Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 690-696.doi: 10.12307/2023.976
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats
Zhang Ya1, Mu Qiuju2, Wang Zilin1, Liu Hongjie1, Zhu Lili2
- 1Teaching and Research Department of Clinical Laboratory Fundamentals and Hematology, School of Medical Laboratory, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-12-05Accepted:2023-01-16Online:2024-02-18Published:2023-08-16 -
Contact:Zhu Lili, Senior technologist, Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ya, Master candidate, Junior technologist, Teaching and Research Department of Clinical Laboratory Fundamentals and Hematology, School of Medical Laboratory, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Project, No. gzwkj2021-366 (to ZLL); a grant from Guiyang Science and Technology Bureau, No. [2018]1-75 (to ZLL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
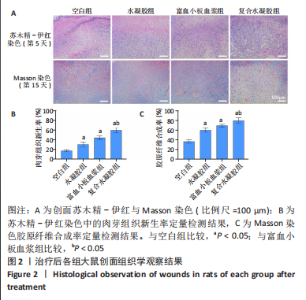
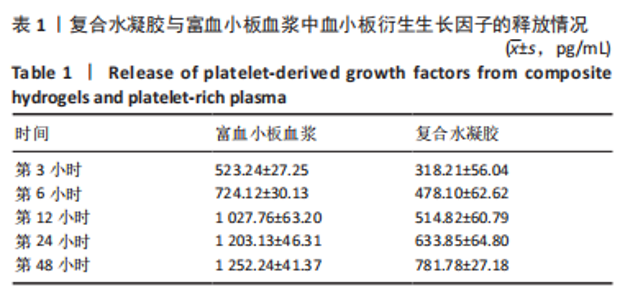
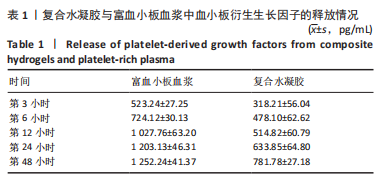
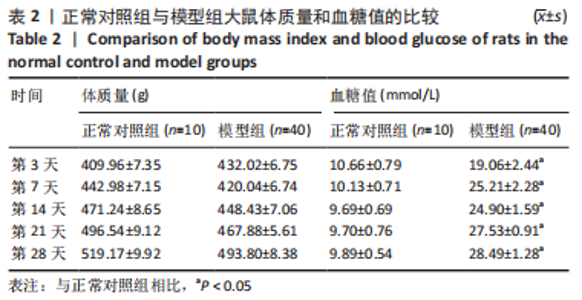
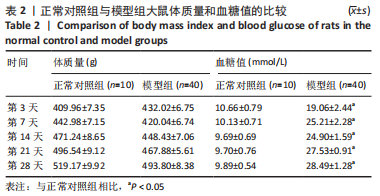
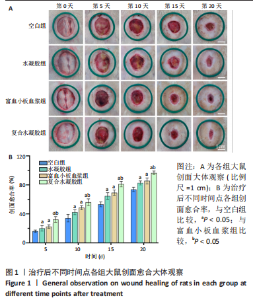
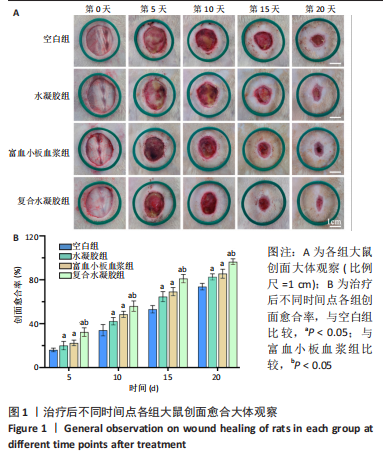
治疗后第5天,各组大鼠创面覆盖有不同程度痂壳,痂壳间隙及创面周围有红肿现象,创面无感染及化脓。治疗后第10天,与空白组创面愈合率相比,其余3组大鼠皮肤创面面积均有不同程度减小。治疗后第15天,与空白组创面愈合率相比,水凝胶组、富血小板血浆组和复合水凝胶组创面愈合率升高,其中复合水凝胶组创面愈合率最高。治疗后第20天,富血小板血浆组创面较前虽有明显缩小,但仍有部分创面未愈合,而复合水凝胶组创面基本愈合完全,提示与富血小板血浆和水凝胶相比,复合水凝胶具有更优异的促愈合能力。 2.4 各组大鼠创面形态学观察 治疗后第5天的苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组大鼠创面组织中炎症细胞稀疏分布,可见大量炎性滲出;水凝胶组创面可见一定数量炎症细胞、新生肉芽组织以及散在孤立的毛细血管;富血小板血浆组创面可见较多新生肉芽组织及毛细血管生成;复合水凝胶组创面有大量的新生肉芽组织生成,肉芽组织中可见大量血管,见图2。"
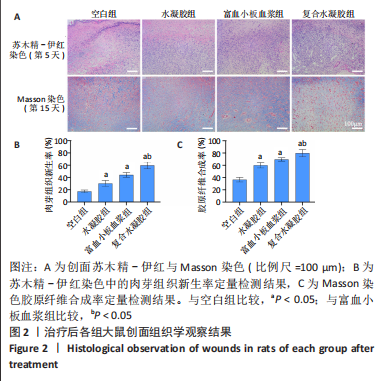
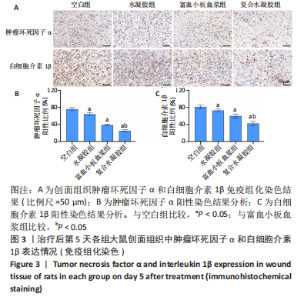
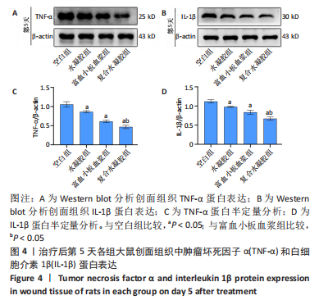
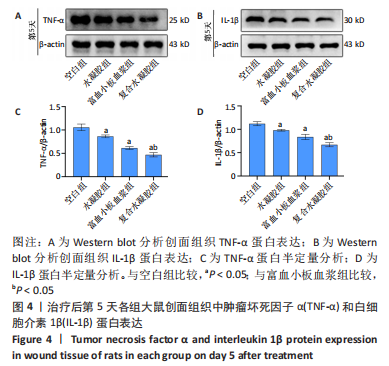
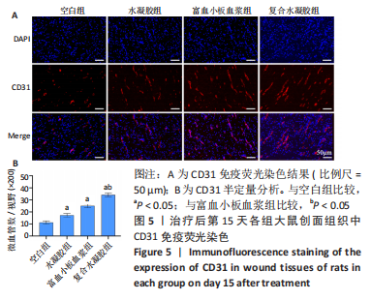
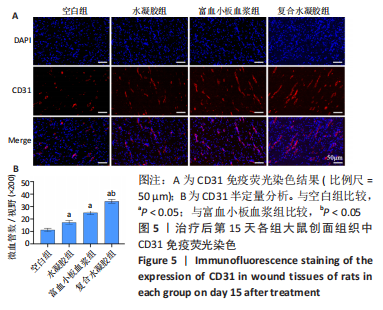
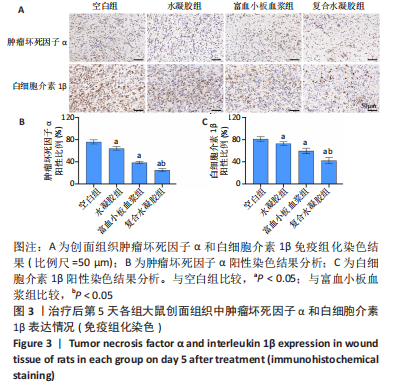
治疗后第15天的Masson染色结果显示,空白组胶原纤维(蓝染)数量少,排列较为无序,分布欠均匀;与空白组相比,水凝胶组、富血小板血浆组胶原纤维有增加,但排列疏松、分布不均匀,复合水凝胶组胶原纤维数量多且分布均匀、致密,排列整齐有序,见图2。 2.5 各组大鼠创面组织中的炎症反应情况 治疗后第5天,创面组织中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β免疫组织化学染色结果显示,复合水凝胶组创面组织中的肿瘤坏死因子α阳性比例(25.01±2.64)%明显低于空白组(75.87±3.75)%、水凝胶组(64.07±3.31)%和富血小板血浆组(38.57±2.18)%(P < 0.05);复合水凝胶组创面组织中的白细胞介素1β阳性比例(42.26±5.62)%明显低于空白组(81.23±4.16)%、水凝胶组(72.88±3.28)%和富血小板血浆组(59.84±4.76)%,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。"
| [1] LIU C, GE HM, LIU BH, et al. Targeting pericyte-endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019; 116(15):7455-7464. [2] SHI Q, QIAN Z, LIU D, et al. GMSC-Derived Exosomes Combined with a Chitosan/Silk Hydrogel Sponge Accelerates Wound Healing in a Diabetic Rat Skin Defect Model. Front Physiol. 2017;8:904. [3] Zarei F, Soleimaninejad M. Role of growth factors and biomaterials in wound healing. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):906-911. [4] MARTÍ-CARVAJAL AJ, GLUUD C, NICOLA S, et al. Growth factors for treating diabetic foot ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 2015(10):CD008548. [5] SHEN YI, CHO H, PAPA AE, et al. Engineered human vascularized constructs accelerate diabetic wound healing. Biomaterials. 2016;102: 107-119. [6] SEIDEL D, STORCK M, LAWALL H, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy compared with standard moist wound care on diabetic foot ulcers in real-life clinical practice: results of the German DiaFu-RCT. BMJ Open. 2020;10(3):e026345. [7] HAN G, CEILLEY R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv Ther. 2017;34(3):599-610. [8] CAKIN MC, OZDEMIR B, KAYA-DAGISTANLI F, et al. Evaluation of the in vivo wound healing potential of the lipid fraction from activated platelet-rich plasma. Platelets. 2020;31(4):513-520. [9] HESSELER MJ, SHYAM N. Platelet-rich plasma and its utility in the treatment of acne scars: A systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(6):1730-1745. [10] SHAIK JA, ESTHARABADI N, FARAH RS, et al. Heterogeneity in amount of growth factors secreted by platelets in platelet-rich plasma samples from alopecia patients. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(10):1004-1011. [11] OUDELAAR BW, PEERBOOMS JC, HUIS IN ‘T VELD R, et al. Concentrations of Blood Components in Commercial Platelet-Rich Plasma Separation Systems: A Review of the Literature. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(2):479-487. [12] SUTHAR M, GUPTA S, BUKHARI S, et al. Treatment of chronic non-healing ulcers using autologous platelet rich plasma: a case series. J Biomed Sci. 2017;24(1):16. [13] LI S, DONG Q, PENG X, et al. Self-Healing Hyaluronic Acid Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Platelet-Rich Plasma Impregnated for Skin Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2022;16(7):11346-11359. [14] LIU X, YANG Y, NIU X, et al. An in situ photocrosslinkable platelet rich plasma - Complexed hydrogel glue with growth factor controlled release ability to promote cartilage defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:179-187. [15] CAO J, WU P, CHENG Q, et al. Ultrafast Fabrication of Self-Healing and Injectable Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Dressing for Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(20):24095-24105. [16] LV X, LIU Y, SONG S, et al. Influence of chitosan oligosaccharide on the gelling and wound healing properties of injectable hydrogels based on carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complexes. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;205:312-321. [17] ALINEJAD Y, ADOUNGOTCHODO A, HUI E, et al. An injectable chitosan/chondroitin sulfate hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties for cell therapy/tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113:132-141. [18] SHARMA S, SWETHA KL, ROY A. Chitosan-Chondroitin sulfate based polyelectrolyte complex for effective management of chronic wounds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;132:97-108. [19] ZHOU L, FAN L, ZHANG FM, et al. Hybrid gelatin/oxidized chondroitin sulfate hydrogels incorporating bioactive glass nanoparticles with enhanced mechanical properties, mineralization, and osteogenic differentiation. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):890-904. [20] LI H, CHENG F, WEI X, et al. Injectable, self-healing, antibacterial, and hemostatic N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized chondroitin sulfate composite hydrogel for wound dressing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111324. [21] FAN M, MA Y, TAN H, et al. Covalent and injectable chitosan-chondroitin sulfate hydrogels embedded with chitosan microspheres for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017; 71:67-74. [22] AYUK SM, ABRAHAMSE H, HOURELD NN. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Diabetic Wound Healing in relation to Photobiomodulation. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:2897656. [23] YANG S, HU L, HAN R, et al. Neuropeptides, Inflammation, Biofilms, and diabetic Foot Ulcers. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022;130(7): 439-446. [24] QIAN Z, WANG H, BAI Y, et al. Improving Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing through an Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Platelet-Rich Plasma Release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(50):55659-55674. [25] TOTTOLI EM, DORATI R, GENTA I, et al. Skin Wound Healing Process and New Emerging Technologies for Skin Wound Care and Regeneration. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(8):735. [26] ZHANG Y, WANG ZL, DENG ZP, et al. Emerging Delivery Strategies of Platelet-Rich Plasma with Hydrogels for Wound Healing. Adv Polym Technol. 2022;(2022):5446291. [27] ZHAO R, LIANG H, CLARKE E, et al. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2085. [28] LIAO X, LIANG JX, LI SH, et al. Allogeneic Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy as an Effective and Safe Adjuvant Method for Chronic Wounds. J Surg Res. 2020;246:284-291. [29] ORTOLANI E, GUERRIERO M, COLI A, et al. Effect of PDGF, IGF-1 and PRP on the implant osseointegration. An histological and immunohistochemical study in rabbits. Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2014; 5(2):66-68. [30] ZHANG X, YAO D, ZHAO WY, et al. Engineering platelet-rich plasma based dual-network hydrogel as a bioactive wound dressing with potential clinical translational value. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;31(8):2009258. [31] EVERTS P, ONISHI K, JAYARAM P, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7794. [32] IRMAK G, GÜMÜŞDERELIOĞLU M. Patients- and tissue-specific bio-inks with photoactivated PRP and methacrylated gelatin for the fabrication of osteochondral constructs. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 125:112092. [33] GROWNEY EA, LINDER HR, GARG K, et al. Bio-conjugation of platelet-rich plasma and alginate through carbodiimide chemistry for injectable hydrogel therapies. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(5): 1972-1984. [34] MEDEIROS LHC, VASCONCELOS BMF, SILVA MB, et al. Chondroitin sulfate from fish waste exhibits strong intracellular antioxidant potential. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021;54(10):e10730. [35] CHANG SH, WU CH, TSAI GJ. Effects of chitosan molecular weight on its antioxidant and antimutagenic properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;181:1026-1032. [36] LIU F, LI HY, WANG Z, et al. Carboxymethyl chitosan reduces inflammation and promotes osteogenesis in a rabbit knee replacement model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):775. [37] KHARKAR PM, KIICK KL, KLOXIN AM. Designing degradable hydrogels for orthogonal control of cell microenvironments. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42(17):7335-7372. [38] CHEN YR, ZHOU ZX, ZHANG JY, et al. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin-Functionalized Chitosan-Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogels for Controlled Release of TGF-β3 and in vitro Neocartilage Formation. Front Chem. 2019;7:745. [39] LI HL, LIU XT, HUANG SM, et al. Repair function of essential oil from Crocodylus Siamensis (Schneider, 1801) on the burn wound healing via up-regulated growth factor expression and anti-inflammatory effect. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;264:113286. [40] MARTIN P, NUNAN R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(2):370-378. [41] KAKUDO N, MORIMOTO N, OGAWA T, et al. Angiogenic effect of platelet-rich plasma combined with gelatin hydrogel granules injected into murine subcutis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(7):1941-1948. [42] WEI S, XU P, YAO Z, et al. A composite hydrogel with co-delivery of antimicrobial peptides and platelet-rich plasma to enhance healing of infected wounds in diabetes. Acta Biomater. 2021;24:205-218. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [3] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [4] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [5] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [6] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [7] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [8] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [9] | Wang Yeyuan, Du Yilang, Yu Dehao, Ning Fengting, Bai Bing. Effect of micro-arc oxidation treatment on biological activity of medical metals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [10] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [11] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [12] | Wang Wu, Fan Xiaolei, Xie Jie, Hu Yihe, Zeng Min. Hydroxyapatite-polyvinyl alcohol/collagen-chitosan-gelatin composite hydrogel for repairing rabbit osteochondral defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 682-689. |
| [13] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [14] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [15] | Long Zhirui, Huang Lei, Xiao Fang, Wang Lin, Wang Xiaobei. Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||