Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 1137-1142.doi: 10.12307/2024.113
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis
Ma Shuwei1, He Sheng2, Han Bing3, Zhang Liaoyun1
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, 2Department of Imaging, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-07Accepted:2023-03-23Online:2024-03-08Published:2023-07-17 -
Contact:Zhang Liaoyun, Master, Professor, Chief physician, PhD supervisor, Department of Infectious Diseases, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Ma Shuwei, Master candidate, Department of Infectious Diseases, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Shanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology Project, No. 201903D421064 (to ZLY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
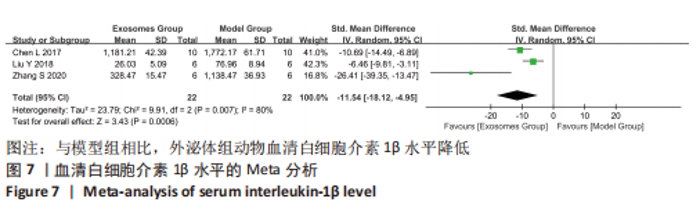
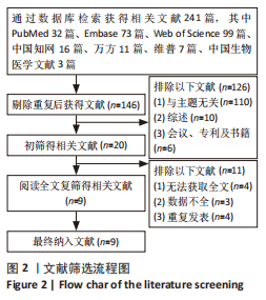
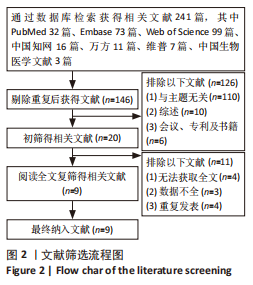
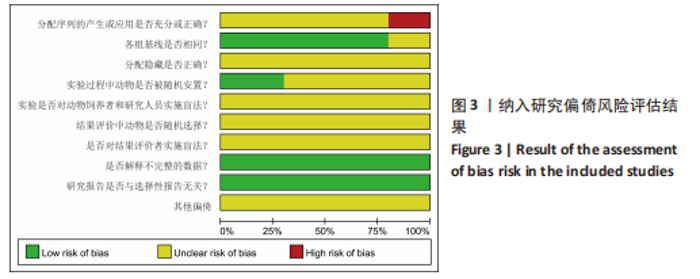
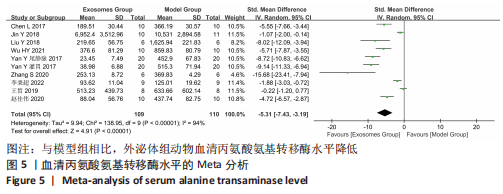
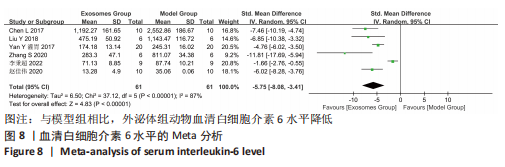
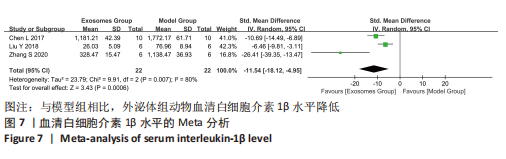
2.4.4 IL-1β水平 共有4个研究报告了急性肝衰竭后MSCs-Ex移植对动物血清IL-1β水平的影响[7-9,12],但JIN等[8]文献中虽然采用蛋白芯片检测了血清细胞因子浓度,结果以柱状图表示且未标误差棒,仅能提取均数而无法提取标准差,且该文献未提供其他能推算出标准差的参数。若按标准差=0处理,则该文章数据在森林图结果中所占权重为0,除增加样本量外对其他参数无影响,因此剔除这项研究。最终只纳入3个研究,合计样本量为44只动物,外泌体组和模型组均为22只。各研究间异质性较高(I2=80%),选择随机效应模型。结果显示,与模型组动物相比,外泌体组动物的血清IL-1β水平明显降低[SMD=-11.54,95%CI(-18.12,-4.95),P=0.000 6],见图7。"
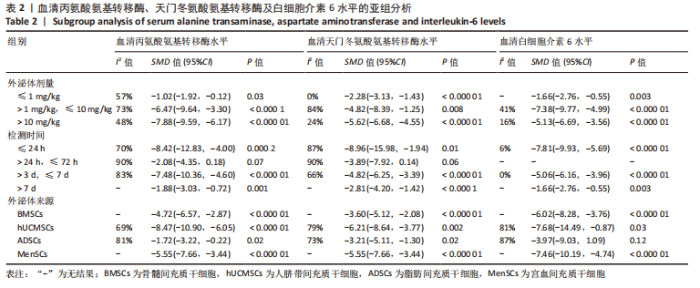
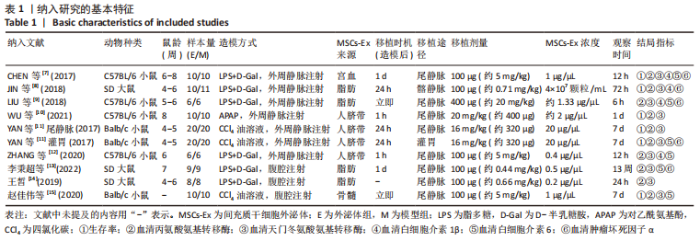
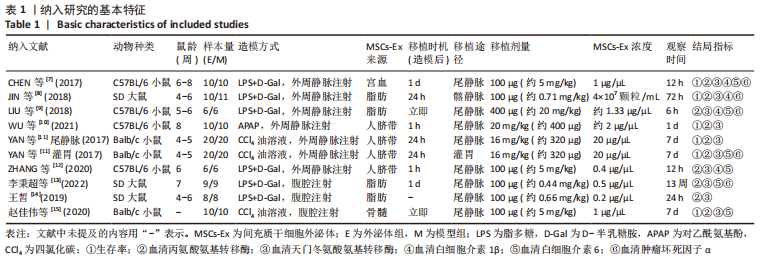
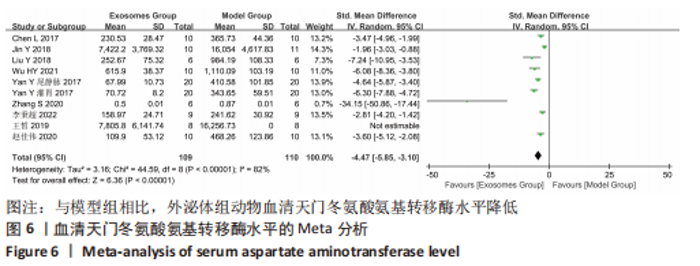
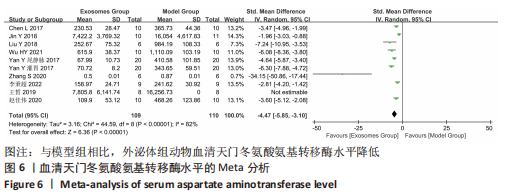
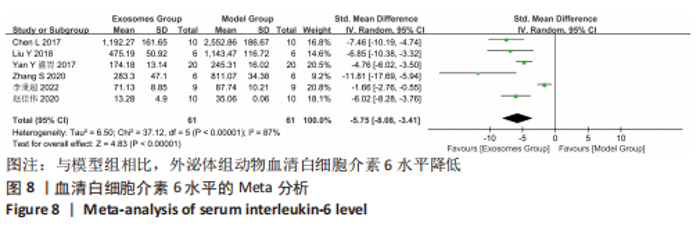
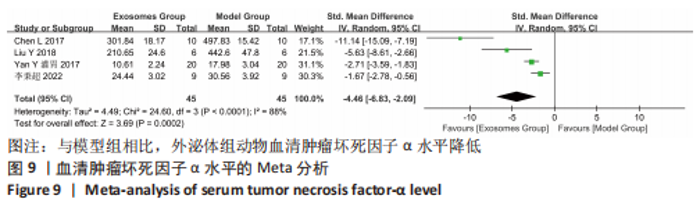
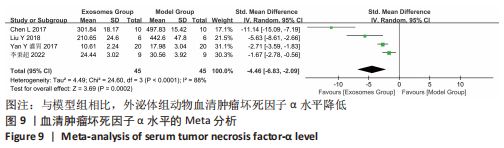
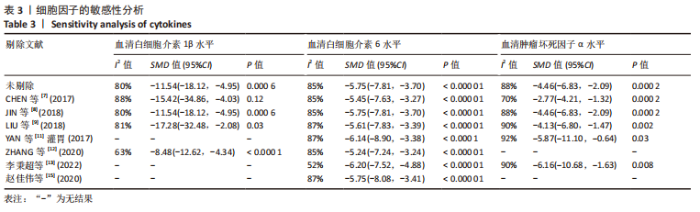
2.4.7 亚组分析 具体数据见表2。①根据外泌体移植剂量分为≤1 mg/kg组、> 1 mg/kg≤10 mg/kg组和>10 mg/kg组。≤1 mg/kg组AST水平(I2=0%)、>1 mg/kg≤10 mg/kg组IL-6水平(I2=41%)、> 10 mg/kg组ALT水平(I2=48%)、AST水平(I2=24%)和IL-6水平(I2=16%)异质性显著降低;②根据检测时间分为≤24 h组、> 24 h≤72 h组、> 3 d≤7 d组和> 7 d组。≤24 h组IL-6水平(I2=6%)和> 3 d≤7 d组IL-6水平(I2=0%)异质性显著降低;但> 24 h≤72 h组中,外泌体组ALT水平(P=0.07)和AST水平(P=0.06)与模型组相比无明显差异;③根据外泌体来源分为骨髓间充质干细胞组、人脐带间充质干细胞组、脂肪间充质干细胞组和宫血间充质干细胞组。在脂肪间充质干细胞组中,外泌体组IL-6水平(P=0.12)与模型组相比无明显差异。"
| [1] 中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组,中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组.肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版) [J] .中华肝脏病杂志,2019,27(1):18-26. [2] SHOKRAVI S, BORISOV V, ZAMAN BA, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and their exosome in acute liver failure (ALF): a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):192. [3] SHI M, LI YY, XU RN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a long-term follow-up analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial. Hepatol Int. 2021;15(6):1431-1441. [4] PSARAKI A, NTARI L, KARAKOSTAS C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: The regenerative impact in liver diseases. Hepatology. 2022;75(6):1590-1603. [5] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [6] 罗秋敏,朱姝,彭亮,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体治疗肝衰竭的研究进展[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2022,30(3):249-252. [7] CHEN L, XIANG B, WANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from human menstrual blood-derived stem cells alleviate fulminant hepatic failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):9. [8] JIN Y, WANG J, LI H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells (hASCs) Improve Survival Rate of Rats with Acute Liver Failure by Releasing lncRNA H19. EBioMedicine. 2018;34:231-242. [9] LIU Y, LOU G, LI A, et al. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. EBioMedicine. 2018; 36:140-150. [10] WU HY, ZHANG XC, JIA BB, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure through activating ERK and IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021; 147(1):143-155. [11] YAN Y, JIANG W, TAN Y, et al. hucMSC Exosome-Derived GPX1 Is Required for the Recovery of Hepatic Oxidant Injury. Mol Ther. 2017;25(2):465-479. [12] ZHANG S, JIANG L, HU H, et al. Pretreatment of exosomes derived from hUCMSCs with TNF-α ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 in macrophage. Life Sci. 2020; 246:117401. [13] 李秉超,冯建恩,何云.人脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对急性肝衰竭大鼠炎症反应的抑制作用及相关机制[J].中西医结合肝病杂志,2022,32(2): 139-144. [14] 王皙.人脂肪干细胞外泌体中microRNA-19b-3p的抑炎作用及对急性肝衰竭动物模型治疗的探索[D].贵阳:贵州医科大学,2019. [15] 赵佳伟,贾蓉蓉,王景辉,等.间充质干细胞外泌体对小鼠急性肝衰竭的保护作用[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(7):1246-1252. [16] LU FB, CHEN DZ, CHEN L, et al. Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice with Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Carrying MicroRNA-223-3p. Mol Cells. 2019;42(12):906-918. [17] ZHANG L, SONG Y, CHEN L, et al. MiR-20a-containing exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2020; 235(4):3698-3710. [18] ZHANG J, GAO J, LIN D, et al. Potential Networks Regulated by MSCs in Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure: Exosomal miRNAs and Intracellular Target Genes. Front Genet. 2021;12:650536. [19] HYUN J, WANG S, KIM J, et al. MicroRNA125b-mediated Hedgehog signaling influences liver regeneration by chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14135. [20] SONG XJ, ZHANG L, LI Q, et al. hUCB-MSC derived exosomal miR-124 promotes rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy via downregulating Foxg1. Life Sci. 2021;265:118821. [21] 郑嵘炅,邓泽润,韩丹,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体调节大鼠肝细胞凋亡的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(1):44-49. [22] ZHENG J, LU T, ZHOU C, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing CD154 Expression on CD4+ T Cells via CCT2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020; 7(18):1903746. [23] JIANG W, TAN Y, CAI M, et al. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018: 6079642. [24] SAMERI MJ, SAVARI F, HOSEINYNEJAD K, et al. The hepato-protective effect of H2S-modified and non-modified mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice: The role of MALAT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;635:194-202. [25] MARDPOUR S, GHANIAN MH, SADEGHI-ABANDANSARI H, et al. Hydrogel-Mediated Sustained Systemic Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improves Hepatic Regeneration in Chronic Liver Failure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(41):37421-37433. [26] ZHAO S, LIU Y, PU Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 2887-2897. [27] LIN D, CHEN H, XIONG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells exosomal let-7a-5p improve autophagic flux and alleviate liver injury in acute-on-chronic liver failure by promoting nuclear expression of TFEB. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(10):865. [28] WU HH, LEE OK. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells induce the conversion of hepatocytes into progenitor oval cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):117. [29] JUN JH, KIM JY, CHOI JH, et al. Exosomes from Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Involved in Liver Regeneration in Hepatic Failure Induced by Bile Duct Ligation. Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:5485738. [30] ARABPOUR M, SAGHAZADEH A, REZAEI N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021; 97:107823. [31] JIANG L, ZHANG S, HU H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute liver failure by reducing the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(3):735-741. [32] TAMURA R, UEMOTO S, TABATA Y. Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on a concanavalin A-induced liver injury model. Inflamm Regen. 2016;36:26. |
| [1] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [2] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [3] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [4] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [5] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [6] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [7] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [8] | Hu Zhixing, Li Qun, Yang Chao, Wang Xiaoxiao, Fang Luochangting, Hou Wuqiong, Lin Na, Chen Weiheng, Liu Chunfang, Lin Ya. Network meta-analysis of the modeling effects of different factors on rabbit models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [9] | Hu Guangzhi, Lu Hongyan. Changes in pulmonary pericytes and tube formation of pulmonary vascular endothelial cells in mouse models of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 522-527. |
| [10] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [11] | Zhou Shibo, Guan Jianbin, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Liu Tao. Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 633-638. |
| [12] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [13] | Bai Xiaotian, Chen Zhaoying, Song Yiling, Wang Ye, Liu Jingmin. Effect of minimalist shoes on foot muscle morphology: systematic evaluation and Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 646-650. |
| [14] | Wang Juan, Wang Ling, Zuo Huiwu, Zheng Cheng, Wang Guanglan, Chen Peng. Rehabilitative efficacy of kinesio taping following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 651-656. |
| [15] | Dai Jing, Liu Shasha, Shen Mingjing. Exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for repairing bone defects around implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||