Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (31): 5055-5062.doi: 10.12307/2024.706
Previous Articles Next Articles
Co-culture technology of mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages
Yang Xiaoqian1, 2, 3, 4, Song Aimei1, 2, 3, 4, Song Hui1, 2, 3, 4
- 1School of Stomatology, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; 2Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Tissue Regeneration, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; 3Shandong Provincial Laboratory of Oral Biomaterials and Tissue Regeneration Engineering, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; 4Shandong Provincial Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-14Accepted:2023-10-08Online:2024-11-08Published:2024-01-23 -
Contact:Song Aimei, MD, Chief physician, School of Stomatology, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Tissue Regeneration, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Laboratory of Oral Biomaterials and Tissue Regeneration Engineering, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China Song Hui, School of Stomatology, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Tissue Regeneration, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Laboratory of Oral Biomaterials and Tissue Regeneration Engineering, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yang Xiaoqian, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Tissue Regeneration, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Laboratory of Oral Biomaterials and Tissue Regeneration Engineering, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; Shandong Provincial Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2020MH184 (to SAM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Xiaoqian, Song Aimei, Song Hui. Co-culture technology of mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5055-5062.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

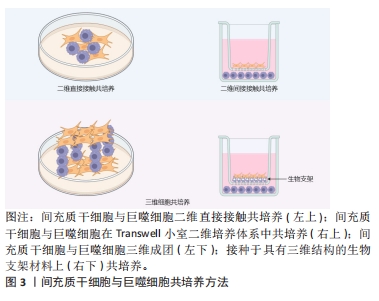
2.1 间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养方法 细胞共培养是指在体外将2种或2种以上细胞置于同一培养系统环境中培养孵育,近似模拟体内生成的微环境[8]。细胞共培养的历史可追溯到20世纪80年代,LAWRENCE等[9]将大鼠卵巢颗粒细胞和小鼠心肌细胞共培养,发现异体细胞通过缝隙连接的方式进行交流。在单一培养技术中,细胞通常以二维形式生长,而组织中具有高度有序的复杂三维网络且相邻细胞类型之间存在相互作用,共培养技术能够更好地模拟生物实验中的体内细胞生理和相互作用,且共培养系统可用于评估两种不同细胞类型的细胞间通讯和组成[10]。组织工程的目标是创建有功能的组织,与传统的组织工程培养条件相比,细胞共培养具有通过辅助细胞反馈控制靶细胞的优势,再现体内发生的相互作用,这在工程组织中建立结构-功能关系至关重要。 细胞共培养为体外研究不同细胞之间的相互作用提供了重要的技术平台,目前此技术已经深入到了多个学科领域,而且发展了多种共培养方法。目前体外细胞共培养根据模型可以分为直接接触共培养、间接接触共培养,而根据维度又可以分为二维细胞共培养和三维细胞共培养[11],二者可交叉使用,见图3。"
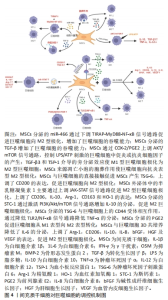
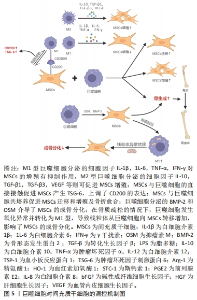
2.1.1 直接接触共培养 即将两种细胞按照一定比例接种于同一培养体系中,细胞之间直接接触相互作用[11]。LU等[12]采用该方法将巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞以5∶1的比例(巨噬细胞:5×104个/孔;间充质干细胞:104个/孔)接种于24孔板,在50%的巨噬细胞培养基和50%的成骨培养基中体外共培养4周,发现间充质干细胞骨矿化程度显著增强,且巨噬细胞负调控骨保护素,表明巨噬细胞在促进骨矿化的同时还可能通过骨保护素/核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)信号通路间接影响破骨细胞的活性。间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞之间存在相互促进的交互作用,LI等[13]将M1型巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞共培养,发现M1型巨噬细胞可以通过直接与间充质干细胞相互作用促进间充质干细胞上CD200的表达,间充质干细胞的CD200与巨噬细胞的CD200R相互作用增强间充质干细胞的免疫抑制能力,从而促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化。 2.1.2 间接接触共培养 即将两种细胞按照一定比例分别接种于不同的载体上,然后将这两种载体置于同一培养环境之中,使不同种类的细胞不直接接触仅有培养液的交换。最常用和最经典的模型是Transwell小室,是一类小室底具有通透性膜的杯状装置,小室和培养板底部接种不同种类的细胞,培养时将小室放入培养板从而建立细胞的共培养[8],观察两种细胞的分泌因子相互作用。高弘斐等[14]将间充质干细胞以1×105/cm2浓度接种于Transwell小室中并与M0型巨噬细胞(1×105/cm2)共培养3 d后,观察到棒状、星状及树枝状形态的巨噬细胞明显减少,白细胞介素10和白细胞介素1β表达增加,肿瘤坏死因子α的表达被抑制,表明间充质干细胞可促进M0型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞极化。YUAN等[15]采用0.4 mm孔径的Transwell小室将脂肪间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞以1∶1的比例共培养24 h,上室接种脂肪间充质干细胞,下室接种巨噬细胞,发现脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的前列腺素E2(Prostaglandin E2,PGE2)能有效促进巨噬细胞从M1表型向M2表型转化。YAO等[16]将巨噬细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞包裹在明胶/海藻酸钠水凝胶微球中,研究发现所构建的3D旁分泌培养系统中精氨酸1(arginase-1,Arg-1)、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10、血管内皮细胞生长因子、趋化因子CXC配体13(CXC chemokine ligand 13,CXCL13)等细胞因子对巨噬细胞表型转化和抗炎性能均有正向调节的作用,从而有利于创口的愈合。 2.1.3 三维共培养体系 人类细胞系在二维模型中不能准确模拟其在体内组织的复杂性,许多研究表明体外的三维培养环境呈现一个更接近体内环境的模型,比二维环境更有利于展现细胞本身的特性。 ROMERO-LóPEZ等[17]将巨噬细胞接种在由光交联甲基丙烯酸明胶制成的3D水凝胶支架中与间充质干细胞以5∶1(1.25×106∶2.5×105)的比例在共培养培养基中直接共培养4周,发现间充质干细胞通过抑制M1型和增强M2型巨噬细胞表型表现出免疫调节活性,且无论加入的巨噬细胞极化状态如何都能促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,其中M1型巨噬细胞最有效地促进新骨形成,表明在急性炎症阶段M1型巨噬细胞对早期骨形成具有潜在的促进作用。SALDA?A等[18]将间充质干细胞接种于高度多孔的聚苯乙烯支架,上室接种间充质干细胞,下室接种巨噬细胞,将共培养物置于含有体积分数12.5%胎牛血清的等体积RPMI和DMEM的混合物中孵育72 h,结果表明巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞共培养的条件培养基对间充质干细胞成骨有抑制作用;然而在1,25-二羟基维生素D3处理的条件培养基中促炎因子减少且间充质干细胞基质成熟和矿化增加。TANG等[19]研究者将脂肪间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞以1∶1(5×105:5×105)通过3D聚乳酸羟基乙酸(poly lactic-co-glycolic acid,PLGA)/聚己内酯(polycaprolactone,PCL)支架在成骨培养基中直接共培养42 d发现巨噬细胞抑制了脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化,这可能与脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的抑瘤素M(oncostatin M,OSM)与骨形态发生蛋白2分泌减少有关,此抑制作用可能来自于巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子或三维支架、巨噬细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞之间的直接相互作用。以上研究表明细胞与细胞之间的相互作用在2D和3D模型中是有差异的。 2.2 间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞共培养相互作用的影响因素 2.2.1 共培养方法 为了比较不同共培养方法的优劣,LUO等[20]将骨髓间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞分别用3种方法共培养,分别为巨噬细胞条件培养液、间接培养和直接培养,研究发现直接接触对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和矿化促进作用最强,细胞-细胞接触似乎增加了培养细胞之间的沟通。间充质干细胞与M1直接共培养和与M1间接共培养相比,直接共培养对抑制促炎因子表达的调节作用更有效[13],直接接触似乎发挥了额外的细胞接触交流作用。也有报道表明,巨噬细胞介导的成骨诱导需要直接的细胞接触。有学者发现间充质干细胞接种在三维底物中会减弱体外M1型巨噬细胞的活化,增强其对巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用[21]。YAO等[16]通过qRT-PCR和ELISA分析结果显示,与2D旁分泌系统相比,3D旁分泌系统中促炎细胞因子的表达显著下调,抗炎细胞因子的表达显著上调,且应用3D旁分泌系统的创面愈合速度要快得多。也有学者表明与2D培养相比,3D培养后促炎和抗炎基因表达和细胞因子分泌水平都较低[17],可能是细胞因子与3D支架的成分相互反应,限制了其对细胞本身的作用。细胞-细胞接触和信号传递可能是直接接触共培养的独特和关键特征,细胞间相互作用更全面且激发其在组织工程中的应用,3D构造模拟了体内复杂的生长环境特点,提示可根据研究目的选择合适的培养方法。由于间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞在体内局部微环境中相互作用的环境是高度复杂、动态和多面性的,体外细胞培养环境并不能反映间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞之间相互的整体影响,因此决定最终细胞共培养命运的关键步骤应采用动物研究建模进行进一步的研究。 2.2.2 两种细胞的共培养条件 细胞在体外培养过程中需要有一定的密度,一般认为细胞培养的密度越高,细胞与细胞之间接触得越多,更有利于信号的传递和功能的调节。共培养中也需要两种细胞有一定的密度比例,细胞共培养的比例是影响细胞间相互作用的关键因素。 LU等[12]以巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞比例为5∶1和1∶1分别进行直接共培养,研究发现在巨噬细胞较高的接种密度下,无论巨噬细胞表型如何,所有巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞共培养的骨矿化都有所增加。ZHANG等[22]研究发现M1型巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞以1∶1的比例直接共培养后矿化增加,而1∶4和4∶1的比例矿化增加不明显,而M2巨噬细胞明显促进了间充质干细胞的矿化,且这种作用与巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞的比例成正比,而M0型巨噬细胞无论比例如何都将会降低间充质干细胞的矿化程度。在Transwell共培养系统中以1∶1的比例将接种在上室巨噬细胞和接种在下室的间充质干细胞共培养3、7、14、28 d,研究发现共培养14 d时碱性磷酸酶活性水平达到峰值[22]。不同的细胞接种比例和共培养时间都会影响细胞之间的相互作用,但目前共培养比例与时间的最佳选择仍难以定论,有待研究。 2.2.3 巨噬细胞的表型 间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养的作用结果与巨噬细胞的表型有关,巨噬细胞可以对间充质干细胞再生过程施加消极或积极的影响,这取决于它们的极化状态[23]。与M2型巨噬细胞相比,M1型巨噬细胞分泌较多的促炎因子,这种微环境可能更有效地激活间充质干细胞,使M1型巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞直接共培养中间充质干细胞的骨矿化程度最为突出,充分发挥其成骨潜能和免疫调节作用[12],因而作者认为M1型巨噬细胞在间充质干细胞骨形成中起到协同作用。ZHANG等[22]以1∶1的比例间接共培养间充质干细胞与不同表型的巨噬细胞,研究发现M0和M1型巨噬细胞仅在早中期刺激间充质干细胞成骨分化,而M2型巨噬细胞对间充质干细胞成骨基因的表达具有延迟的刺激作用,由此可以确定不同表型巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞共培养的最佳时间,以利用巨噬细胞最大限度地促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化。但也有学者研究发现M1和M2型巨噬细胞均抑制了脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化[19],从而可能影响骨愈合,其中M2巨噬细胞的抑制作用强于M1巨噬细胞[24]。 上述研究结果的不同可能是由于细胞种类来源、诱导巨噬细胞极化的方法、共培养比例和培养基种类不同所导致的,且有研究发现M2型巨噬细胞比M1型巨噬细胞存活时间更长[25],说明不同表型巨噬细胞的存活差异也可能会影响共培养系统,因此巨噬细胞在间充质干细胞成骨分化中的确切作用仍需要更全面、更准确的研究。 2.2.4 间充质干细胞的来源 所有间充质干细胞亚群不仅具有自我更新能力和多向分化潜力,还具有免疫调节特性,不同来源的间充质干细胞具有不同的治疗潜力。高弘斐等[14]将外周血间充质干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞与M0型巨噬细胞分别共培养3 d后采用Bio-Plex免疫微球法检测各组上清液的细胞因子含量,结果表明两种间充质干细胞与M0共培养均可促进白细胞介素10、白细胞介素1β的表达同时抑制肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,促进M0型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞极化,且骨髓间充质干细胞的调节能力强于外周血间充质干细胞,表明外周血间充质干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞均具有炎症免疫调节潜力并具有差异性。 JIN等[26]比较了骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪间充质干细胞和脐血间充质干细胞的抗炎活性,脐血间充质干细胞最能抑制脂多糖刺激的大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞释放的炎症细胞因子(包括白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8);研究结果表明,与成人来源的脐血间充质干细胞相比,原始脐血间充质干细胞更具有生物学优势,这使脐血间充质干细胞成为临床应用细胞治疗的有用模型。PESHKOVA等[27]比较脂肪组织、骨髓、牙龈、胎盘和脐带来源的间充质干细胞在2D和3D培养条件下细胞因子和生长因子的分泌量,并评估了不同间充质干细胞来源的条件培养基对体外巨噬细胞极化的影响,结果表明脐带来源的间充质干细胞条件培养基中细胞因子和生长因子水平最高,对巨噬细胞有显著的抗炎作用,具有广阔的应用前景。ALANAZI等[28]也提出脐带似乎是间充质干细胞的最佳来源,因为与体内其他部位相比,脐带具有易于提取、无创采集、更强的自我更新能力和免疫调节特性。 与来自正常宫颈(normal cervix,NCx)的间充质干细胞相比,来自宫颈癌(cervical cancer,CeCa)的间充质干细胞有更大的潜力促进M2型巨噬细胞极化,并增加吞噬型巨噬细胞的百分比;M2型巨噬细胞内白细胞介素10和吲哚胺2-3双加氧酶(indoleamine 2-3 dioxygenase,IDO)表达增加,且具有降低T细胞增殖的能力[29],这提示了CeCa-间充质干细胞在体外抗肿瘤免疫中的作用,但有必要在动物模型中评估这些能力,以分析肿瘤环境中M2巨噬细胞亚群的增加。 尽管这些间充质干细胞具有相似的分化能力,但当用于治疗目的时,它们可能发展出不同的抗炎或修复潜能。评估不同来源间充质干细胞的潜力,以选择最佳来源进行细胞治疗,这些信息为间充质干细胞在不同疾病状态下的治疗应用提供了新的实验依据,但目前不同来源间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养的比较研究还较为缺乏。 2.3 间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养中相互调控的可能机制 目前发现间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养可能通过可溶性因子、细胞外囊泡,细胞间接触及代谢途径进行相互调控,间充质干细胞通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphoinositide 3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt),髓样分化因子 88(myeloid differentiation factor 88,MyD88)-核转录生长因子κB及Janus激酶(Janus kinase,JAK)/信号转导子和转录活化子(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT)等信号通路调节巨噬细胞的免疫功能,巨噬细胞也通过上述途径对间充质干细胞的增殖、迁移及成骨能力产生一定影响,间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞的相互作用的调控机制的重要性越来越不可忽视,见图4,5。"
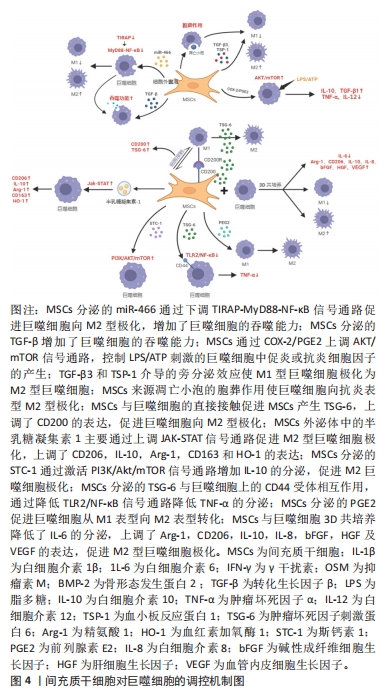
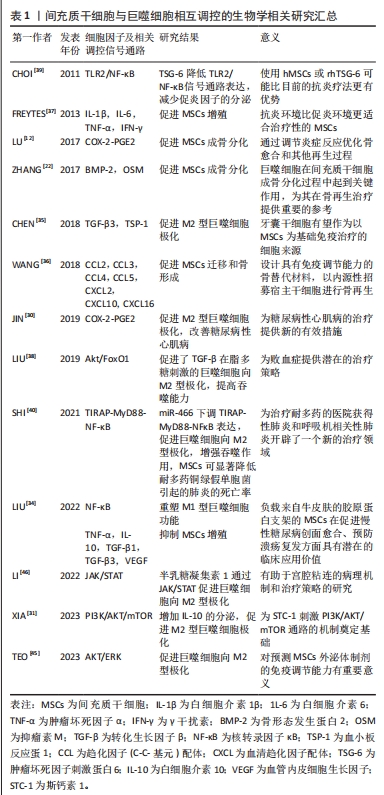
2.3.1 共培养中巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞分泌的可溶性因子促进生物学功能的改变——旁分泌效应 无论是直接接触共培养还是间接接触共培养,细胞在培养过程中会释放一些可溶性分子至培养液中,从而作用于周围细胞,发生功能改变。环氧合酶2(cyclooxygenase-2,COX-2)在炎症过程中负责将花生四烯酸转化为PGE2等类型前列腺素,有研究报道间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞直接共培养通过COX-2-PGE2途径促进间充质干细胞早期骨形成[12],间充质干细胞亦通过此途径增加M2型巨噬细胞来改善心脏损伤[30]。XIA等[31]通过实验证明经Transwell系统将人脐带间充质干细胞与小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞NR8383以5∶1的比例共培养,人脐带间充质干细胞分泌的斯钙素1(stanniocalcin-1,STC-1)通过激活NR8383 PI3K/Akt/ 哺乳动物雷帕霉素(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路增加白细胞介素10的分泌,促进M2巨噬细胞极化。也有学者提出间充质干细胞衍生的COX-2/PGE2在THP-1分化的人巨噬细胞中负责Akt/mTORC1/磷酸化4E结合蛋白1[phopho-4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1,4E-BP1]的激活和抗炎极化[32]。ZHOU等[33]也提出经Transwell系统共培养(巨噬细胞∶间充质干细胞=5∶1),巨噬细胞白细胞介素10和白细胞介素37表达的增加部分与PI3K/Akt通路的调节有关。LIU等[34]发现间充质干细胞通过旁分泌作用抑制促炎型巨噬细胞的极化可能是通过影响肿瘤坏死因子α/核转录因子κB信号通路重塑M1型巨噬细胞功能实现的。另外当巨噬细胞在牙囊干细胞条件培养液共培养时转化生长因子β3(transforming growth factor-β3,TGF-β3)和血小板反应蛋白1(Thrombospondin-1,TSP-1)介导的旁分泌效应也能够使M1型巨噬细胞极化为M2型巨噬细胞[35]。通过收集检测间接共培养的培养基和极化巨噬细胞的条件培养基发现骨形态发生蛋白2和OSM成骨因子的分泌介导了间充质干细胞的成骨分化[22]。提取巨噬细胞接种于骨诱导双相磷酸钙陶瓷培养后的上清液,并将其与间充质干细胞共培养,结果发现巨噬细胞趋化因子可促进间充质干细胞迁移和骨形成[36]。不同极化状态来源巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子对间充质干细胞的作用不一,经Transwell系统共培养M1型巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α及γ干扰素等对间充质干细胞的增殖有抑制作用,M2型巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor-β1,TGF-β1)、TGF-β3及血管内皮生长因子等则可促进间充质干细胞增殖[37]。通过间接共培养间充质干细胞分泌的TGF-β可通过Akt/叉头框转录因子O亚族1(forkhead box transcription factor O1,FoxO1)信号通路使脂多糖刺激的巨噬细胞向M2型极化,减轻炎症反应,提高吞噬能力[38]。间充质干细胞分泌的肿瘤坏死因子刺激蛋白6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated protein 6,TSG-6)与巨噬细胞上的CD44受体相互作用,通过降低TLR2/核转录因子κB信号通路降低促炎因子的分泌[39]。 2.3.2 细胞外囊泡 近年来越来越多的研究表明,间充质干细胞通过释放细胞外囊泡的方式来发挥旁分泌功能,从而对巨噬细胞功能发挥影响。SHI等[40]通过Transwell系统共培养证明间充质干细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡中含有的miR-466抑制了Toll/白细胞介素1受体衔接蛋白(Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein,TIRAP)表达,导致MyD88-核转录因子κB信号通路下调,从而使表型平衡向M2极化倾斜,发挥免疫调节作用并增强吞噬作用,进一步减轻肺炎的严重程度。间充质干细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡也可以通过直接与巨噬细胞培养把miR-223-3p转移到巨噬细胞中,改变基因表达和生物活性,降低巨噬细胞的炎症反应[41]。XU 等[42]则是使用生物活性玻璃(bioactive glasses,BG)预处理间充质干细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡,使其miR-125a-5p表达上调,与巨噬细胞直接培养促进巨噬细胞向抗炎型和血管生成表型的极化。 目前,间充质干细胞外泌体已经成为治疗炎症性疾病的一种新的无细胞替代方法。间充质干细胞来源的凋亡小泡(apoptotic vesicles,APOVs)的胞葬作用使巨噬细胞在2型糖尿病肝中向抗炎表型转化,恢复肝巨噬细胞的稳态,改善2型糖尿病病情[43]。与巨噬细胞培养的脂肪间充质干细胞来源的外泌体主要通过线粒体DNA的转移,有效改善巨噬细胞的线粒体完整性和氧化磷酸化水平,从而恢复气道巨噬细胞的代谢和免疫稳态,减轻肺部炎症病理反应[44]。TEO等[45]发现间充质干细胞外泌体通过催化腺苷的产生,进而与腺苷受体A2A和A2B结合,激活AKT/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)依赖的信号通路,从而促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化。通过Transwell系统共培养发现肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的间充质干细胞(T-MSCs)外泌体中的半乳糖凝集素1主要通过JAK/STAT信号通路促进子宫内膜巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,从而减轻子宫内膜的纤维化[46]。 关于巨噬细胞外泌体对间充质干细胞作用的研究则比较少,有研究表明,极化状态不同的巨噬细胞来源的细胞外囊泡中的miRNA也参与了骨再生正向或负向的调节,采用Transwell系统间接共培养研究表明M1-EVs 抑制骨再生,而M2-EVs对骨再生具有诱导作用[47]。 2.3.3 细胞-细胞接触 虽然大多数报道认为间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性依赖于其可溶性因子的分泌,但细胞间直接接触对其功能也起着重要作用。NICOLAIDOU等[48]研究表明间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞是通过细胞间直接接触激活了STAT3信号通路,促进了OSM分泌,联合其他可溶性因子,促进了间充质干细胞成骨分化。LI等[13]也发现间充质干细胞来源TSG-6介导的旁分泌效应的增强依赖于间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞直接接触作用,促使M1型巨噬细胞极化为M2型巨噬细胞;细胞间接触作用还上调了间充质干细胞CD200的表达,而上调的CD200介导了两细胞之间的直接相互作用,由此证实间充质干细胞是免疫调节器和免疫传感器,可感知可溶性因子和细胞接触介导的信号引起的动态微环境。 2.3.4 代谢途径 除了通过可溶性因子和细胞接触靶向作用于巨噬细胞外,代谢途径的调节在间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞相互调控中占有重要地位。 最近的研究证明,糖酵解通过代谢重编程在调节巨噬细胞极化过程中起着重要作用。YUAN等[15]通过Transwell系统共培养研究发现脂肪间充质干细胞通过防止M1型巨噬细胞过度表达缺氧诱导因子1α(Hypoxia inducible factor-1α,HIF-1α)来重新编程M1型巨噬细胞的糖酵解途径,从而抑制巨噬细胞的M1型极化;同时,M1型巨噬细胞分泌的琥珀酸促使脂肪间充质干细胞分泌PGE2,促进巨噬细胞从M1表型转变为M2表型,从而来减轻结肠炎症。DENG等[49]的进一步实验也表明骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体是通过抑制细胞糖酵解来调节小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞系MH-S细胞的极化。氧化应激在巨噬细胞对间充质干细胞的调控中也起到重要作用,巨噬细胞以类似于使用抗氧化剂N-乙酰半胱氨酸(N-acetyl cysteine,NAC)的方式降低骨髓间充质干细胞产生的细胞内活性氧的增加水平进而调控成骨分化[20],但若巨噬细胞转移异常线粒体则会改变了间充质干细胞的代谢状态,进而导致成骨分化障碍[50]。TEISSIER等[51]也发现M0型巨噬细胞与线粒体代谢受损的间充质干细胞共培养可纠正氧化还原失衡,恢复稳态代谢。在慢性炎症中,将间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养来重新编程糖酵解途径及线粒体生物能以调节炎症优化骨稳态。 综上所述,间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养中相互调控的可能机制具有复杂性和多样性,细胞外微环境对共培养细胞的功能发挥具有重要作用,间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞的相互靶向作用是调节炎症反应和促进骨再生的有效策略。了解间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞之间的协同串扰,根据临床需求精准调控两种细胞的共培养结果使治疗水平达到最优,对于实现有益的生物学功能和改善再生结果的应用具有重要意义,见表1。"
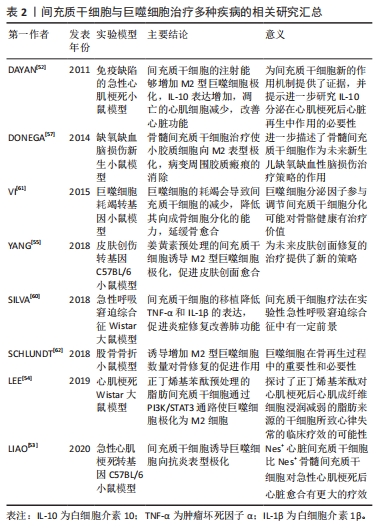
2.4 间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养与疾病治疗的关系 近年来研究发现,间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞在治疗缺血性心脏病中有着密切联系。DAYAN等[52]将间充质干细胞注入小鼠急性心肌梗死模型中,实验发现M2型巨噬细胞在心脏中的比例增加,其心脏功能显著改善。LIAO等[53]发现心肌内注射的间充质干细胞可通过分泌血清骨膜蛋白诱导M2型巨噬细胞的极化,减少梗死面积且显著改善急性心肌梗死后的心功能。预处理的脂肪间充质干细胞可通过PI3K/STAT3通路调节心肌梗死大鼠的巨噬细胞极化,减少心肌的纤维化从而改善心功能[54]。 对于皮肤损伤的修复,YANG等[55]通过姜黄素促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖,诱导M2型巨噬细胞极化,为皮肤创面愈合创造了再生免疫微环境。DI等[56]研究发现局部移植的间充质干细胞分泌的TSG-6使角膜上皮细胞增殖增加,促进M2型巨噬细胞极化,增强其吞噬能力,进而促进糖尿病小鼠角膜上皮创面愈合。 鼻内给予间充质干细胞可导致新生小鼠缺氧缺血脑损伤模型中反应性星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞减少,小胶质细胞向M2表型极化,病变周围瘢痕的消除[57]。LI等[58]研究发现间充质干细胞的早期干预可通过免疫调节和旁分泌作用有效抑制糖尿病大鼠肾巨噬细胞的浸润和炎症细胞因子的表达,恢复了免疫微环境的稳态,改善了肾功能和肾小球硬化。ASAMI等[59]将鼻内接种肺炎链球菌的小鼠静脉注射间充质干细胞,促炎因子和肺炎球菌感染后肺部的细菌负荷均显著降低。巨噬细胞在肺损伤早期分泌白细胞介素1β,于急性呼吸窘迫综合征模型Wistar大鼠中注射骨髓和脂肪来源的间充质干细胞后肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β水平降低,促进炎症修复改善肺功能[60]。 提高间充质干细胞的成骨性能从而促进其成骨分化是治疗骨缺损性疾病的关键。而不同状态下的巨噬细胞所形成的微环境也会影响到间充质干细胞的成骨性能。VI等[61]建立巨噬细胞耗竭转基因小鼠模型,研究发现巨噬细胞的耗竭会导致间充质干细胞的减少,降低其向成骨细胞分化的能力,延缓骨愈合。在截骨模型中加入白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13诱导骨折区域的M2表型,干预第21天后相较于对照组有更多的骨形成[62],证明了诱导增加M2型巨噬细胞数量对骨修复的促进作用。 巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞的相互作用似乎是从调节局部巨噬细胞的数量及极化状态来维持骨稳态和促进骨折修复。而改善组织微环境炎症状态是组织修复保护的前提和基础,巨噬细胞具有高度可塑性,间充质干细胞可调控巨噬细胞极化,进而对组织炎症反应进行调节,治疗炎症性疾病,促进局部损伤修复。未来可通过将特定状态下的间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞共培养来构建促进间充质干细胞成骨分化或促进组织修复的模型,为临床骨缺损、肺炎、心血管疾病等的治疗和组织再生提供新的方法和策略,见表2。"
| [1] SHARIATI A, NEMATI R, SADEGHIPOUR Y, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) for neurodegenerative disease: a promising frontier. Eur J Cell Biol. 2020;99(6):151097. [2] MAQSOOD M, KANG M, WU X, et al. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020;256:118002. [3] ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801. [4] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020; 877:173090. [5] HE X, DONG Z, CAO Y, et al. MSC-derived exosome promotes M2 polarization and enhances cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7132708. [6] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89. [7] LU D, XU Y, LIU Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and maintenance of inflammatory microenvironment homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:681171. [8] 谢丽,孟芮,商澎.细胞共培养技术在骨组织生物学中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学报, 2013,35(2):216-223. [9] LAWRENCE TS, BEERS WH, GILULA NB. Transmission of hormonal stimulation by cell-to-cell communication. Nature. 1978;272(5653):501-506. [10] PANDURANGAN M, HWANG I. Application of cell co-culture system to study fat and muscle cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(17):7359-7364. [11] 张楚晗,张东敏,徐稳安.牙髓再生组织工程中的细胞共培养体系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(15):2379-2384. [12] LU LY, LOI F, NATHAN K, et al. Pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote osteogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells via the COX-2-prostaglandin E2 pathway. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(11): 2378-2385. [13] LI Y, ZHANG D, XU L, et al. Cell-cell contact with proinflammatory macrophages enhances the immunotherapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in two abortion models. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(12):908-920. [14] 高弘斐,张潜,陈龙,等.间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养体系的细胞因子表达模式研究[J].免疫学杂志,2017,33(11):930-936. [15] YUAN Y, NI S, ZHUGE A, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reprogram M1 macrophage metabolism via PHD2/HIF-1α pathway in colitis mice. Front Immunol. 2022;13:859806. [16] YAO H, YUAN X, WU Z, et al. Fabrication and performance evaluation of gelatin/sodium alginate hydrogel-based macrophage and MSC cell-encapsulated paracrine system with potential application in wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1240. [17] ROMERO-LÓPEZ M, LI Z, RHEE C, et al. Macrophage effects on mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis in a three-dimensional in vitro bone model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(19-20):1099-1111. [18] SALDAÑA L, VALLÉS G, BENSIAMAR F, et al. Paracrine interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages are regulated by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14618. [19] TANG H, HUSCH JFA, ZHANG Y, et al. Coculture with monocytes/macrophages modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells on poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid/polycaprolactone scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(5):785-798. [20] LUO ML, JIAO Y, GONG WP, et al. Macrophages enhance mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis via down-regulation of reactive oxygen species. J Dent. 2020;94:103297. [21] SWARTZLANDER MD, BLAKNEY AK, AMER LD, et al. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells combats the foreign body response to cell-laden synthetic hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;41:79-88. [22] ZHANG Y, BÖSE T, UNGER RE, et al. Macrophage type modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue MSCs. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;369(2):273-286. [23] SPILLER KL, KOH TJ. Macrophage-based therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:74-83. [24] TANG H, ZHANG Y, JANSEN JA, et al. Effect of monocytes/macrophages on the osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in 3D co-culture spheroids. Tissue Cell. 2017;49(4):461-469. [25] HUANG SC, EVERTS B, IVANOVA Y, et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(9):846-855. [26] JIN HJ, BAE YK, KIM M, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17986-18001. [27] PESHKOVA M, KORNEEV A, SULEIMANOV S, et al. MSCs’ conditioned media cytokine and growth factor profiles and their impact on macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023; 14(1):142. [28] ALANAZI A, ALASSIRI M, JAWDAT D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: a review of clinical trials for multiple sclerosis. Regen Ther. 2022;21:201-209. [29] CORTÉS-MORALES VA, CHÁVEZ-SÁNCHEZ L, ROCHA-ZAVALETA L, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from cervical cancer promote M2 macrophage polarization. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1047. [30] JIN L, DENG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote type 2 macrophage polarization to ameliorate the myocardial injury caused by diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):251. [31] XIA TT, HU R, SHAO CJ, et al. Stanniocalcin-1 secreted by human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells regulates interleukin-10 expression via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in alveolar macrophages. Cytokine. 2023;162:156114. [32] KO JH, OH JY. Mesenchymal stromal cells regulate THP-1-differentiated macrophage cytokine production by activating Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway. Cytotherapy. 2023;25(8):858-865. [33] ZHOU T, SUN Y, WANG Y, et al. Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells enhance lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-10 and IL-37 production in THP-1 cells. Inflammation. 2019; 42(3):987-993. [34] LIU H, YANG R, ZHAO S, et al. Collagen scaffolds derived from bovine skin loaded with MSC optimized M1 macrophages remodeling and chronic diabetic wounds healing. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;8(3):e10467. [35] CHEN X, YANG B, TIAN J, et al. Dental follicle stem cells ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by secreting TGF-β3 and TSP-1 to elicit macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2290-2308. [36] WANG M, CHEN F, WANG J, et al. Calcium phosphate altered the cytokine secretion of macrophages and influenced the homing of mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(29):4765-4774. [37] FREYTES DO, KANG JW, MARCOS-CAMPOS I, et al. Macrophages modulate the viability and growth of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(1):220-229. [38] LIU F, QIU H, XUE M, et al. MSC-secreted TGF-β regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage M2-like polarization via the Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):345. [39] CHOI H, LEE RH, BAZHANOV N, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 2011;118(2):330-338. [40] SHI MM, ZHU YG, YAN JY, et al. Role of miR-466 in mesenchymal stromal cell derived extracellular vesicles treating inoculation pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e287. [41] HOU L, ZHU Z, JIANG F, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviated silica induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice via circPWWP2A/miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;251:114537. [42] XU H, ZHU Y, HSIAO AW, et al. Bioactive glass-elicited stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate M2 macrophage polarization and angiogenesis to improve tendon regeneration and functional recovery. Biomaterials. 2023;294:121998. [43] ZHENG C, SUI B, ZHANG X, et al. Apoptotic vesicles restore liver macrophage homeostasis to counteract type 2 diabetes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(7):e12109. [44] XIA L, ZHANG C, LV N, et al. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics. 2022;12(6):2928-2947. [45] TEO KYW, ZHANG S, LOH JT, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes mediate M2-like macrophage polarization through CD73/Ecto-5’-nucleotidase activity. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(5):1489. [46] LI J, PAN Y, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α-primed mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage polarization via Galectin-1 and modify intrauterine adhesion on a novel murine model. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945234. [47] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627. [48] NICOLAIDOU V, WONG MM, REDPATH AN, et al. Monocytes induce STAT3 activation in human mesenchymal stem cells to promote osteoblast formation. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e39871. [49] DENG H, WU L, LIU M, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate LPS-induced ARDS by modulating macrophage polarization through inhibiting glycolysis in macrophages. Shock. 2020;54(6):828-843. [50] CAI W, ZHANG J, YU Y, et al. Mitochondrial transfer regulates cell fate through metabolic remodeling in osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(4):e2204871. [51] TEISSIER V, GAO Q, SHEN H, et al. Metabolic profile of mesenchymal stromal cells and macrophages in the presence of polyethylene particles in a 3D model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):99. [52] DAYAN V, YANNARELLI G, BILLIA F, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells mediate a switch to alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages after acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):1299-1310. [53] LIAO Y, LI G, ZHANG X, et al. Cardiac nestin+ mesenchymal stromal cells enhance healing of ischemic heart through periostin-mediated M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Ther. 2020; 28(3):855-873. [54] LEE TM, HARN HJ, CHIOU TW, et al. Preconditioned adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate cardiac fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization in infarcted rat hearts through the PI3K/STAT3 pathway. Lab Invest. 2019;99(5):634-647. [55] YANG Z, HE C, HE J, et al. Curcumin-mediated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets create a favorable immune microenvironment for adult full-thickness cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):21. [56] DI G, DU X, QI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote diabetic corneal epithelial wound healing through TSG-6-dependent stem cell activation and macrophage switch. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(10):4344-4354. [57] DONEGA V, NIJBOER CH, VAN TILBORG G, et al. Intranasally administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2014;261:53-64. [58] LI Y, LIU J, LIAO G, et al. Early intervention with mesenchymal stem cells prevents nephropathy in diabetic rats by ameliorating the inflammatory microenvironment. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 41(5):2629-2639. [59] ASAMI T, ISHII M, NAMKOONG H, et al. Anti-inflammatory roles of mesenchymal stromal cells during acute Streptococcus pneumoniae pulmonary infection in mice. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(3):302-313. [60] SILVA JD, LOPES-PACHECO M, PAZ AHR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and lung tissue differentially mitigate lung and distal organ damage in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(2):e132-e140. [61] VI L, BAHT GS, WHETSTONE H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1090-102. [62] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. [63] NATHAN K, LU LY, LIN T, et al. Precise immunomodulation of the M1 to M2 macrophage transition enhances mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and differs by sex. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(10):481-488. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [4] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [5] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [6] | Zeng Fanzhuo, Li Yuxin, Sun Jiachen, Gu Xinyang, Wen Shan, Tian He, Mei Xifan. Efficient strategies for microglia replacement in spinal cord injury models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [7] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [8] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [9] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [10] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [12] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [13] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [14] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [15] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||