al. The effect of kampo formulae on bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. II. Detailed study of berberine. Biol Pharm Bull. 1999;22(4):391-396. [17] LI H, MIYAHARA T, TEZUKA Y, et al. Effect of berberine on bone mineral density in SAMP6 as a senile osteoporosis model. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26(1):110-111. [18] LEE HW, SUH JH, KIM HN, et al. Berberine promotes osteoblast differentiation by Runx2 activation with p38 MAPK. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(8):1227-1237. [19] CHOI JS, KIM JH, ALI MY, et al. Coptis chinensis alkaloids exert anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by downregulating C/EBP-αand PPAR-γ. Fitoterapia. 2014;98:199-208. [20] TAO K, XIAO D, WENG J, et al. Berberine promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Toxicol lett. 2016;240(1):68-80. [21] XIN BC, WU QS, JIN S, et al. Berberine promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through activating EGFR-MAPK-Runx2 pathways. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020;26(3):1677-1685. [22] CHEN QC, PU YL, BI J, et al. Protective effects of berberine on senile osteoporosis in mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(5):748-756. [23] 佚名. 合成黄连素试制成功[J].医药工业,1972(4):4-5. [24] 佚名. 常压合成黄连素的工艺方法[J].医药工业,1973(7):1-4. [25] 佚名. 全合成黄连素技术鉴定会在沈阳召开[J].医药工业,1975(8):43. [26] 合成黄连素取得成功[J].辽宁化工,1976(1):56. [27] WONG SK, CHIN KY, IMA-NIRWANA S. Berberine and musculoskeletal disorders: the therapeutic potential and underlying molecular mechanisms. Phytomedicine. 2020;73:152892. [28] CUI Y, XIE J, FU Y, et al. Berberine mediates root remodeling in an immature tooth with apical periodontitis by regulating stem cells from apical papilla differentiation. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):18. [29] LI W, LIU Y, WANG B, et al. Protective effect of berberine against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(6):4041-4048. [30] ZHANG W, SU X, GAO Y, et al. Berberine protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32(8):1335-1342. [31] 张艳波,王军,王勇,等.小檗碱对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤脑组织Bcl-2、Bax表达及凋亡活性影响[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2011,25(2):126-129. [32] ZHENG H, LAN J, LI J, et al. Therapeutic effect of berberine on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its effect on Bax and Bcl-2. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(3):2008-2012. [33] 王海霞,张蕾,刘玲娟,等. Wnt/β-catenin通路激活促进慢性缺氧H9c2细胞中抗凋亡因子bcl-2及survivin表达[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(11):1509-1513. [34] CHEN P, XIA C, MO J, et al. Interpenetrating polymer network scaffold of sodium hyaluronate and sodium alginate combined with berberine for osteochondral defect regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;91:190-200. [35] JIANG W, XIANG X, SONG M, et al. An all-silk-derived bilayer hydrogel for osteochondral tissue engineering. Materials today Bio. 2022;17:100485. [36] ZHOU Y, MING J, DENG M, et al. Berberine-mediated up-regulation of surfactant protein D facilitates cartilage repair by modulating immune responses via the inhibition of TLR4/NF-ĸB signaling. Pharmacol Res. 2020;155:104690. [37] 王智. 黄连素对福美双诱导的肉鸡胫骨软骨发育不良的影响[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2016. [38] HAN Y, JIN Y, LEE SH, et al. Berberine bioisostere Q8 compound stimulates osteoblast differentiation and function in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 2017;119:463-475. [39] HAN Y, KIM MJ, LEE KY. Berberine derivative, Q8, stimulates osteogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;504(1):340-345. [40] CHEN L, TIAN M, YANG J, et al. Berberine-encapsulated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-hydroxyapatite (PLGA/HA) microspheres synergistically promote bone regeneration with DOPA-IGF-1 via the IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15403. [41] 李琼静,罗琪.小檗碱通过激活PI3K/AKT通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(29):4620-4624. [42] LIU J, ZHAO X, PEI D, et al. The promotion function of Berberine for osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK-FOS pathway mediated by EGFR. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2848. [43] BOYCE BF. Advances in the regulation of osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res. 2013;92(10):860-867. [44] ZHOU L, SONG F, LIU Q, et al. Berberine sulfate attenuates osteoclast differentiation through RANKL Induced NF-κB and NFAT pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):27087-27096. [45] DINESH P, RASOOL M. Berberine inhibits IL-21/IL-21R mediated inflammatory proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through the attenuation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IL-21 mediated osteoclastogenesis. Cytokine. 2018;106:54-66. [46] HU JP, NISHISHITA K, SAKAI E, et al. Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;580(1-2):70-79. [47] HAN SY, KIM YK. Berberine suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting c-Fos and NFATc1 expression. Am J Chin Med. 2019;47(2):439-455. [48] SUJITHA S, RASOOL M. Berberine coated mannosylated liposomes curtail RANKL stimulated osteoclastogenesis through the modulation of GSK3β pathway via upregulating miR-23a. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105703. [49] ISHIKAWA S, TAMAKI M, OGAWA Y, et al. Inductive effect of palmatine on apoptosis in RAW 264.7 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016; 2016:7262054. [50] 张少坤,梁庆威,王赫,等.盐酸巴马汀抑制聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯颗粒诱导骨溶解的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2012,41(6):507-510. [51] ISHIKAWA S, OGAWA Y, TAMAKI M, et al. Influence of palmatine on bone metabolism in ovariectomized mice and cytokine secretion of osteoblasts. In vivo. 2015;29(6):671-677. [52] LEE JW, IWAHASHI A, HASEGAWA S, et al. Coptisine inhibits RANKL-induced NF-κB phosphorylation in osteoclast precursors and suppresses function through the regulation of RANKL and OPG gene expression in osteoblastic cells. J Nat Med. 2012;66(1):8-16. [53] WEI P, JIAO L, QIN LP, et al. Effects of berberine on differentiation and bone resorption of osteoclasts derived from rat bone marrow cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2009;7(4):342-348. [54] 宋方茗.抗骨溶解中药单体筛选及圣草酚、木犀草苷、硫酸小檗碱对破骨细胞作用机制研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2016. [55] WILLIAMS JP, MICOLI K, MCDONALD JM. Calmodulin-an often-ignored signal in osteoclasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:358-364. [56] MA C, TANG K, LIU Q, et al. Calmodulin as a potential target by which berberine induces cell cycle arrest in human hepatoma Bel7402 cells. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013;81(6):775-783. [57] YE F, ZHOU Q, TIAN L, et al. The protective effect of berberine hydrochloride on LPS induced osteoclastogenesis through inhibiting TRAF6 Ca2+ calcineurin NFATcl signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):6228-6233. [58] QIN L, HAN T, ZHANG Q, et al. Antiosteoporotic chemical constituents from Er-Xian Decoction, a traditional Chinese herbal formula. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;118(2):271-279. [59] REN MS, XIE HH, DING Y, et al. Er-Xian Decoction drug-containing serum promotes Mc3t3-e1 cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation via regulating BK channel. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;302(Pt A):115887. [60] 年华,马明华,徐泯,等.小檗碱对去卵巢大鼠骨量丢失的保护作用[J].中国药师,2014,17(6):894-898. [61] HOLICK MF, LAMB JJ, LERMAN RH, et al. Hop rho iso-alpha acids, berberine, vitamin D3 and vitamin K1 favorably impact biomarkers of bone turnover in postmenopausal women in a 14-week trial. J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(3):342-350. [62] LAMB JJ, HOLICK MF, LERMAN RH, et al. Nutritional supplementation of hop rho iso-alpha acids, berberine, vitamin D₃, and vitamin K₁ produces a favorable bone biomarker profile supporting healthy bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Res. 2011;31(5):347-355. [63] TYAGI AM, SRIVASTAVA K, MANSOORI MN, et al. Estrogen deficiency induces the differentiation of IL-17 secreting Th17 cells:a new candidate in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44552. [64] AWANG RA, LAPPIN DF, MACPHERSON A, et al. Clinical associations between IL-17 family cytokines and periodontitis and potential differential roles for IL-17A and IL-17E in periodontal immunity. Inflamm Res. 2014;63(12):1001-1012. [65] CHEN XT, CHEN LL, TIAN JY, et al. Th17 and Th1 lymphocytes are correlated with chronic periodontitis. Immunol Invest. 2016;45(3):243-254. [66] EBELING PR, NGUYEN HH, ALEKSOVA J, et al. Secondary osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2022;43(2):240-313. [67] XU D, YANG W, ZHOU C, et al. Preventive effects of berberine on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rats. Planta Med. 2010;76(16):1809-1813. [68] 许碧莲,徐道华,陈文双,等.小檗碱对糖皮质激素性骨质疏松大鼠松质骨和皮质骨的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(7):965-970. [69] XIE H, WANG Q, ZHANG X, et al. Possible therapeutic potential of berberine in the treatment of STZ plus HFD-induced diabetic osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:280-287. [70] ADIL M, MANSOORI MN, SINGH D, et al. Pioglitazone-induced bone loss in diabetic rats and its amelioration by berberine: a portrait of molecular crosstalk. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:1010-1019. [71] LONDZIN P, KOCIK S, KISIEL-NAWROT E, et al. Lack of berberine effect on bone mechanical properties in rats with experimentally induced diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;146:112562. [72] ROLVIEN T, AMLING M. Disuse osteoporosis: clinical and mechanistic insights. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(5):592-604. [73] RAHMATI M, EHTERAMI A, SABERANI R, et al. Improving sciatic nerve regeneration by using alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing berberine. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021;11(5):1983-1993. [74] MARTINIAKOVA M, BABIKOVA M, OMELKA R. Pharmacological agents and natural compounds:available treatments for osteoporosis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2020.3.01. [75] LI T, WANG P, GUO W, et al. Natural berberine-based Chinese herb medicine assembled nanostructures with modified antibacterial application. ACS Nano. 2019;13(6):6770-6781. [76] XIA Z, LI Q, TANG Z. Network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental pharmacology explored Ermiao wan protected against periodontitis via the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/MAPK signal pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;303:115900. [77] WANG H, TU S, YANG S, et al. Berberine modulates LPA function to inhibit the proliferation and inflammation of FLS-RA via p38/ERK MAPK pathway mediated by LPA1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:2580207. [78] SHARMA A, TIRPUDE NV, BHARDWAJ N, et al. Berberis lycium fruit extract and its phytoconstituents berberine and rutin mitigate collagen-CFA-induced arthritis (CIA) via improving GSK3β/STAT/Akt/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling axis mediated oxi-inflammation and joint articular damage in murine model. Inflammopharmacology. 2022;30(2):655-666. [79] LI X, HE P, HOU Y, et al. Berberine inhibits the interleukin-1 beta-induced inflammatory response via MAPK downregulation in rat articular chondrocytes. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(5):637-645. [80] JIA L, XUE K, LIU J, et al. Anticolitic effect of berberine in rat experimental model: impact of PGE2/p38 MAPK pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:9419085. [81] HAN Y, GUO S, LI Y, et al. Berberine ameliorate inflammation and apoptosis via modulating PI3K/AKT/NFκB and MAPK pathway on dry eye. Phytomedicine. 2023;121:155081. [82] HAFTCHESHMEH SM, ABEDI M, MASHAYEKHI K, et al. Berberine as a natural modulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the immune system: focus on NF-κB, JAK/STAT, and MAPK signaling pathways. Phytother Res. 2022;36(3):1216-1230. [83] CHOI YY, KIM MH, HAN JM, et al. The anti-inflammatory potential of Cortex Phellodendron in vivo and in vitro:down-regulation of NO and iNOS through suppression of NF-κB and MAPK activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;19(2):214-220. [84] ZOU Q, LI Y, ZHANG L, et al. Antibiotic delivery system using nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan bone cement consisting of berberine. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89(4):1108-1117. [85] HUANG D, ZUO Y, ZOU Q, et al. Antibacterial chitosan coating on nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide66 porous bone scaffold for drug delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011;22(7):931-944. [86] CAI B, ZOU Q, ZUO Y, et al. Injectable gel constructs with regenerative and anti-infective dual effects based on assembled chitosan microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(30):25099-25112. [87] 宋淼.小檗碱-壳聚糖温敏性水凝胶的制备及其对犬感染性骨缺损的治疗作用[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2023. [88] 李雪琪.载黄连素硫酸钙(CSH/β-TCP/BBR)颗粒抗菌性、生物安全性及骨修复功能的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2023. [89] CAMARGO WA, VRIES RD, LUIJK JV, et al. Diabetes mellitus and bone regeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(5):471-479. [90] LECKA-CZERNIK B. Diabetes, bone and glucose-lowering agents: basic biology. Diabetologia. 2017;60(7):1163-1169. [91] HOFBAUER LC, BUSSE B, EASTELL R, et al. Bone fragility in diabetes:novel concepts and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(3):207-220. [92] AKDAD M, AMEZIANE R, KHALLOUKI F, et al. Antidiabetic phytocompounds acting as glucose transport stimulators. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023;23(2):147-168. [93] 张祥伟, 李美子.小檗碱降糖机制研究进展[J].糖尿病新世界,2023,26(8):185-188. [94] RAHIGUDE AB, KAULASKAR SV, BHUTADA PS. Possible therapeutic potential of berberine in diabetic osteopathy. Med Hypotheses. 2012;79(4):440-444. [95] LI D, CHEN K, TANG H, et al. A logic-based diagnostic and therapeutic hydrogel with multistimuli responsiveness to orchestrate diabetic bone regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022;34(11):e2108430. [96] TAO SC, LI XR, WEI WJ, et al. Polymeric coating on β-TCP scaffolds provides immobilization of small extracellular vesicles with surface-functionalization and ZEB1-Loading for bone defect repair in diabetes mellitus. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121465. [97] 张瑞. 黄连素对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化作用的初步研究[D].南京:南京大学,2017. [98] ZHANG Y, WANG T, LI J, et al. Bilayer membrane composed of mineralized collagen and chitosan cast film coated with berberine-loaded PCL/PVP electrospun nanofiber promotes bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:684335. [99] SADOWSKA JM, GINEBRA MP. Inflammation and biomaterials:role of the immune response in bone regeneration by inorganic scaffolds. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(41):9404-9427. [100] WANG D, ZHANG P, MEI X, et al. Repair calvarial defect of osteoporotic rats by berberine functionalized porous calcium phosphate scaffold. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(3):rbab022. [101] FRANZ S, RAMMELT S, SCHARNWEBER D, et al. Immune responses to implants - a review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2011;32(28):6692-6709. [102] GIRAULT E, BIGUENET F, EIDENSCHENK A, et al. Fibrous biomaterials: effect of textile topography on foreign body reaction. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(10):1512-1524. [103] KYRIAKIDES T, KIM HJ, ZHENG C, et al. Foreign body response to synthetic polymer biomaterials and the role of adaptive immunity. Biomed Mater. 2022. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac5574. [104] MA L, YU Y, LIU H, et al. Berberine-releasing electrospun scaffold induces osteogenic differentiation of DPSCs and accelerates bone repair. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1027. [105] SHABAN NZ, KENAWY MY, TAHA NA, et al. Cellulose acetate nanofibers: incorporating hydroxyapatite (HA), HA/Berberine or HA/Moghat composites, as scaffolds to enhance in vitro osteoporotic bone regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(23):4140. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [3] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [7] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [8] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [9] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [10] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [11] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [12] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [13] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [14] | Lan Weiwei, Yu Yaodong, Huang Di, Chen Weiyi. In vitro degradation behavior of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 717-723. |
| [15] | Zhou Xiaowen, Fu Zuchang, Huang Fei, Ai Jianguo, Zhao Feng. Bone defect blocked by bone cement segmental filling in single-plane tibial bone transport [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 736-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||